Arithmetic Chapter 4 Rule Of Three
If three values of two related variable quantities are known then the process of determining the fourth value is known as Rule of Three.
The unknown value of the second quantity
= Known value of the second quantity x \(\frac{\text { one value of } 1 \text { st quantity }}{\text { other value of the } 1 \text { st quantity }}\)
At the time of problem-solving by Rule of Three or more quantities
The required value of the given item
= known value of the given items x \(\frac{\text { a value of the } 1 \text { st item }}{\text { other value of the } 1 \text { st item }} \times \frac{\text { a value of the } 2 \text { nd item }}{\text { other value of the } 2 \text { nd item }}\)

Arithmetic Chapter 4 Rule Of Three Examples
Example 1. If the price of 6 pens is ₹30, then find the price of 20 pens.
Solution: Let the price of 20 pens be ₹x [x > 0].
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths
In the mathematical language, the problem is,
No. of pens
6
20
Price of pens (in ₹)
30
x
If the number of pen increases the price is also increases.
So the number of pens and price is directly proportional.
So, 6: 20 : :30: x
⇒ \(\frac{6}{20}\) = \(\frac{30}{x}\)
⇒ 6x = 30 x 20
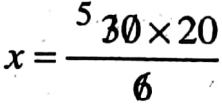
∴ The cost price of 20 pens is 100.
| WBBSE Class 8 English Functional Grammar | WBBSE Class 8 English Reading Skills |
| WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 English | WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths |
Example 2. Anita travels 3 km in 20 mins. What is the speed of Anita?
Solution: In the mathematical language the problem is:
Time (mins.)
20
60
Distance (km)
3
? (x) [Let x > 0]
Time and distance are directly proportional.
So, 20: 60 : : 3: x
⇒ \(\frac{20}{60}\) = \(\frac{3}{x}\)
⇒ \(x =\frac{3 \times 60}{20}\)
⇒ x = 9
∴ The speed of Anita is 9 km/hr.
Example 3. If 8 labourers can cultivate 32 bighas of land, then how many bighas of land will be cultivated by 5 laborers?
Solution: In Mathematical language, the problem is:
Number of laborers (in heads)
8
5
Quantity of land (in bighas)
32
?
If the number of labourers increases the quantity of land will also increase and if the number of labourers decreases, the quantity of land will also decrease.
So, the number of labourers (heads) and quantity of land is directly proportional.
∴ 8: 5 : : 32: ?
∴ The required quantity of land = \(\frac{5 \times 32}{8}\) Bighas = 20 Bighas.
20 Bighas of land will be cultivated by 5 laborers
Example 4. 6 plumbers can complete the filling in a bathroom in 5 hours. Now if it is required to be done in 3 hours, how many more plumbers would be needed?
Solution: Let x plumbers can complete the fitting in a bathroom in 3 hours.
In mathematical language, the problem is:
Time (hrs.)
5
3
Number of plumbers
6
x
Number of plumbers and times are inversely proportional.
So, 3: 5 : : 6: x ⇒ \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{6}{x}\)
⇒ x = \(\frac{5 \times 6^2}{3}\) = 10
∴ (10 – 6) or 4 more plumbers would be needed.
Example 5. A wall clock takes 10 seconds to beat 10. How much time will take by it to beat 12?
Solution: Let x seconds will taken to beat 12. There are 9 intervals among 10 beats and 11 intervals among 12 beats.
In the mathematical language the problem is:
Interval
9
11
Time taken (in secs)
10
x
The proportion is 9: 11: 10: x ⇒ x = \(\frac{11 \times 10}{9}=\frac{110}{9}=12 \frac{2}{9}\)
∴ 12\(\frac{2}{9}\) sec. time will taken to beat 12.
Example 6. There was a stock of food grains for 9 days to cater the needs of 4000 people at a shelter camp. After 3 days 1000 people left the camp for another place. How many days the rest of the people will consume the remaining food grains?
Solution: Let x days the rest of people will consume the remaining food grains. [x>0]
In the mathematical language, the problem is:
No. of people (in heads)
4000
4000 – 1000 = 3000
Time (in days)
9-3=6
x
With the same quantity of food, the less number of people will cover less days.
So, the number of people and the number of days are inversely proportional.
∴ 3000: 4000 :: 6: x
⇒ \(\frac{3000}{4000}=\frac{6}{x} \Rightarrow x=\frac{6 \times 4000}{3000} \Rightarrow x=8\)
∴ 8 days the rest of the people will consume the remaining food grains.
Example 7. A power loom is 2 1/4 times more powerful than a handloom. 12 handlooms weave 1080 meters in length of cloth in 18 days. How many power looms will be required to weave 2700 meters length of cloth in 15 days?
Solution: Let x handlooms will be required to weave 2700 meters of length of cloth in 15 days.
In the mathematical language the problem is:
Length of cloth (in metre)
1080
2700
Time (in days)
18
15
Number of handlooms
12
x
If time is constant, length of cloths and number of handlooms are inversely proportional.
If length of cloths are constant, then the required time and number of handlooms are inversely proportional.
∴ (1080 x 15): (18 x 2700): : 12: x
⇒ \(\frac{1080 \times 15}{18 \times 2700}=\frac{12}{x} \Rightarrow x=\frac{12 \times 18 \times 2700}{1080 \times 15} \Rightarrow x=36\)
36 handlooms will be required to weave 2700 meters length of cloth in 15 days.
As powerloom is 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) or \(\frac{9}{4}\) times more powerful than a handloom.
∴ The required number of powerloom is \(\left(36 \div \frac{9}{4}\right) \text { or }\left(36 \times \frac{4}{9}\right)\) or 16.
Example 8. If 50 men can do a piece of work in 12 days working 8 hours a day. How many hours a day would 60 men have to work in order to do another piece of work twice as great in 16 days?
Solution: Let the number of hours required be x.
In the mathematical language, the problem is:
No. of persons
50
60
No. of days
12
16
No. of hours
8
x
Here the number of hours is inversely proportion to the number of person and to the number of days.
∴ (60 x 16: 50 x 12): : 8: x
⇒ \(\frac{60 \times 16}{50 \times 12}=\frac{8}{x} \Rightarrow x=\frac{8 \times 50 \times 12}{60 \times 16}\)
∴ In order to do another piece of work twice as great in 16 days is (5 x 2) hours or 10 hours.
Example 9. A ship takes 18 days to reach its designated part. It starts with food for its crew of 450 men at the rate of 720 gm per day per head. After 11 days of its journey, they rescued 180 passengers from a Sinking ship. While rescuing the captain noticed a technical problem in the ship’s engine and estimated the ship would reach the destination after 9 days. How much food should they now consume per day per head so that it lasts for the rest of the journey?
Solution: In the mathematical language the problem is:
Men (by head)
450
450 + 180 = 630
Time (in days)
18-11 = 7
9
Quantity of food per day per head (in gm)
720
?
If the time is fixed, the number of men and quantity of food taken per head are inversely proportional.
Here the number of men increases.
∴ The quantity of food per head per day taken will be less.
So the fraction will be less than 1 i.e. \(\frac{450}{630}\)
If the number of men are fixed, the quantity of food per head per day is inversely proportional to time.
Here number of days increases. The fraction will be less than 1 i.e. \(\frac{7}{9}\)
So the required quantity of food per head per day
= 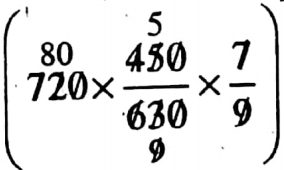 gms = 400 gm
gms = 400 gm
400 gm food should they now consume per day per head so that it lasts for the rest of the journey
Example 10. Choose the correct answer:
1. If the price of 3 kg dal is ₹270 then the amount of dal for ₹450 is
- 4 kg
- 5 kg
- 6 kg
- 4.5 kg
Solution: Let the amount of dal for ₹450 is x kg.
In the mathematical language, the problem is:
Price of dal (in ₹)
270
450
Amount of dal (kg)
3
x
The amount of dal and price of dal is directly proportional.
270: 450 : : 3: x ⇒ \(\frac{270}{450}=\frac{3}{x}\)
⇒ 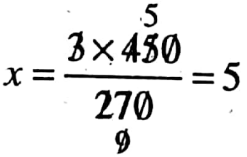
∴ The correct answer is 2. 5 kg
The amount of dal for ₹450 is 2. 5 kg.
2. If 15 men can do a piece of work in 12 days, then how many days can 20 men do that works?
- 16 days
- 25 days
- 9 days
- 6 days
Solution: Let 20 men can do the work in x days.
In the mathematical language, the problem is:
Men
15
20
Time taken (days)
12
x
So, 20: 15 : : 12: x
⇒ 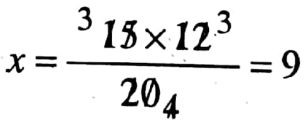
20 men can do the work in 9 days.
∴ So the correct answer is 3. 9 days
3. 9 days can 20 men do that works
Example 11. Write ‘True’ or ‘False’:
1. A poultry farm having 5000 hens has provision for 250 days. If 1000 hens must be sold after 50 days so that remaining provisions may last 250 days more.
Solution: In the mathematical language the problem is:
Hens (in heads)
5000
5000 – 1000 = 4000
No. of days
250-50 = 200
?
No. of hens and no. of days are inversely proportional.
∴ 4000: 5000 :: 200: ?
The required no. of days
= 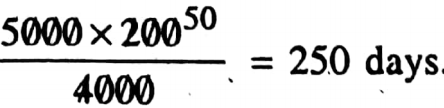
∴ The statement is true.
2. A man takes 40 mins. to reach his office from his home, traveling at a rate of 20 km/hr. The distance of the office from his house is 13 km.
Solution: In the mathematical language the problem is:
Time (mins)
60
40
Distance (km)
20
x (say)
The proportion is 60: 40 : : 20: x ⇒
Distance is 13\(\frac{1}{3}\)km.
∴ So the statement is false.
Example 12. Fill in the blanks
1. 6 men can do a piece of work in 7 days. Then _______ men will be required for that work in 21 days.
Solution: Let the required number of men are x [x > 0]
Time (days)
7
21
Men (in heads)
6
x
Number of men and days are inversely proportional.
So, 21: 7 : : 6: x
⇒ 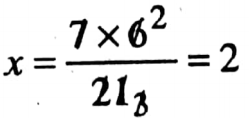
∴ Two men will be required.
2. A wheel revolves 51 times to transverse a distance of 170 metres. That wheel revolves _____ times to transverse a distance of 1700 metres.
Solution:
Distance (metre)
170
1700
No. of revolves of wheel
51
?
Distance and number of revolves of wheel are directly proportional.
∴ 170: 1700 : : 51: ?
∴ The required no. of revolves
= 
= 510 times
