WBBSE Class 9 Maths Geometry Chapter 2 Transversal And Mid Point Theorem Multiple Choice Questions
Example 1. In the triangle PQR, ∠PQR = 90° and PR = 10 cm. If S is the midpoint of PQ, then the length of QS is
- 4 cm
- 5 cm
- 6 cm
- 3 cm
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 Maths Multiple Choice Questions
Solution: The correct answer is 2. 5 cm

⇒ In ΔPQR, ∠PQR = 90°
⇒ As S is the midpoint of hypotenuse PR
∴ QS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)PR = (\(\frac{1}{2}\) x 10) cm = 5 cm
The length of QS is = 5 cm
Example 2. In the trapezium ABCD, AB || DC and AB = 7 cm, and DC = 5 cm. The midpoints of AD and BC are E and F respectively, the length of EF is
- 5 cm
- 6 cm
- 7 cm
- 12 cm
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 7 cm
⇒ In trapezium ABCD, AB || DC and the midpoints of AD and BC are E and F respectively.
∴ EF = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(AB + DC) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(7 + 5) cm = 6 cm
The length of EF is = 6 cm
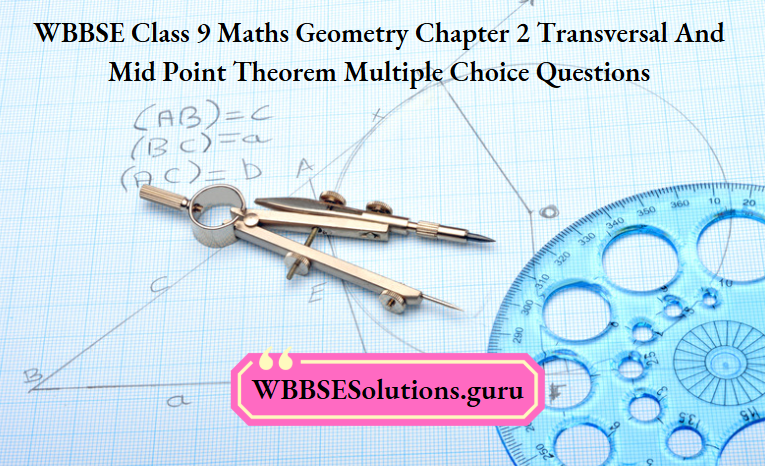
Example 3. In the triangle ABC, E is the midpoint of the median AD; the entended BE intersects AC at the point F. If AC = 10.5 cm, then the length of AF is
- 3 cm.
- 3.5 cm
- 2.5 cm
- 5 cm
Solution: The correct answer is 2. 3.5 cm
⇒ Through the midpoint D of the side BC a line segment parallel to the side BF is drawn which intersects AC at the point G.
⇒ In, ΔBFC, D is the midpoint of BC and DG || BF [According to construction]
∴ G is the midpoint of FC i.e. FG = GC
⇒ Again, In ΔADG, E is the midpoint of AD and EF || DG
∴ F is the midpoint of AG i.e. AF = FG
∴ AF = FG = GC = \(\frac{\mathrm{AF}+\mathrm{FG}+\mathrm{GC}}{3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3} \mathrm{AC}=\left(\frac{1}{3} \times 10.5\right) \mathrm{cm}\) = 3.5 cm
The length of AF is 3.5 cm
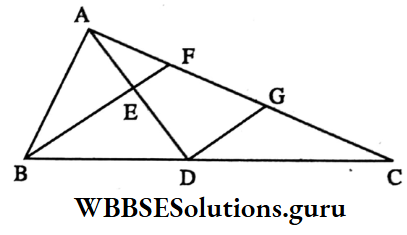
Example 4. In the ΔABC, the midpoints of BC, CA, and AB are D, E, and F respectively. BE and DF intersect at point X and CF and DE intersect at the point Y, the length of XY is equal to
- \(\frac{1}{2}\) BC
- \(\frac{1}{4}\) BC
- \(\frac{1}{3}\) BC
- \(\frac{1}{8}\) BC
Solution: The correct answer is 2. \(\frac{1}{4}\) BC
⇒ In ΔABC, F and E are the midpoints of AB and AC respectively
∴ FE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) BC and FE || BC i.e. FE || BD
⇒ Again, D and E are the midpoints of BC and AC respectively.
∴ DE || AB i.e. DE || FB
⇒ In quadrilateral BDEF, BD || EF and DE || FB
∴ BDEF is a parallelogram.
⇒ The diagonals DF and BE of a parallelogram are bisects each other at X.
∴ X is the midpoint of DF
⇒ Similarly, DCEF is a parallelogram whose diagonals FC and DE bisect each other at Y
∴ Y is the midpoint of DE
⇒ In ΔDEF, X, and Y are the midpoints of DF and DE
∴ XY = \(\frac{1}{2}\) EF = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x \(\frac{1}{2}\) BC = \(\frac{1}{4}\) BC
Example 5. In the parallelogram ABCD, E is the midpoint of the side BC; DE and extended AB meet at the point F. The length of AF is equal to
- \(\frac{3}{2}\) AB
- 2 AB
- 3 AB
- \(\frac{5}{4}\) AB
Solution: The correct answer is 2. 2 AB
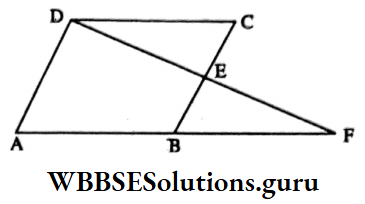
⇒ In ΔDCF and ΔBEF,
⇒ CE = BE [E is the midpoint of BC]
⇒ ∠DEC = ∠BEF [vertically opposite angles]
⇒ and ∠DEC = alternate ∠EBF [DC || AF and BC is intersection]
∴ ΔDCF ≅ ΔBEF [by A-A-S criterion of congruency]
∴ DC = BF
⇒ Again, DC = AB [opposite sides of parallelogram ABCD]
∴ AB = BF
⇒ AF = AB + BF = AB + AB = 2 AB
The length of AF is equal to = 2 AB
Example 6. In ΔABC, D, and E are two midpoints of side AB and AC respectively. If DE = (a + b) cm the length of BC is
- \(\frac{a + b}{2}\)cm
- 2(a + b) cm
- (a – b) cm
- \(\frac{a – b}{2}\)cm
Solution: The correct answer is 2. 2(a + b) cm

⇒ As D and E are two midpoints of side AB and AC respectively.
∴ DE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) BC
⇒ or, BC = 2DE = 2(a + b) cm
The length of BC is = 2(a + b) cm
Example 7. In ΔABC, ∠A = 50°, ∠B = 60° and ∠C = 70°; P and Q are two midpoints of AB and AC respectively. The value of ∠APQ is
- 50°
- 70°
- 60°
- None of them
Solution: The correct answer is 3. 60°
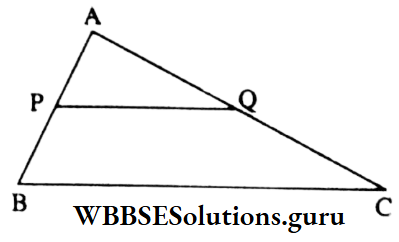
⇒ As, P, and Q are midpoints of side AB and AC
∴ PQ || BC
∴ ∠APQ corresponding ∠ABC = 60°
The value of ∠APQ is = 60°
Example 8. In ΔABC, E and F are the midpoints of AC and AB respectively. The altitude AP to BC intersects FE at Q. If PQ = 6 cm, then the length of AQ is
- 6 cm
- 3 cm
- 12 cm
- none of them.
Solution: The correct answer is 1. 6 cm
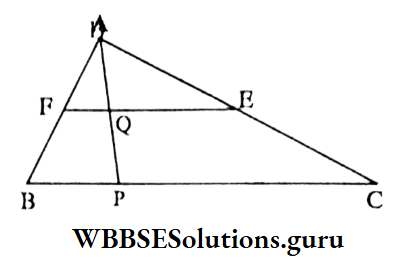
⇒ In ΔABC, E and F are midpoints of sides AC and A respectively.
∴ EF || BC
⇒ FQ || BP
⇒ In ΔABP, F is the midpoint of AB and FQ || BP
∴ Q is the midpoint of AP
⇒ i.e. AQ = QP = 6 cm
The length of AQ i= 6 cm
