WBBSE Class 9 Maths Geometry Chapter 3 Theorems On Area Multiple Choice Questions
Example 1. D, E, and F are midpoints of sides BC, CA, and AB respectively of a triangle ABC. If ΔABC = 16 sq. cm, then the area of the trapezium-shaped region FBCE.
- 50 sq. cm
- 8 sq. cm
- 12 sq. cm
- 100 sq. cm
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 12 sq. cm
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 Maths Multiple Choice Questions
⇒ In ΔABC, F and E are the midpoints of AB and AC respectively.

∴ FE || BC or, FE || BD
⇒ Similarly, DE || BF
⇒ In quadrilateral BDEF, FE || BD and BF || DE
∴ BDEF is a parallelogram whose one diagonal is FD
∴ ΔBDF ≅ ΔDEF
∴ ΔBDF = ΔDEF
⇒ Similarly, ΔDEF = ΔAEF and ΔDEF = ΔCDE
∴ ΔDEF = ΔBDF = ΔAEF = ΔCDE
⇒ ΔDEF + ΔBDF + ΔAEF + ΔCDE = ΔABC
∴ ΔDEF + ΔDEF + ΔDEF +ΔDEF
⇒ or, 4 ΔDEF 16 sq. cm
⇒ or, ΔDEF = 4 sq. cm
∴ ΔBDF = ΔCDE = 4 cq. cm
∴ Area of the trapezium shaped region FBCE = ΔBDF + ΔDEF + ΔCDE
∴ Area of the trapezium shaped region FBCE = (4 + 4 + 4) sq. cm = 12 sq. cm
Example 2. A, B, C, and D are the midpoints of sides PQ, QR, RS, and SP respectively of the parallelogram PQRS. If area of the parallelogram-shaped region PQRS = 36 sq. cm then area of the region ABCD is
- 24 sq. cm
- 18 sq. cm
- 30 sq. cm
- 36 sq. cm
Solution: The correct answer is 4. 36 sq. cm
I join D, B.

⇒ In quadrilateral PQBD, PD || QB [PS || QR]
⇒ and PD = QB [\(\frac{1}{2}\) PS = \(\frac{1}{2}\) QR]
∴ PQRS is a parallelogram, ∴ DB || PQ
⇒ Similarly, DBRS is a parallelogram
⇒ ΔABD and parallelogram PQBD, are on same base DB and between same parallels DB and PQ
⇒ ΔABD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram PQBD
⇒ Similarly, ΔBCD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram DBRS
⇒ ΔABD = ΔBCD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [parallelogram PQBD + parallelogram DBRS]
⇒ i.e. quadrilateral ABCD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram PQRS
∴ Area of quadrilateral ABCD = (\(\frac{1}{2}\) x36) sq cm = 18 sq. cm

Example 3. O is any a point inside parallelogram ABCD. If ΔAOB + ΔCOD = 16 sq. cm, then area of the parallelogram-shaped region ABCD is
- 8 sq. cm
- 4 sq. cm
- 32 sq. cm
- 64 sq. cm
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 32 sq. cm
⇒ Through the point O a straight line parallel to AB or CD is drawn which intersects the sides AD and BC at the points E and F respectively.
⇒ In quadrilateral ΔBFE, AB || EF and AE || BF
∴ ABFE is a parallelogram.
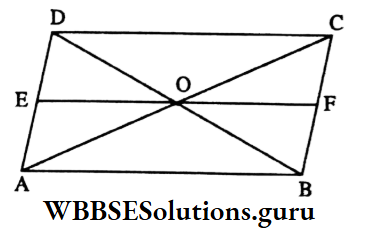
⇒ ΔAOB and parallelogram ABFE, are on same base AB and between same parallels AB and EF
∴ ΔAOB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram ABFE
⇒ Similarly, ΔCOD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram CDEF
⇒ ΔAOB+ ΔCOD = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(parallelogram ABFE + parallelogram CDEF)
⇒ 16 sq. cm = \(\frac{1}{2}\) parallelogram ABCD
⇒ or, Area of parallelogram = 32 sq. cm
Example 4. D is the midpoint of side BC of triangle ABC. E is the midpoint of side BD and O is the midpoint of AE; area of triangular field BOE is
- \(\frac{1}{3}\) x Area of ΔABC
- \(\frac{1}{4}\) x Area of ΔABC
- \(\frac{1}{6}\) x Area of ΔABC
- \(\frac{1}{8}\) x Area of ΔABC
Solution: The correct answer is 4. \(\frac{1}{8}\) x Area of ΔABC
⇒ I join A and D.
⇒ AD is a median of ΔABC
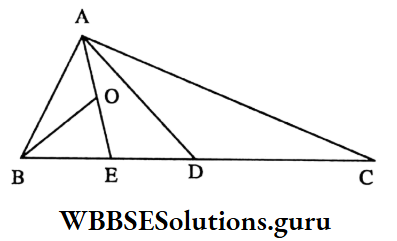
∴ ΔABD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABC
⇒ AE is a median of ΔABD
∴ ΔABE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABD
⇒ BO is a median of ΔABE
∴ ΔBOE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABD = \(\frac{1}{4}\) x \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABC = \(\frac{1}{8}\) ΔABC
Example 5. A parallelogram, a rectangle, and a triangular region stand on same base and between same parallel, and it their area are P, R, and T respectively then
- P = R = 2T
- P = R = \(\frac{T}{2}\)
- 2P = 2R = T
- P = R = T
Solution: The correct answer is 1. P = R = 2T
⇒ If a parallelogram and a rectangle are on same base and between same parallel, then area of the parallelogram and rectangle are equal [As the rectangle is a parallelogram]
∴ P = R
⇒ Again a parallelogram and a triangle are on same base and between same parallel.

∴ Area of triangle is equal to half of area of parallelogram.
∴ T = \(\frac{P}{2}\)
or, P = 2T
∴ P = R = 2T
Example 6. The points D and E on sides BC of a triangle ABC such that BD = DE = EC; If the area of ΔABC is 12 sq. cm then the area of ΔABC is
- 6 sq. cm
- 12 sq. cm
- 18 sq. cm
- 24 sq. sm
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 18 sq. cm
⇒ AD is a median of ΔABE
∴ ΔADE = ΔABD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔABE
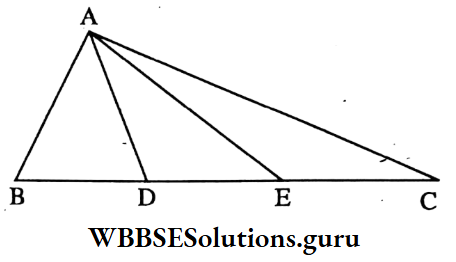
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) x 12) sq. cm = 6 sq. cm
⇒ AE is a median of ΔADC
∴ ΔABC = ΔABD + ΔADE + ΔAEC
= (6+6+6) sq. cm = 18 sq. cm
Example 7. In ΔABC, P is the midpoint of median AD. If area of ΔAPC is 12 sq. em then the area of ΔBPC is
- 6 sq. cm
- 12 sq. cm
- 15 sq. cm
- 24 sq. cm
Solution: The correct answer is 4. 24 sq. cm
⇒ CP is a median of ΔADC,

⇒ ΔDPC = ΔAPC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ΔACD
⇒ or, ΔADC = 2 ΔAPC (2 x 12) sq. cm = 24 sq. cm
⇒ PD is a median of ΔBPC
∴ ΔBPD = ΔDPC = 12 sq. cm [ΔAPC = ΔDPC]
⇒ ΔBPC = ΔBPD + ΔDPC
ΔBPC = (12 + 12) sq. cm = 24 sq. cm
Example 8. In ΔABC, D, E, and F are midpoints of sides BC, CA, and AB respectively. If area of trapezium ABDE is 15 sq. cm, then area of ΔABC is
- 7.5 sq. cm
- 12 sq. cm
- 20 sq. cm
- 30 sq. cm
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 20 sq. cm
⇒ I join E, F and F, D.
⇒ In ΔABC, D, and E are the midpoints of BC and AC respectively.

∴ DE || AB i.e. DE || AF and DE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) AB
⇒ or DE = AF
∴ AFDE is a parallelogram whose diagonal is EF.
∴ ΔDEF = ΔAEF
⇒ Similarly, ΔDEF= ΔBDF and ΔDEF = ΔCDE
∴ ΔAEF = ΔBDF = ΔCDE = ΔDEF = x sq. cm [say, x > 0]
⇒ Area of trapezium of ABDE = ΔAEF + ΔDEF + ΔBDF
=(x+x+x) sq. cm = 3x cm
⇒ According to question 3x = 15 or x = 5
⇒ ΔABC = ΔAEF + ΔBDF + ΔDEF+ ΔCDE = (5+5+5+5) sq. cm = 20 sq. cm
