WBBSE Class 10 Maths Geometry Chapter 1 Theorems Related To Circle Multiple Choice Questions
Example 1. The length of two chords of a circle with centre O are equal. If ∠AOB = 60°, then the value of ∠COD is
- 40°
- 30°
- 60°
- 90°
Solution:
⇒ In a circle with its centre O,
⇒ Chord AB = Chord CD
∴ ∠AOB = ∠COD
Read And Learn Also WBBSE Class 10 Maths Multiple Choice Questions
∴ 60° = ∠COD
∴ The correct answer is 3. 60°.
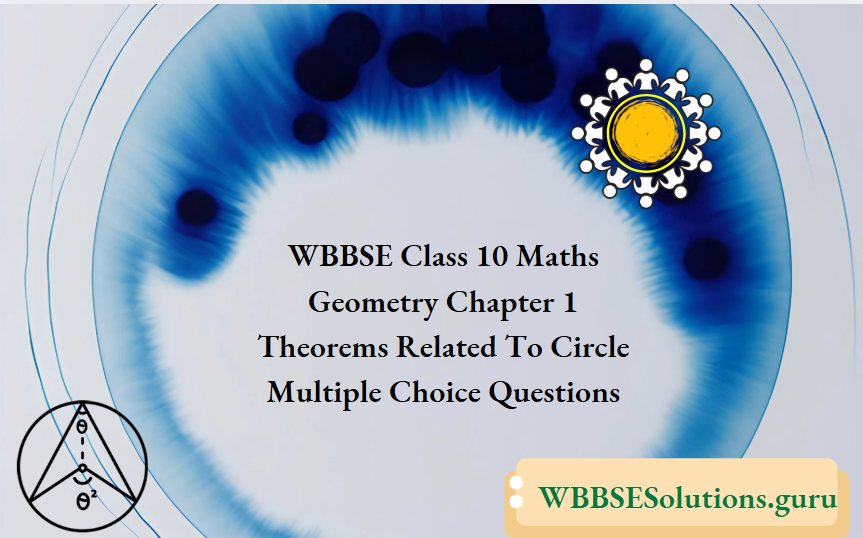
Example 2. The length of a radius of a circle is 13 cm. and the length of a chord of a circle is 10 cm, the distance of the chord from the centre of the circle is
- 12.5 cm
- 12 cm
- √69 cm
- 24 cm
Solution:
⇒ In a circle with its centre O, OP is the perpendicular distance of the chord AB.
⇒ join O, B.
⇒ OB = 13 cm ; AB = 10 cm
∵ OP ⊥ AB
∴ BP = \(\frac{1}{2}\) AB =\(\frac{1}{2}\) x 10 cm = 5 cm
⇒ In ΔBOP, OP2 + BP2 = OB2 [From Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ OP2 + 52 = 132
⇒ OP = \(\sqrt{169-25}\) = √144 cm = 12 cm
∴ The correct answer is 2. 12 cm
Class 10 Maths Geometry Chapter 1 Mcqs
Example 3. AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle with its centre O. If the distance of the chord AB from the point O is 4 cm. then the distance of the chord from the centre O of the circle
- 2 cm
- 4 cm
- 6 cm
- 8 cm
Solution:
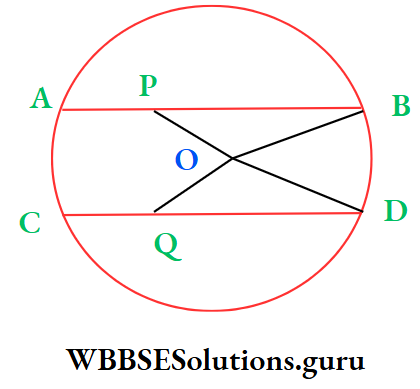
⇒ From the point O, two perpendiculars OP and OQ are drawn on the chord AB and CD respectively which intersect AB at the point P and CD at the point Q.
⇒ OP = 4 cm
⇒ Join O, B and O, D and OP ⊥ AB and OQ ⊥ CD
∴ BP = \(\frac{1}{2}\) AB and DQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CD
⇒ Again AB = CD [given]
⇒ \(\frac{1}{2}\) AB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CD
∴ BP = DQ
⇒ From ΔBOP, ∠BPO = 90°
∴ OP2 + BP2 = OB2
⇒ 42 + BP2 = OB2 [From Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ 16 + BP2 = OB2
⇒ In ΔDOQ, ∠OQD = 90°
∴ OQ2 + DQ2 = OD2
⇒ OQ2+ BP2 = OD2 [∵ BP = DQ]
⇒ As OB = OD [radii of same circle]
⇒ or, OB2 = OD2
⇒ 16 + BP2 = OQ2 + BP2
⇒ OQ2 = 16 cm2
⇒ OQ = √16 cm = 4 cm
∴ The correct answer is 2. 4 cm
Example 4. The length of each of two parallel chords is 16 cm. If the length of the radius of the circle is 10 cm, then the distance between two chord is
- 12 cm
- 16 cm
- 20 cm
- 5 cm
Solution:
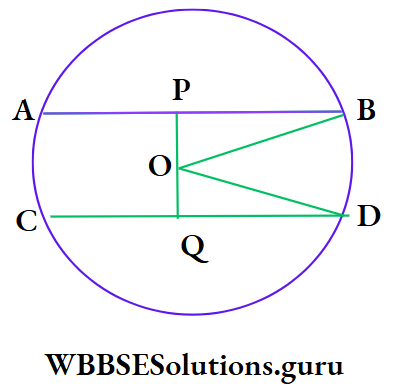
⇒ In the circle with its centre O, chord AB = chord CD = 16 cm and AB || CD ;
⇒ OP ⊥ AB and OQ ⊥ CD
∴ PB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) AB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 16 cm = 8 cm
⇒ DQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 16 cm = 8 cm
From ΔBOP, OP2 + PB2 = OB2
⇒ OP2 + 82 = 102 [OB is the radius of the circle]
⇒ OP = \(\sqrt{100-64}\) cm = 6 cm
Similarly, OQ = 6 cm
⇒ PQ = OP + OQ = (6 + 6) cm = 12 cm
∴ The correct answer is 1. 12 cm
Basic Geometry Mcqs Class 10
Example 5. The centre of two concentric circle is O; a straight line intersects a circle at the points A and B and another circle at the points C and D. If AC = 5 cm, then the length of BD is
- 2.5 cm
- 5 cm
- 10 cm
- none of these
Solution:

The centre of two concentric circle is O; a straight line intersects a circle at the points A and B and another circle at the points C and D.
From the point O a perpendicular OP is drawn on AB which intersects AB at the point P.
As OP ⊥ AB
∴ AP = BP
Again OP ⊥ CD ∴ CP = DP
⇒ BP- DP = AP – CP
⇒ or, BD = AC = 5 cm
∴ The correct answer is 2. 5 cm
Example 6. If ‘O’ is the centre of circle and PQ is a diameter then the value of X is
- 140
- 40
- 80
- 20
Solution:
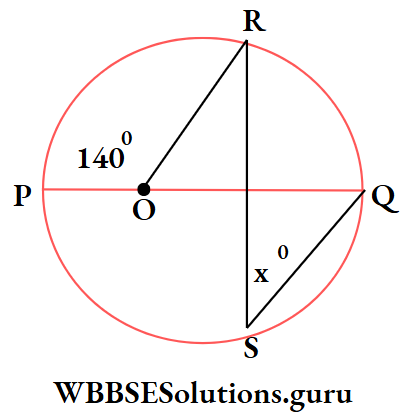
∠QOR = 180° – ∠POR = 180° – 40° = 40°
⇒ since the angle ∠QOR is at the centre of the circle and ∠QSR is on, the circle formed by circular arc QR of a circle with centre.
∴ 2∠QSR = ∠QOR
2x° = 40° or, x° = 20°
∴The correct answer is 4. 20.
Class 10 Geometry Chapter 1 Mcqs With Answers
Example 7. O is the centre of circle, ∠QPR = x°, ∠POR = 80° and ∠POQ = 140°, then the value of x is
- 70
- 60
- 100
- 80
Solution:
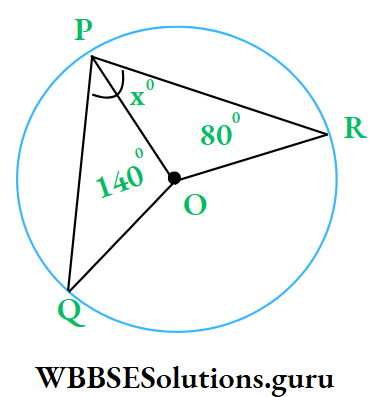
⇒ ∠QOR = 360° – ∠POQ – ∠POR
= 360° – 140° – 80° = 140°
⇒ ∠QPR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠QOR
⇒ x° = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 140°
⇒ x° = 70°
∴ The correct answer is 1. 70.
Example 8. O is the centre of circle, and BC is the diameter then the value of x is
- 60
- 50
- 100
- 80
Solution:

⇒ In ΔAOB, OA = OB [radii of same circle]
∴ ∠OBA = ∠OAB = 50°
⇒ i.e. ∠ABC = 50°
⇒ ∠ADC = ∠ABC [angles in the same segment]
⇒ x° = 50°
∴ The correct answer is 2. 50
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Geometry Solutions
Example 9. O is the circumcentre of ΔABC and ∠OAB = 50°, then the value of ∠ACB is
- 50°
- 100°
- 40°
- 80°
Solution:
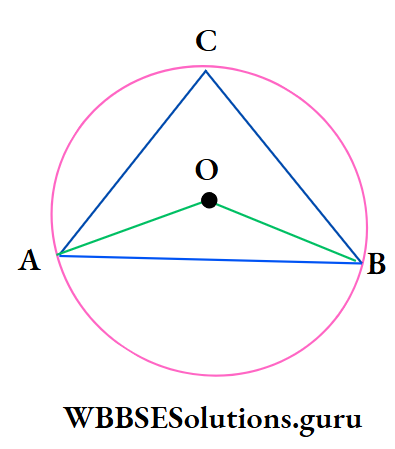
⇒ O is the circumcentre of ∠ABC
⇒ OA = OB [radii of same circle]
∴ ∠OBA = ∠OAB = 50°
⇒ ∠AOB = 180° – ∠OAB – ∠OBA
= 180° – 50° – 50° = 80° .
⇒ ∠ACB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠AOB
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 80° = 40°.
∴ The correct answer is 3. 40°
Example 10. If O is centre of circle, the value of ∠POR is
- 20°
- 40°
- 60°
- 80°
Solution:
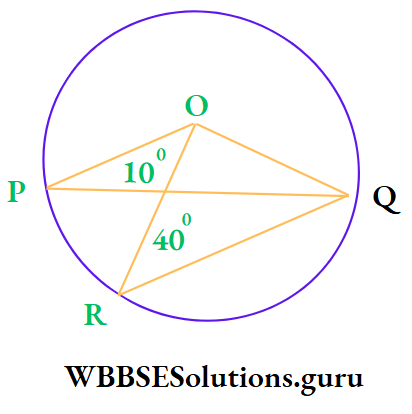
⇒ In ΔPOQ, OP = OQ [radii of same circle]
∴ ∠OQP = ∠OPQ = 10°
⇒ In ΔQOR, OR = OQ
∴ ∠OQR = ∠ORQ = 40°
∴ ∠PQR = ∠OQR – ∠OQP = 40° – 10° = 30°
⇒ ∠POR = ∠PQR = 2 x 30° = 60°
∴ The correct answer is 3. 60°
Example 11. O is the centre of the circle, if ∠ACB = 30°, ∠ABC = 60°, ∠DAB = 35° and ∠DBC = x°, the value, of x is
- 35
- 70
- 65
- 55
Solution:
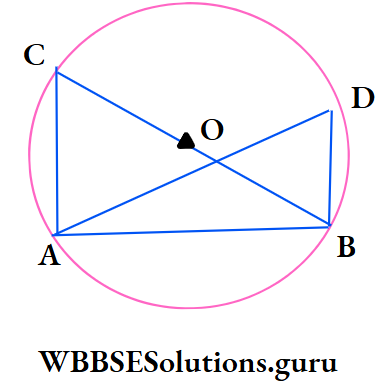
⇒ In ΔABC, ∠BAC = 180° – (∠ACB + ∠ABC)
= 180° – (30° + 60°) = 90°
⇒ ∠DAB = 35°
⇒ ∠CAD = 90° – ∠DAB = 90° – 35° = 55°
⇒ ∠DBC = ∠CAD = 55°
∴ The correct answer is 4. 55°
Wbbse Class 10 Maths Geometry Notes
Example 12. O is the centre of the circle, if ∠BAD = 65°, ∠BDC = 45°, then the value of ∠CBD is
- 65°
- 45°
- 40°
- 20°
Solution:
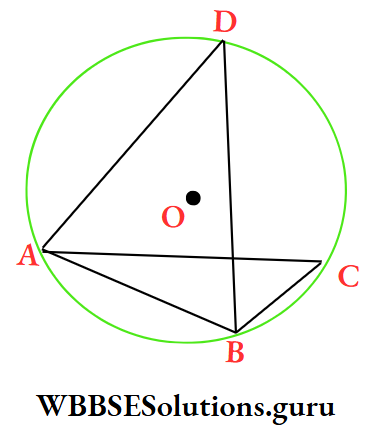
⇒ ∠BAC = ∠BDC [angles, in the same segment] = 45°
⇒ ∠CAD = ∠BAD – ∠BAC = 65° – 45° = 20°
⇒ ∠CBD = ∠CAD [angles in the same segment] = 20°
∴ The correct answer is 4. 20°
Example 13. The O is the centre of circle, if ∠AEB = 110° and ∠CBE = 30°, the value of ∠ADB is
- 70°
- 60°
- 80°
- 90°
Solution:

In ΔBEC,
⇒ Exterior ∠AEB = ∠ECB + ∠CBE
⇒ 110° = ∠ECB + 30°
⇒ or, ∠ECB = 110° – 30° = 80°
⇒ i.e. ∠ACB = 80°
⇒ ∠ADB = ∠ACB [angles in the same segment] = 80°
∴ The correct answer is 3. 80°.
Example 14. O is the centre of the circle, if ∠BCD = 28°, ∠AEC = 38°, then the value of ∠AXB is
- 56°
- 86°
- 38°
- 28°
Solution:
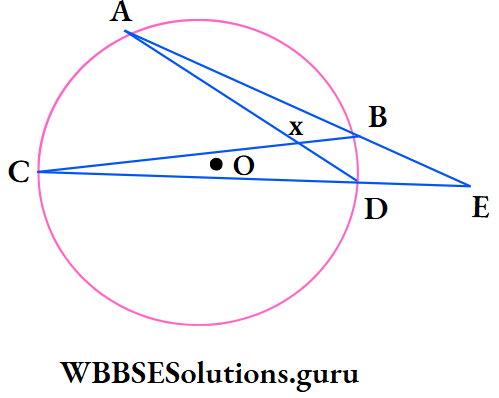
⇒ ∠BAD = ∠BCD [angles in the same segment] = 28°
⇒ In ΔADE, Exterior ∠ADC = ∠BAD + ∠AED
= 28° + 38° = 66°
⇒ In ΔCDX, ∠CXD = 180° – ∠XCD – ∠XDC
= 180° – 28° – 66° = 86°
∴ The correct answer is 2. 86°.
Geometry Mcqs With Solutions Class 10
Example 15. O is the centre of the circle and AB is diameter. If AB || CD, ∠ABC = 25°, the value of ∠CED is
- 80°
- 50°
- 25°
- 40°

Solution:
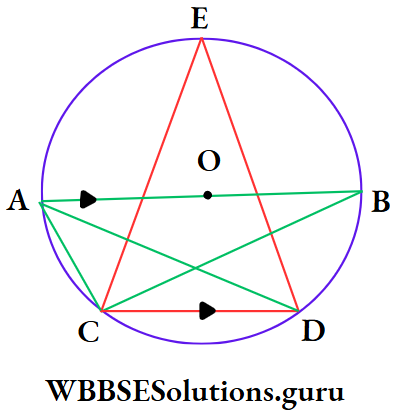
⇒ Join A, C and A, D
⇒ ∠ACB = 90° [semi-circular angle]
⇒ AB || CD and BC is intersection
⇒ ∠BCD = alternate ∠ABC = 25°
⇒ ∠ACD = ∠ACB + ∠BCD
= 90° + 25° = 115°
⇒ ∠ADC = ∠ABC [angles in the same segment]
= 25°
⇒ In ΔACD, ∠CAD = 180° – ∠ACD – ∠ADC
= 180° – 115° – 25° = 40°
⇒ ∠CED = ∠CAD [angles in the same segment]
∴ The correct answer is 4. 40°
Example 16. PQ is a diameter of a circle with centre O, and PR = RQ the value of ∠RPQ is
- 30°
- 90°
- 60°
- 45°
Solution:

⇒ ∠PRQ = 90° [semi-circular angle]
⇒ In ΔPQR, PR = RQ
∴ ∠RPQ = ∠PQR = \(\frac{180^{\circ}-90^{\circ}}{2}\) = 45°
∴ The correct answer is 4. 45°.
Example 17. QR is a cord of a circle and POR is a diameter of a circle. OD is perpendicular on QR. If OD = 4 cm, the length of PQ is
- 4 cm
- 2 cm
- 8 cm
- none of these
Solution:
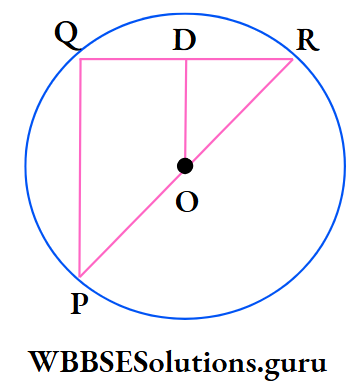
⇒ ∠PQR = 90°
⇒ ∠ODR = 90° [∵ OD ⊥ QR]
∴ ∠PQR = ∠ODR
∴ OD || PQ
∴ ΔPQR ~ ΔDOR
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{OD}}{\mathrm{PQ}}=\frac{\mathrm{OR}}{\mathrm{PR}}\)
\(\frac{4 \mathrm{~cm}}{\mathrm{PQ}}=\frac{\mathrm{OR}}{2 \mathrm{OR}}\)
∴ PQ = 8 cm
∴ The correct answer is 3. 8 cm
Geometry Mcqs With Solutions Class 10
Example 18. AOB is a diameter of a circle. The two chords AC and BD when entended meet at point E. If ∠COD = 40°, the value of ∠CED is
- 40°
- 80°
- 20°
- 70°

Solution:

I join A, D and B, C
⇒ since ∠COD is at the centre of the circle and ∠CAD is on the circle formed by circular arc CD of a circle with centre,
⇒ ∠CAD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠COD
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 40° = 20°
⇒ ∠ADB = 90° [semi-circular angle]
∴ ∠ADE = 180° – 90° = 90°
⇒ In ΔADE, ∠AED = 180° – ∠ADE – ∠CAD
= 180° – 90° – 20° = 70°
i.e. ∠CED = 70°
∴The correct answer is 4. 70°.
Example 19. ADB is diameter of a circle. If AC = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm, then the length of AB is
- 3 cm
- 4 cm
- 5 cm
- 8 cm
Solution:
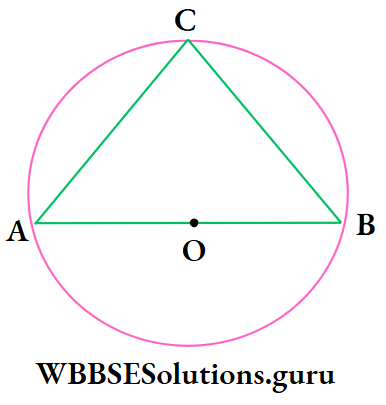
⇒ In ΔABC, ∠ACB = 90° [semi circular angle]
⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2 [From Pythagoras theorem]
= (32 + 42) cm2 = 25 cm2
⇒ AB = √25 = 5 cm
∴ The correct answer is 3. 5 cm
Example 20. O is the centre of circle and AB is a diameter, if ∠BCE = 20°, ∠CAE = 25°, the value of ∠AEC is
- 50°
- 90°
- 45°
- 20°
Solution:
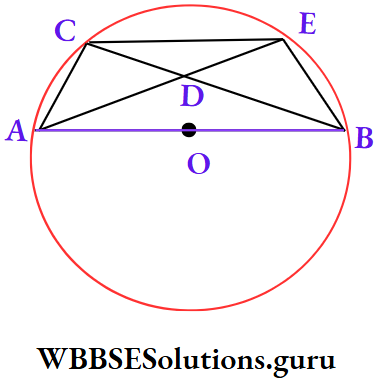
⇒ ∠ACB = 90° [semi circular angle]
⇒ ∠BCE = 20°
⇒ ∠ACE = ∠ACB + ∠BCE
= 90° + 20° = 110°
⇒ In ∠ACE, ∠AEC = 180° – ∠ACE – ∠CAE
= 180° – 110° – 25° = 45°
⇒ ∴ The correct answer is 3. 45°
Example 21. In the picture beside O is the centre of circle and AB is a diameter. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If ∠ADC = 120°, then the value of ∠BAC is
- 50°
- 60°
- 30°
- 40°
Solution:

ABCD is quadrilateral
∴ ∠ABC + ∠ADC = 180° [The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary]
⇒ ∠ABC + 120° =180°
⇒ ∠ABC = 60°
⇒ ∠ACB = 90° [semi-circular angles]
⇒ ∠BAC = 180° – 90° – 60° = 30°
∴ The correct answer is 3. 30°
Example 22. In picture beside O is the centre of circle and AB is a diameter. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If ∠ABC = 65°, ∠DAC = 60° then the value of ∠BCD is
- 75°
- 105°
- 115°
- 80°
Solution:
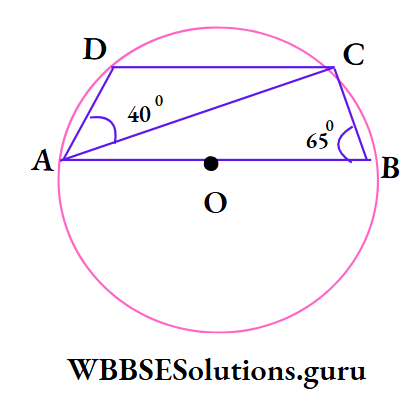
In ΔABC, ∠ACB = 90° [semi circular angle]
∠ABC = 65°
∴ ∠BAC = 180° – 65° – 90° = 25°
∴ ∠BAD = ∠BAC + ∠DAC
= 25° + 40° = 65°
⇒ ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral
∴ ∠BCD + ∠BAD = 180°, ∠BCD + 65° = 180°, ∠BCD = 115°
∴ The correct answer is 3. 115°
Class 10 Maths Important Mcqs For Board Exam
Example 23. In picture beside O is the centre of circle and AB is diameter. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AB || DC and if ∠BAC = 25° then the value of ∠DAC is
- 50°
- 25°
- 130°
- 40°
Solution:
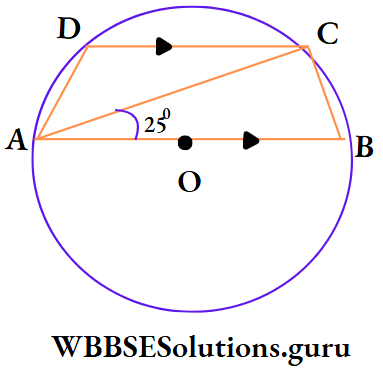
⇒ DC || AB and AC is the intersection
∴ ∠ACD = ∠BAC [alternate angle]
= 25°
⇒ ∠ACB = 90° [semi-circular angle]
∠BCD = ∠ACD + ∠ACB
= 25° + 90° = 115°
⇒ ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral
∴ ∠BAD + ∠BCD = 180°
⇒ ∠BAD + 115° = 180°
⇒ ∠BAD = 65°
⇒ ∠DAC = ∠BAD – ∠BAC
= 65° – 25° = 40°
∴ The correct answer is 4. 40°.
Example 24. In picture beside ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. BA is produced to the point F. If AE || CD, ∠ABC = 92° and ∠FAE = 20°, then the value of ∠BCD is
- 20°
- 88°
- 108°
- 72°
Solution:
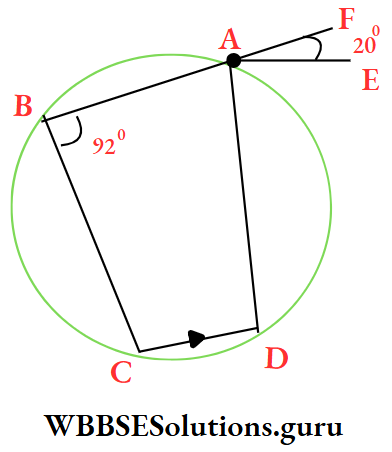
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral
∴ ∠ADC + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ∠ADC + 92° = 180°
⇒ or, ∠ADC = 88°
⇒ AE || DC and AD is the intersection
∴ ∠EAD = ∠ADC [alternate angle]
= 88°
⇒ ∠FAD = ∠EAD + ∠EAF
= 88° + 20° = 108°
⇒ For cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, exterior ∠FAD = interior opposite ∠BCD
∴ ∠BCD = 108°
∴ The correct answer is 3. 108°
Class 10 Maths Important Mcqs For Board Exam
Example 25. In picture beside two circles intersect each other at the points C and D. Two straight lines through A the point D and C intersect one circles at the points E and F respectively. If ∠DAB = 75°, then the value of DEF is
- 75°
- 70°
- 60°
- 105°
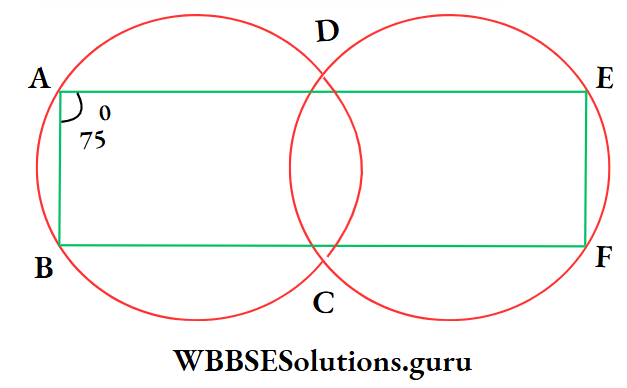
Solution:

I join D, C;
⇒ For cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, exterior ∠DCF = interior opposite ∠BAD = 75°
⇒ CDEF is a cyclic quadrilateral,
⇒ ∠DEF + ∠DCF = 180°
⇒ ∠DEF + 75° = 180°
⇒ ∠DEF = 175°
∴ The correct answer is 4. 105°