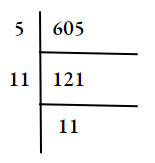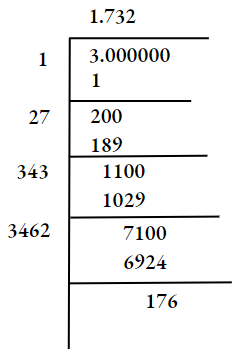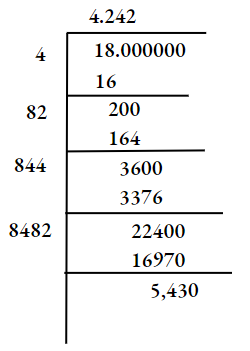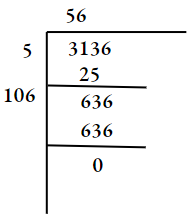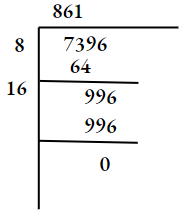Class 7 Maths Solutions For Arithmetic Chapter 5 Square Root Of Fractions
Question 1. Choose the correct answers.
The least positive integer which will multiply \(\frac{144}{605}\) to make it perfect square is
- 3
- 5
- 7
- 11
⇒ \(\frac{144}{605}=\frac{2 \times 2 \times 6 \times 6}{5 \times 11 \times 11}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2^2 \times 6^2}{11^2 \times 5}\)

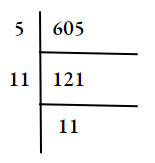
So \(\frac{144}{605}\) is to be divided by the least positive integer
5 so as to make it a perfect square fraction.
So the correct answer is (2) 5
Class 7 Arithmetic Chapter 5 Exercise Solutions
Question 2. Write true or False
1.5128 is a perfect decimal Square → False
2. The value of \(\sqrt{0.0256}+\sqrt{2.56}+\sqrt{0.000256}\) is 1.776.
⇒ \(\sqrt{0.0256}+\sqrt{2.56}+\sqrt{0.000256}\)
⇒ 0.16 + 1·6+0-016
⇒ 1.776 → True
3. The square root of \(3 \frac{109}{225} \text { is } 1 \frac{13}{15}\)
⇒ \(3 \frac{109}{225}\)
⇒ \(\frac{784}{225}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{784}{225}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{28}{15}\)
⇒ \(1 \frac{13}{15}\) → True
Question 3. Fill In the blanks:
1. If \(\sqrt{\frac{x}{225}}=\sqrt{\frac{9}{25}}\) then the value of x is 81
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{x}{225}}=\sqrt{\frac{9}{25}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{225}}=\frac{\sqrt{9}}{\sqrt{25}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\sqrt{x}}{15}=\frac{3}{5}\)
⇒ \(5 \sqrt{x}=3 \times 15\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{x}=\frac{45}{5}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{x}=9\)
squaring on Both sides.
⇒ \((\sqrt{x})^2=(9)^2\)
x =81
2. If \(\sqrt{1024}\) = 32 then the value of \(\sqrt{10.24}+\sqrt{0.1024}+\sqrt{0.001024}\) is 3.552
⇒ \(\sqrt{10.24}+\sqrt{0.1024}+\sqrt{0.001024}\)
Given \(\sqrt{1024}=32\)
⇒ \(10.24=10.24 \times 1=(32 \times 0.32)=\left(\frac{32}{10}\right)^2\)
⇒\(\sqrt{10.24}=\sqrt{\left(\frac{32}{10}\right)^2}=\frac{32}{10}=3.2\)
⇒ \(0.1024=0.1024 \times 1=\left(\frac{32}{100}\right)^2=\left(\frac{32}{10^2}\right)^2\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{0.1024}=\sqrt{\left(\frac{32}{100}\right)^2}=\frac{32}{100}=0.32\)
⇒ \(0.001024=0.001024 \times 1=\left(\frac{32}{1000}\right)^2=\left(\frac{32}{10^3}\right)^2\)
⇒\(\sqrt{0.001024}=\sqrt{\left(\frac{32}{1000}\right)^2}=\frac{32}{1000}=0.032\)
⇒\(\sqrt{10.24}+\sqrt{0.1024}+\sqrt{0.001024}\)
⇒ 3.2 + 0.32 + 0.032
⇒ 3.552
Class 7 Arithmetic Chapter 5 Important Questions
Question 4. Find the value of \(\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{1 \cdot 44}{0.25}}+\sqrt{\frac{0.64}{0.25}}}\)
Solution.
Given
⇒ \(\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{1 \cdot 44}{0.25}}+\sqrt{\frac{0.64}{0.25}}}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{\sqrt{1.44}}{\sqrt{0.25}}+\frac{\sqrt{0.64}}{\sqrt{0.25}}}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{1.2}{0.5}+\frac{0.8}{0.5}}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{2 \cdot 4+1 \cdot 6}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{4}\)
= 2
⇒ \(\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{1 \cdot 44}{0.25}}+\sqrt{\frac{0.64}{0.25}}}\) = 2
Question 5. Find the length of each side of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the two squares having the lengths of each side 1.2m and 0.5m respectively
Solution:
Given:
Length of First Square side = 1.2m
Length of second square side = 0.5m
The area of the First square
Area 1 = (1.2m)2 = 1044 m2
The area of the second square
Arear = (0.5m)2 = 0.25 m2
Total Area = Area 1 + Area2 = 1.44m2 +0.25 m2 = 1.69m2
Side length = \(\sqrt{\text { Total Area }}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{1.69 \mathrm{~m}^2}\)
= 1.3m
∴ The length of each side of the new square is 1.3 meters.
Class 7 Maths Arithmetic Chapter 5 Notes
Question 6. If product of two positive number is \(\frac{12}{25}\) and their quotient is \(1 \frac{26}{49}\) then find the numbers.
Solution:
Let the two positive numbers be ‘x’ and ‘y’.
According to Question xxy = \(\frac{12}{25}\) and \(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(1 \frac{26}{49}\)
⇒ \(x \times y \times \frac{x}{y}=\frac{12}{25} \times \frac{75}{49}\)
⇒ \(x^2=\frac{900}{1225}\)
⇒ \(x=\sqrt{\frac{900}{1225}}\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{30}{35}=\frac{6}{7}\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{6}{7}\)
⇒ xxy = \(\frac{12}{25}\)
⇒ \(\frac{6}{7} x y=\frac{12}{25}\)
⇒ \(y=\frac{12}{25} \times \frac{7}{6}\)
⇒ \(y=\frac{14}{25}\)
The two numbers are $ and \(\frac{6}{7}\) and \(\frac{14}{25}\)
Question 7. Find the approximate value of the following Upto 3 decimal places:-
- \(\sqrt{3}\)
- \(\sqrt{5}\)
- \(\sqrt{18}\)
1. \(\sqrt{3}\)
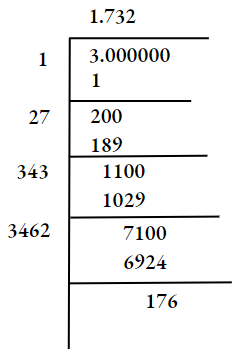
∴ \(\sqrt{3} \simeq 1.732\)
2. \(\sqrt{5}\)

∴ \(\sqrt{5}=2.236\)
3. \(\sqrt{18}\)
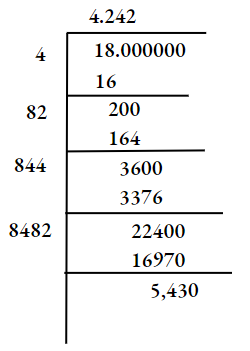
∴ \(\sqrt{18}=4.242\)
Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic PDF
Question 8. Find the square root of the following.
Solution:
1. \(4 \frac{220}{729}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3136}{729}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{3136}{729}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{56}{27}\)
= 2.0740
∴ \(\sqrt{4 \frac{220}{729}}=\frac{56}{27}\)
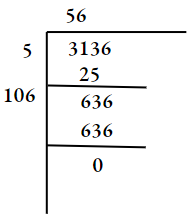

2. 206.094736
⇒ \(\sqrt{206.094736}\) = 14.357

3. 10732.96
⇒ \(\sqrt{10732.96}\) = 103.6

4. \(3 \frac{1321}{2025}\)
⇒ \(\frac{7396}{2025}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\frac{7396}{2025}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{86}{45}\)
⇒ \(1 \frac{41}{45}\)
∴ \(\sqrt{3 \frac{1321}{2025}}=1 \frac{41}{45}\)
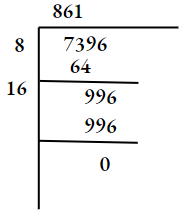
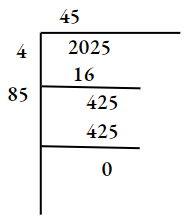
Question 9. What is the least number that must be subtracted From 0.001528?
Solution:
⇒ \(0.001528 \approx \sqrt{\frac{1528}{1000000}} \approx \frac{\sqrt{1528}}{1000} \approx \frac{39.08}{1000} \approx 0.03908\)
⇒ \((0.039)^2=0.039^2=0.001521\)
⇒ \((0.040)^2=0.040^2=0.001600\)\
The closest perfect square less than 0.001528 is 0.001521
Now subtract this value from 0·001528:
0.001528 – 0.001521 = 0·000007.
∴ The least number that must be subtracted from 0.001528 to make it a perfect Square number is 0.000007.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic PDF
Question 10. Find the value of \(\sqrt{1-(0.05)^2}\) upto 3 decimal places.
Solution:
⇒ \(\sqrt{1-(0.05)^2}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{1-0.0025}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{0.9975}\)
= 0·998749
Rounded upto 3 decimals = 0.998

Question 11. By which Fraction should \(\frac{35}{91}\) be multiplied so that the square root of the product is 3?
Solution:
Let the Fraction be \(\frac{a}{b}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{\left(\frac{35}{91} \times \frac{a}{b}\right)}=3\)
⇒ \(\frac{35}{91} \times \frac{a}{b}=3^2\)
⇒ \(\frac{35}{91} \times \frac{a}{b}=9\)
⇒ \(\frac{35}{91}=\frac{5 \times 7}{7 \times 13}=\frac{5}{13}\)
Substitute \(\frac{5}{13} \text { for } \frac{35}{91}\)
⇒ \(\frac{a}{b}=9 \times \frac{13}{5}=\frac{117}{5}\)
⇒ \(\frac{35}{91} \times \frac{117}{5}=\frac{35 \times 117}{91 \times 5}=\frac{5 \times 7 \times 117}{7 \times 13 \times 5}=\frac{117}{13}=9\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{9}=3\)
Hence the Fraction \(\frac{117}{5}\) is correct.
Thus the Fraction by which \(\frac{35}{91}\) should be multiplied so that the square root of the product is 3 is
⇒ \(\frac{117}{5} \Rightarrow 23 \frac{2}{5}\)