WBBSE Class 9 Maths Geometry Chapter 1 Properties Of Parallelogram Multiple Choice Questions
Example 1. In the parallelogram ABCD, ∠BAD = 75° and ∠CBD = 60°, then the value of ∠BDC is
- 60°
- 75°
- 45°
- 50°
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 45°
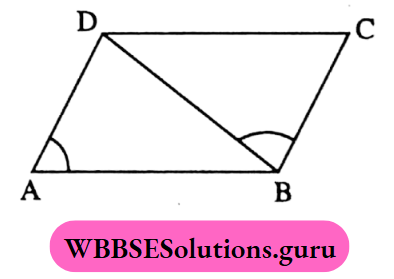
⇒ In the parallelogram ABCD, ∠C = ∠A = 75°
⇒ In ΔBCD, ∠BDC+ ∠CBD + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠BDC +60° + 75° = 180°
⇒ or, ∠BDC = 180° – (60° + 75°) = 45°
The value of ∠BDC is 45°
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 Maths Multiple Choice Questions
Example 2. Which of the following geometric diagonals equal in length
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Trapezium
- Rectangle
Solution: The correct answer is 4. Rectangle
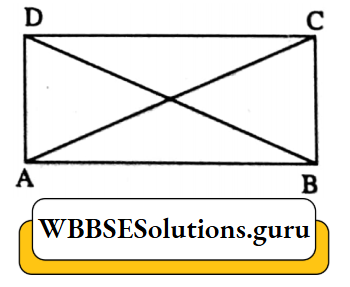
⇒ The diagonals of each rectangle are equal in length.

Example 3. In the parallelogram ABCD, ∠BAD = ∠ABC, the parallelogram ABCD is a
- Rhombus
- Trapezium
- Rectangle
- None of them
Solution: The correct answer is 3. Rectangle
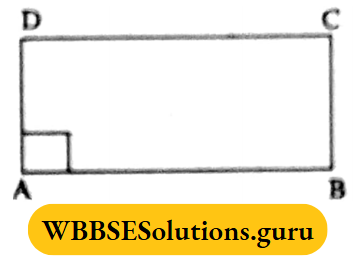
⇒ In a parallelogram, ABCD, AD || BC, and AB is the intersection
∴ ∠BAD + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ∠BAD + ∠BAD = 180°
2 ∠BAD = 180°
⇒ ∠BAD = 90°
∴ Parallelogram ABCD is a rectangle
Example 4. In the parallelogram ABCD, M is the midpoint of the diagonal BD; if BM bisects ∠ABC, then the value of ∠AMB is
- 45°
- 60°
- 90°
- 75°
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 90°

⇒ In parallelogram ABCD, AB || DC and BD its intersection.
∴ ∠ADB = alternate ∠DBC
⇒ ∠ADB = ∠ABD [BM is the bisector of ∠ABC]
∴ AB = AD
⇒ In ΔABM and ΔADM,
⇒ AB = AD, BM = DM [M is the midpoint of BD] and AM = AM [common side]
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔADM [by S.S.S. criterion of congruency)
∴ ∠AMB = ∠AMD
⇒ Again, ∠AMB+ ∠AMD = 180°
⇒ ∠AMB + ∠AMB = 180°
⇒ 2 ∠AMB = 180°
⇒ ∠AMB = 90°
The value of ∠AMB is 90°
Example 5. In the rhombus ABCD, ∠ACB = 40°, the value of ∠ADB is
- 50°
- 110°
- 90°
- 120°
Solution: The correct answer is 1. 50°
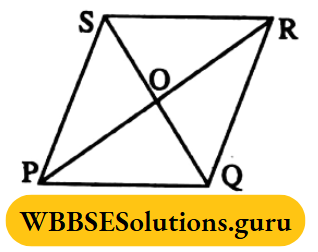
⇒ Let O is the point of intersection of diagonals AC and BD of rhombus ABCD.
⇒ The diagonals of rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly.
∴ ∠BOC = 90°
⇒ In ΔBOC, ∠OBC + ∠BOC + ∠OCB = 180°
⇒ ∠OBC + 90° + 40° = 180° [∠ACB = 40°]
⇒ or, ∠OBC = 50° i.e. ∠DBC = 50°
⇒ As DC || AB and BD is the intersection
∴ ∠ADB = alternate ∠DBC = 50°
The value of ∠ADB is 50°
Example 6. In parallelogram ABCD, if ∠A : ∠B = \(\frac{1}{2}\):\(\frac{1}{3}\),then the value of ∠C is
- 90°
- 36°
- 72°
- 108°
Solution: The correct answer is 4. 108°
⇒ ∠A: ∠B = \(\frac{1}{2}\):\(\frac{1}{3}\) = 3: 2
⇒ ∠A + ∠B = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 180°x \(\frac{3}{3 + 2}\) = 180° x \(\frac{3}{5}\)=108°
⇒ ∠C = ∠A = 108°
⇒ [Opposite angle of parallelogram are equal]
The value of ∠C is 108°
Example 7. The perimeter of a parallelogram is 22 cm. If the longer side measures 6.5 cm, then the measure of the shorter side is
- 9 cm
- 7.5 cm
- 4.5 cm
- 11 cm
Solution: The sum of two longer sides is (6.5 x 2) cm or 13 cm.
⇒ The sum of two shorter sides is (22 – 13) cm or 9 cm.
∴ The length of the shorter side is \(\frac{9}{2}\) cm or 4.5 cm.
∴ The correct answer is 3. 4.5 cm
Example 8. If the ratio of consecutive angles of a quadrilateral is 2: 1:3: 4, then the quadrilateral will be
- Parallelogram
- Square
- Rhombus
- None of them
Solution: The correct answer is 4. None of them
⇒ Let the angles are 2x°, x°, 3x°, 4x° [Where x is common multiple and x > 0]
⇒ 2x + x + 3x + 4x = 360°
⇒ 10x = 360 ⇒ x = 36
∴ The angles are 36 x 2° 72°, 36°, 3 x 36° or 108°, 4 x 36° or 144°
{Opposite angle are not equal}
