Geometry Chapter 3 Similarity
Two polygons with same number of sides will be similar if,
⇔ Their corresponding angles are equal.
⇔ Corresponding sides are proportional.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
ΔABC and ΔDEF will be similar if
- ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E, ∠C = ∠F
- \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}=\frac{\mathrm{CA}}{\mathrm{FD}}\)
Two similar triangles ΔABC and ΔDEF can be written as ΔABC ~ ΔDEF
Class 10 Maths Geometry Chapter 3 Solutions
⇔ Necessary theorems:
- A straight line parallel to any side of any triangle divides two sides (or the extended two sides) proportionally.
- If a straight line divides any two sides (or their extended sides) in the same ratio, it will be parallel to the third side.
- If two triangles are similar then their corresponding sides are in the same ratio i.e. their corresponding sides are proportional.
- If the sides of two triangles are in same ratio, then their corresponding angles are equal i.e. two triangles are similar.
- If in two triangles, an angle of one triangle is equal to the angle of another triangle and the adjacent sides of the angle are proportional, then two triangles are similar.
- In any right angled triangle if a perpendicular is drawn from right angular point on the hypotenuse then the two triangles on both sides of this perpendicular are similar and each of them is similar to original triangle.
[In case of asterisk marks proofs are not included in the evaluation]

Geometry Chapter 3 Similarity True Or False
Example 1. Two similar triangles are always congruent.
Solution: Two congruent triangles are always similar. So the statement is false.
Example 2. If DE || BC then \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{CE}}\).
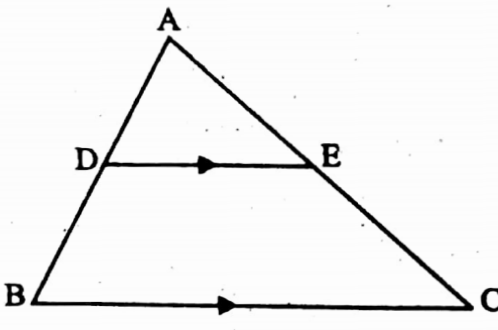
Solution: As DE || BC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{BD}}\) + 1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}+\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}+\mathrm{EC}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
i.e. \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
∴ The statement is true.
Constructions Class 10 Solutions
Example 3. If the corresponding angles of two quadrilaterals are equal, then they are similar.
Solution: Two quadrilaterals are similar if
- Corresponding sides are proportional and
- Corresponding angles are equal.
∴ The statement is false.
Example 4. If ∠ADE = ∠ACB then ΔADE ~ ΔACB.
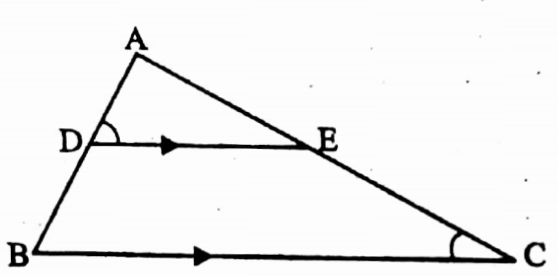
Solution: In ΔADE and ΔACB,
∠ADE = ∠ACB
∠DAE = ∠BAC [common angle] and remaining ∠AED = remaining ∠ABC
∴ ΔADE ~ ΔACB
∴ The statement is true.
Example 5. In ΔPQR, D is a point on the side QR so that PD ⊥ QR; So ΔPQD ~ ΔRPD
Solution:
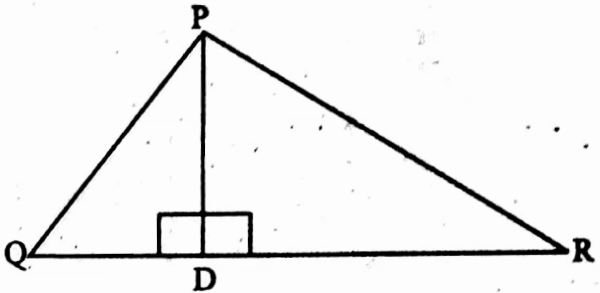
In ΔPQD and ΔRPD,
∠PDQ = ∠PDR = 90°
∴ The statement is false.
Geometry Chapter 3 Similarity Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. The line segment parallel to any side of a triangle divides other two sides or the extended two side.
Solution: Proportional.
Example 2. If the bases of two triangles are situated on a same line apd the other vertex of the two triangles are common, then the ratio of the areas of the two triangles are to the ratio of their bases.
Solution: Equal.
Example 3. The straight line parallel to the parallel sides of a trapezium divides _______ other two sides.
Solution: Proportional.
Class 10 Geometry Chapter 3 Solved Examples
Example 4. Two triangles are similar if their ______ sides are proportional.
Solution: Corresponding.
Example 5. The perimeters of ΔABC and ΔDEF are 30 cm. and 18 cm respectively. ΔABC ~ ΔDEF; BC and EF are corresponding sides. If BC = 9 cm, then EF = ______ cm
Solution: ΔABC ~ ΔDEF; BC and EF are corresponding sides.
∴ ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E and ∠C = ∠F
∴ \(\frac{AB}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{DF}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}+\mathrm{AC}+\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{DE}+\mathrm{DF}+\mathrm{EF}}\) [By applying addendo process]
= \(\frac{30}{18}=\frac{5}{3}\)
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}=\frac{5}{3}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{EF}=\frac{3 \times \mathrm{BC}}{5}=\frac{3}{5} \times 9 \mathrm{~cm}=5.4 \mathrm{~cm}\)
∴ 5.4
Geometry Chapter 3 Similarity Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. If in ΔABC, \(\frac{AD}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\) and ∠ADE = ∠ACB, then write the type of the triangle according to side.

Solution: As \(\frac{AD}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
∴ DE || BC
∴ ∠ADE = ∠ABC [corresponding angle]
Again ∠ADE = ∠ACB
∴ ∠ABC = ∠ACB
∴ AC = AB
∴ ΔABC is as isosceles triangle.
Wbbse Class 10 Geometry Notes
Example 2. If DE || BC and AD: BD = 3:5, then write area of ΔADE: area of ΔCDE.

Solution: As DE || BC
∴ \(\frac{AE}{\mathrm{EC}}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{BD}}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Bases of ΔADE and ΔCDE lies on the same straight line and has same vertex.
∴ \(\frac{\text { Area of } \triangle \mathrm{ADE}}{\text { Area of } \triangle \mathrm{CDE}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}=\frac{3}{5}\)
∴ ΔADE: ΔCDE = 3 : 5
Example 3. If LM || AB and AL = (x – 3) unit, AC = 2x unit BM = (x – 2) unit and BC = (2x + 3) unit, then determine the value of x.
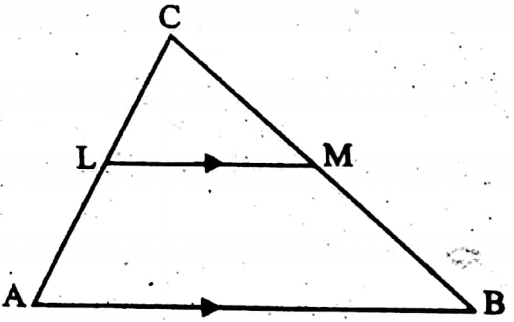
Solution: LM || AB
∴ \(\frac{CL}{\mathrm{AL}}=\frac{\mathrm{CM}}{\mathrm{BM}}\)
i.e. \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}-\mathrm{AL}}{\mathrm{AL}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}-\mathrm{BM}}{\mathrm{BM}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{Al}}-1=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{BM}}-1\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{AL}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{BM}}\)
∴ \(\frac{2 x}{x-3}=\frac{2 x+3}{x-2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2(x-3)+6}{x-3}=\frac{2(x-2)+7}{x-2}\)
⇒ \(2+\frac{6}{x-3}=2+\frac{7}{x-2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{6}{x-3}=\frac{7}{x-2}\)
⇒ 7x – 21 = 6x-12 ⇒ x = 9
Geometric Constructions Class 10
Example 4. If in ΔABC, DE || PQ || BC and AD = 3 cm, DP = x cm, PB = 4 cm, AE = 4 cm, EQ = 5 cm, QC = y cm, then determine the value of x and y.
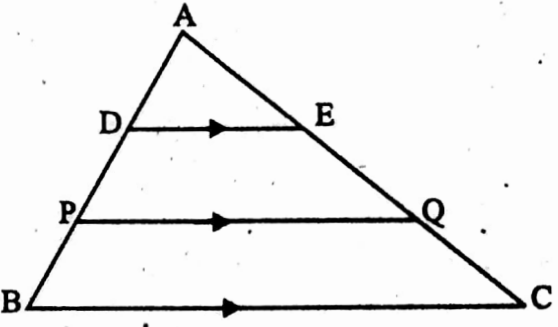
Solution: In ΔAPQ, DE || PQ
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DP}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EQ}}\)
∴ \(\frac{3}{x}=\frac{4}{5} \quad \Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{15}{4} \quad therefore \quad \mathrm{DP}=\frac{15}{4} \mathrm{~cm}\)
In ΔABC, PQ || BC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AP}}{\mathrm{PB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AQ}}{\mathrm{QC}}\)
i.e. \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}+\mathrm{DP}}{\mathrm{PB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}+\mathrm{EQ}}{\mathrm{QC}}\)
∴ \(\frac{3+\frac{15}{4}}{4}=\frac{4+5}{y}\)
⇒ \(\frac{27}{16}=\frac{9}{y}\)
⇒ \(y=\frac{16 \times 9}{27}=\frac{16}{3}\)
∴ The values of x is \(\frac{15}{4}\) and value of y is \(\frac{16}{3}\)
Example 5. If DE || BC, BE || XC and \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{2}{1}\) then determine the value of \(\frac{\mathrm{AX}}{\mathrm{XB}}\)
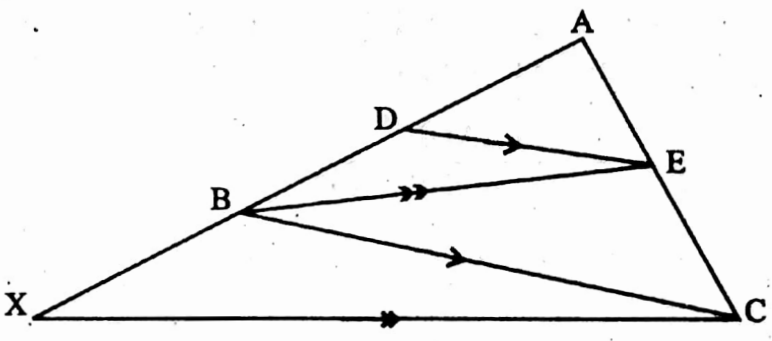
Solution: DE || BC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{2}{1}\)
again BE || XC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{XB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{AX}-\mathrm{XB}}{\mathrm{XB}}=\frac{2}{1}\)⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AX}}{\mathrm{XB}}-1=2\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AX}}{\mathrm{XB}}=3\)
Example 6. If ∠ACB = ∠BAD, AC = 8 cm, AB = 10 cm, and AD = 3 cm, then find the length of BD.

Solution: AD ⊥ BC,
∴ ∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
In ΔABC and ΔADC, ∠ADB = ∠ADC, ∠BAD = ∠ACD and remaining ∠ABD = remaining ∠CAD
∴ ΔABD ~ ΔACD
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}=\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{AD}}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{BD}=\frac{\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{AC}}=\frac{16 \times 3}{8} \mathrm{~cm}=6 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Example 7. ∠ABC = 90° and BD ⊥ AC, if AB = 5.7 cm BD = 38 cm, and CD = 5.4 cm, then determine the length of BC.
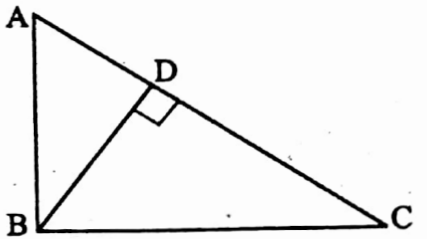
Solution: ∠ADB = ∠BDC = 90° [∵ BD ⊥ AC]
∠ABC = 90° [given]
In ΔABD, ∠ADB = 90°
∴ ∠BAD + ∠ABD = 90°
∴ ∠ABC = ∠BAD + ∠ABD
i.e. ∠ABD + ∠CBD = ∠BAD + ∠ABD
⇒ ∠CBD = ∠BAD
In ΔABD and ΔCBD, ∠ADB = ∠CDB = 90°
∠BAD = ∠CBD remaining ∠ABD = remaining ∠BCD
∴ ΔABD ~ ΔCBD
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{CD}}\)
⇒ BC = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{5.7 \times 5.4}{3.8}\) cm = 8.1 cm
Class 10 Maths Geometry Important Questions
Example 8. ∠ABC = 90° and BD ⊥ AC, if BD = 8 cm and AD = 4 cm, then find the length of CD.
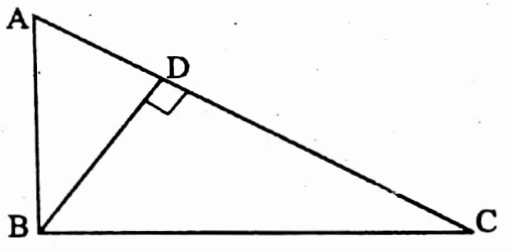
Solution: In ΔABC, ∠ABC = 90° and BD ⊥ AC, ∴ ∠ADB = ∠BDC = 90°
∴ ΔABD ~ ΔBCD
∴ \(\frac{A D}{B D}=\frac{B D}{C D}\)
⇒ \(C D=\frac{\mathrm{BD}^2}{\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{8 \times 8}{4} \mathrm{~cm}=16 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Example 9. In trapezium ABCD, BC || AD and AD = 4 cm. The two diagonals AC and BD intersect at the point O in such a way that, \(\frac{\mathrm{AO}}{\mathrm{OC}}=\frac{\mathrm{DO}}{\mathrm{OB}}=\frac{1}{2}\) Calculate the length of BC.
Solution: AD || BC and BD is the intersection
∴ ∠ADB = alternate ∠DBC
i.e. ∠ADO = ∠OBC
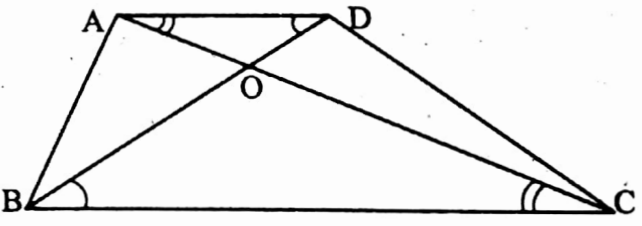
Again, AD || BC and AC is the intersection
∴ ∠CAD = alternate ∠ACB i.e. ∠OAD = ∠OCB
In ΔAOD and ΔBOC,
∠ADO = ∠OBC, ∠AOD = ∠BOC [opposite angle]
∠OAD = ∠OCB
∴ ΔAOD – ΔBOC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{\mathrm{AO}}{\mathrm{OC}}=\frac{\mathrm{DO}}{\mathrm{OB}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ BC = 2AD = (2 x 4) cm = 8 cm
Example 10. ΔABC – ΔDEF and in ΔABC and ΔDEF, the corresponding sides of AB, BC and CA are DE, EF and DF respectively, if ∠A = 47° and ∠E = 83°, then find the value of ∠C.
Solution:
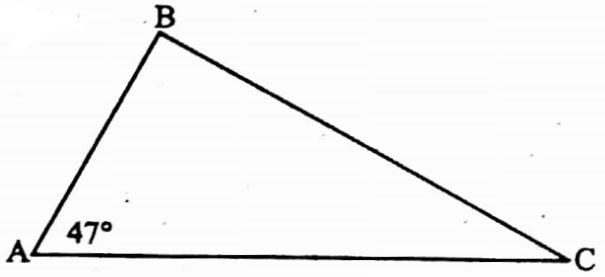
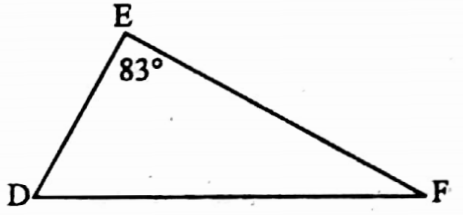
ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and in AABC and ADEF, corresponding findings of AB, BC and CA DE, EF and DF respectively.
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}=\frac{\mathrm{CA}}{\mathrm{DF}}\)
∴ ∠D = ∠A = 47° and ∠B = ∠F = 83°
∠C = 180° – (∠A + ∠B) = 180° – (47° + 83°) = 50°
Example 11. AD = 3 cm, AB = 8 cm, AC = 12 cm and EC = 7.5 cm. Write down the relation between DE and BC.
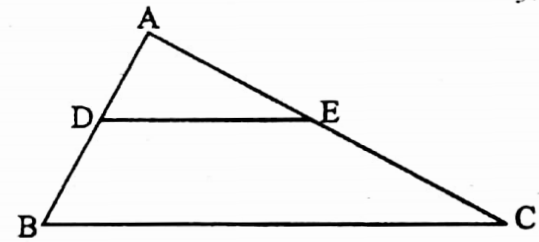
Solution: AD = cm, AB = 8 cm, DB = (8 – 3) cm = 5 cm, AC = 12 cm, EC = 7.5 cm
∴ AE = (12 – 7.5) cm = 4.5 cm
\(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{3}{5}, \frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}=\frac{4 \cdot 5}{7 \cdot 5}=\frac{3}{5}\)∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
∴ DE || BC [This is the relation]
Class 10 Maths Board Exam Solutions
Example 12. In ΔABC and ΔDEF, ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E and ∠C = ∠F. Areas of ΔABC and ΔDEF are 9 sq. cm and 16 sq. cm. Find the value of AB: DE.
Solution:
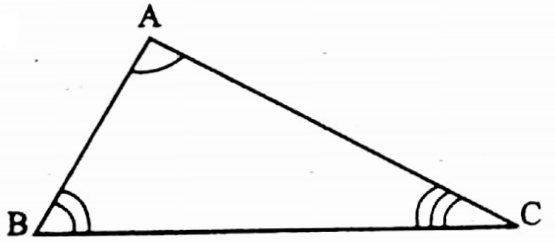
In ΔABC and ΔDEF, ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E and ∠C = ∠F
∴ ΔABC ~ ΔDEF
AB and DE are corresponding sides \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{ABC}}{\Delta \mathrm{DEF}}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}^2}{\mathrm{DE}^2}\)
\(\frac{9}{16}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}^2}{\mathrm{DE}^2}\)⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{3}{4}\)
⇒ AB : DE = 3 : 4
Example 13. Two chords AB and CD of a circle with centre O intersecting of P. If AP = 3 cm, BP = 4 cm, and CP = 6 cm then find the length of DP.
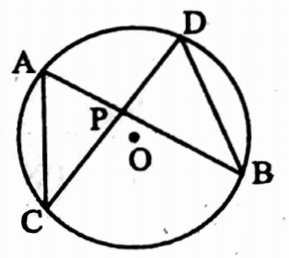
Solution: In ΔAPC and ΔBPD
∠CAP = ∠PDB [angles in the same segment]
∠ACP = ∠PBD [angles in the same segment]
∠APC = ∠BPD [opposite angles]
∴ ∠APC – ∠BDP
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AP}}{\mathrm{DP}}=\frac{\mathrm{CP}}{\mathrm{BP}}\)
or, \(\mathrm{DP}=\frac{\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{BP}}{\mathrm{CP}}=\frac{3 \times 4}{6} \mathrm{~cm}=2 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Class 10 Maths Geometry Chapter 3 Solutions
Example 14. PQ is a diameter of a circle with centre O. Two tangents are drawn at points P and Q. Tangent drawn at T intersects the tangents drawn at P and Q at the points R and S respectively. If RT = 9 cm and ST = 4 cm then find the length of radius of the circle.
Solution: I join O, R; O, T and O, S
As RP and RT are two tangents of a circle with centre O.

∠POR = ∠ROT = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠POT and ∠TOS = ∠QOS = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠QOT
∠ROS = ∠ROT + ∠TOS
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠POT + ∠QOT) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠POQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 180° = 90°
RS is tangent to the circle at T and OT is a radius
∴ OT ⊥ RS, ∠OTR = ∠OTS = 90°
ΔROT ~ ΔTOS
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{RT}}{\mathrm{OT}}=\frac{\mathrm{OT}}{\mathrm{ST}}\) or, OT2 + RT x ST = (9 x 4) cm2
OT = √36 cm = 6 cm
∴ Radius of the circle is 6 cm.
Example 15. ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC; BD = 2 cm, AD = 3 cm, Find the length of CD.
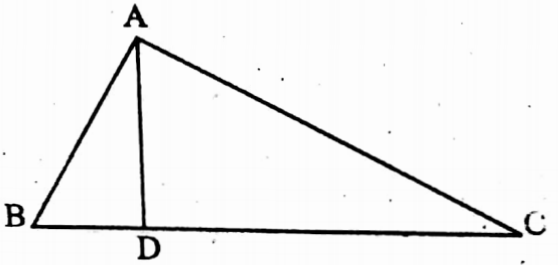
Solution: In ΔABC, ∠BAC = 90°, AD ⊥ BC
∴ ∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
In ΔABD, ∠BAD + ∠ABD = ∠BAC
ie. ∠BAD + ∠ADB = ∠BAD + ∠CAD
⇒ ∠ABD = ∠CAD
In ΔABD and ΔACD, ∠ADB = ∠CAD, ∠ADB = ∠ADC and remaining ∠BAD = remaining ∠ACD
∴ ΔABD ∼ ΔACD
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{CD}}\)
or, \(\mathrm{CD}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}^2}{\mathrm{BD}}=\frac{3 \times 3}{2} \mathrm{~cm}=4.5 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Class 10 Geometry Chapter 3 Solved Examples
Example 16. In ΔPQR, two point M and N on PQ and PR such that MN || QR ; If PM = a unit, MQ = b unit, PN = c unit and NR = d unit. Then calculate the values of (a2d2 + b2c2 – 2abcd)
Solution: In ΔPQR, MN || QR
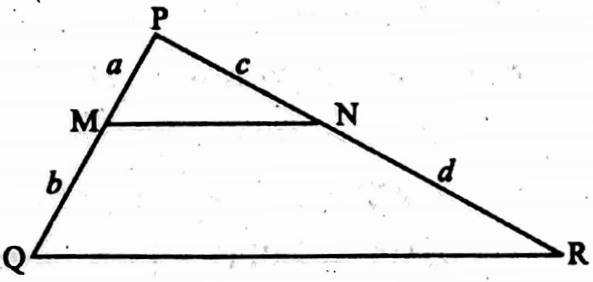
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{PM}}{\mathrm{MQ}}=\frac{\mathrm{PN}}{\mathrm{NR}}\)
∴ \(\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\)
⇒ ad = bc
⇒ ad – bc = 0
a2d2 + b2c2– 2abcd = (ad- bc)2 = (0)2 = 0
Example 17. DE || BC; If AD: DB = 2:3 then calculate of values of area of ΔADE: area of □DBCE.
Solution: \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{2}{3} \Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{DB}}{\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{3}{2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{DB}}{\mathrm{AD}}+1=\frac{3}{2}+1 \Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{DB}+\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{5}{2}\)
i.e., \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{5}{2}\)
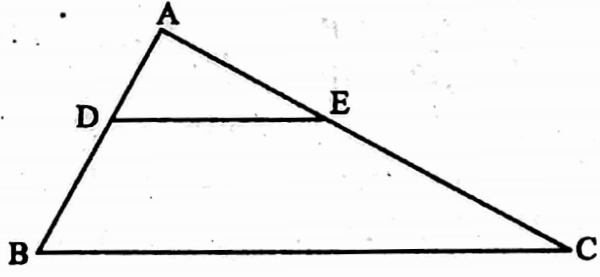
In, ∠ABC, DE || BC, AB and AC are the intersection
∴ ∠ADE = ∠ABC and ∠AED = ∠ACB
In ΔABC and ΔADE, ∠ABC = ∠ADE, ∠ACB = ∠AED and ∠BAC = ∠DAE
∴ ΔABC ~ ΔADE
∴ \(\frac{\triangle \mathrm{ABC}}{\triangle \mathrm{ADE}}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}^2}{\mathrm{AD}^2}=\left(\frac{5}{2}\right)^2=\frac{25}{4}\)
\(\frac{\triangle \mathrm{ABC}}{\Delta \mathrm{ADE}}-1=\frac{25}{4}-1\)⇒ \(\frac{\triangle \mathrm{ABC}-\triangle \mathrm{ADE}}{\triangle \mathrm{ADE}}=\frac{21}{4}\)
i.e. □DBCE/ΔADE = \(\frac{21}{4}\)
∴ \(\triangle \mathrm{ADE}\): □DBCE = 4: 21
Example 18. In ΔABC, AD ⊥ BC and AD2 = BD.DC; Find the value of ∠BAC.
Solution: In ΔABD, AD ⊥ BC, ∴ ∠ADB = 90°
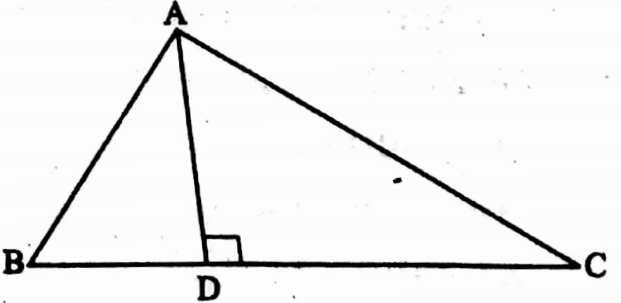
∴ AB2 = AD2 + BD2 [By Pythagorus theorem]
ΔACD, AC2 = AD2 + DC2
AB2 + AC2 = AD2 + BD2 + AD2 + DC2
= 2AD2 + BD2 + DC2
= 2BD.DC + BD2 + DC2
= (BD + DC)2
i.e., AB2 + AC2 = BC2
∴ ΔABC is a right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is BC,
∴ ∠BAC = 90°
Example 19. AD is a median of ΔABC and EF || BC; If OE = 3 cm, then find the length of EF.
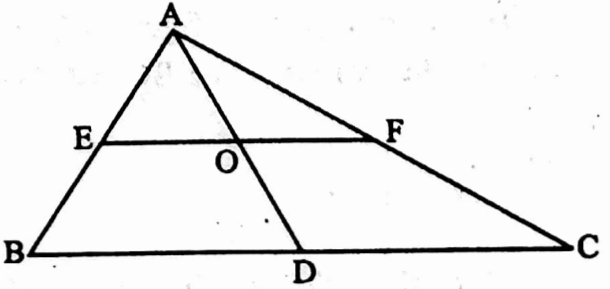
Solution: ln ΔAOE and ΔABD,
∠AEO = corresponding ∠ABD
[∵ EF || BC, AB is intersected]
∠AOE = ∠ADB and ∠EAO = ∠BAD [common angle]
∴ ΔAOE – ΔABD
∴ \(\frac{E O}{B D}=\frac{A O}{A D}\) ……(1)
Similarly, ΔAOF ~ ΔADC
∴ \(\frac{O F}{D C}=\frac{A O}{A D}\)………(2)
From(1)and(2), \(\frac{E O}{B D}=\frac{O F}{D C} \Rightarrow \frac{E O}{B D}=\frac{O F}{B D}\)
⇒ OF = OE = 3 cm
EF = (OE + OF) = (3 + 3) cm = 6 cm
∴ The length of EF is 6 cm.
Wbbse Class 10 Geometry Notes
Example 20. DE || BC ; AD = (2x – 1) unit, AB = (3x + 1) unit, EC = (3x – 2) unit and AC = (4x – 1) unit ; what the values of x? [x > 0]
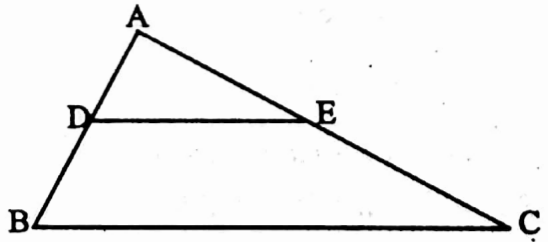
Solution: DE || BC
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
i.e. \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{AB}-\mathrm{AD}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}-\mathrm{EC}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
∴ \(\frac{2 x-1}{(3 x+1)-(2 x-1)}=\frac{(4 x-1)-(3 x-2)}{3 x-2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2 x-1}{x+2}=\frac{x+1}{3 x-2}\)
⇒ (2x- 1) (3x- 2) = (x + 1) (x + 2)
⇒ 6x2 – 7x + 2 = x2 + 3x + 2
⇒ 5x2 – 10x = 0 ⇒ 5x (x – 2) = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) = 0
⇒ x ≠ 0,
= x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = 2
