WBBSE Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry Chapter 1 Distance Formulas Multiple Choice Questions
Example 1. The distance between the two points (a + b, c – d) and (a -b, c + d) is
- \(2 \sqrt{a^2+c^2}\)
- \(2 \sqrt{b^2+d^2}\)
- \(\sqrt{a^2+c^2}\)
- \(\sqrt{b^2+d^2}$\)
Solution: The distance between the two points (a + b, c – d) and (a – b, c + d) is
\(\sqrt{\{(a+b)-(a-b)\}^2+\{(c-d)-(c+d)\}^2}\) units
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 Maths Multiple Choice Questions
= \(\sqrt{(a+b-a+b)^2+(c-d-c-d)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{(2 b)^2+(-2 d)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{4 b^2+4 d^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{4\left(b^2+d^2\right)} \text { units }=2 \sqrt{b^2+d^2} \text { units }\)
∴ So the correct answer is 2. \(2 \sqrt{b^2+d^2}\)
∴ The distance between the two points (a + b, c – d) and (a -b, c + d) is \(2 \sqrt{b^2+d^2}\)
Example 2. If the distance between the two points (x, -7) and (3, -3) is 5 units, then the values of x are
- 0 or 6
- 2 or 3
- 5 or 1
- – 6 or 0
Solution: The distance between the points (x, -7) and (3, -3) is
\(\sqrt{(x-3)^2+\{(-7)-(-3)\}^2} \text { units }\)= \(\sqrt{x^2-6 x+9+(-7+3)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{x^2-6 x+9+(-4)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{x^2-6 x+9+16} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{x^2-6 x+25} \text { units }\)
According to question, \(\sqrt{x^2-6 x+25}=5\)
⇒ x2 – 6x + 25 = 25
⇒ x2 – 6x = 0
⇒ x (x – 6) = 0
⇒ x = 6
either x = 0,. or, x – 6 = 0 ⇒ x = 0 or 6
∴ So the correct answer is 1. 0 or 6
∴ The values of x are 0 or 6
Example 3. If the distance of the point (x, 4) from origin is 5 units, then the values of x are
- ±4
- ±5
- ±3
- None of these
Solution: The distance of the point (x, 4) from origin is \(\sqrt{x^2+4^2}\) units
= \(\sqrt{x^2+16}\) units
According to question, \(\sqrt{x^2+16}\) = 5
⇒ x2 + 16 = 25
⇒ x2 = 9
⇒ x = ±√9
⇒ x = ±3
∴ The correct answer is 3. ±3
∴ The values of x is ±3.

Example 4. The triangle formed by the points (3, 0), (-3, 0), and (0, 3) is
- Equilateral
- Isosceles
- Scalene
- Isosceles right-angled
Solution: A (0, 3), B (3, 0) and C (-3, 0) are three points
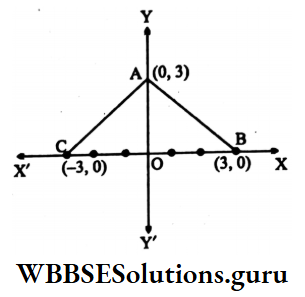
The length of AB = \(\sqrt{(0-3)^2+(3-0)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{9+9} \text { units }=\sqrt{18} \text { units }\)
The length of AC = \(\sqrt{\left\{(0-(-3)\}^2+(3-0)^2\right.} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{9+9} \text { units }=\sqrt{18} \text { units }\)
The length of BC = \(\sqrt{\{3-(-3)\}^2+(0-0)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{(3+3)^2+0} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{6^2} \text { units }=6 \text { units }\)
In ΔABC, AB = AC = √18 units
∴ ΔABC is a isosceles triangle
Again, AB2 + AC2 = (√18)2 +(√18)2
= 18+ 18 = 36 = 62 = BC2
∴ ΔABC is a right-angled triangle whose ∠BAC = 90°
So ΔABC is a right-angle isosceles triangle.
∴ The correct answer is 4. Isosceles right-angled
The triangle formed by the points (3, 0), (-3, 0), and (0, 3) is Isosceles right-angled triangle.
Example 5. The coordinates of the centre of the circle are (0, 0) and the coordinates of a point on the circumference are (3, 4), the length of the radius of the circle is
- 5 units
- 4 units
- 3 units
- None of these
Solution: The distance between the point (3, 4) on the circumference and the centre (0, 0) of the circle is \(\sqrt{(3-0)^2+(4-0)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{9+16} units =\sqrt{25}=5 units\)
The length of the radius of the circle is 5 units.
∴ So the correct answer is 1. 5 units
∴ The length of the radius of the circle is 5 units
Example 6. The distance of points (a + b, a- b) from origin is
- \(2 \sqrt{a^2+b^2}\) units
- \(2 \sqrt{a b}\) units
- \(\sqrt{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)}\) units
- None of these
Solution: The distance of points (a + b, a – b) from origin (0, 0) is \(\sqrt{(a+b)^2+(a-b)^2}\) units
= \(2 \sqrt{a^2+b^2}\) units
∴ The correct answer is 3. \(\sqrt{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)}\) units
∴ The distance of points (a + b, a- b) from origin is \(\sqrt{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)}\) units
Example 7. If the coordinates of two extreme points of the greatest chord of a circle is (5, 3) and (3,3) then the length of radius of the circle is
- 2 units
- 3 units
- 4 units
- 5 units
Solution: The greatest chord of the circle is diameter of that circle.
The length of diameter is the distance between the points (5, 3) and (- 3,-3)
= \(\sqrt{\{5-(-3)\}^2+\{3-(-3)\}^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{(5+3)^2+(3+3)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{(8)^2+(6)^2} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{64+36} \text { units }\)
= \(\sqrt{100} \text { units }=10 \text { units }\)
∴ The length of radius is \(\frac{10}{2}\) units = 5 units
∴ So the correct answer is 4. 5 units
∴ The length of radius of the circle is 5 units.
Example 8. If the point (x, y) is equidistant from two points (2, -3) and (-2, 3), then the relation between x and y is
- 2x + 3y = 0
- 2x = 3y
- 3x – 2y = 0
- 3x + 2y = 0
Solution: The point (x, y) is equidistant from points (2, -3) and (-2, 3)
The distance between (x, y) and (2, -3) is \(\sqrt{(x-2)^2+\{y-(-3)\}^2}\) units
= \(\sqrt{(x-2)^2+(y+3)^2}\) units
The distance between (x, y) and (-2, 3) is \(\sqrt{\{x-(-2)\}^2+(y-3)^2}\) units
= \(\sqrt{(x+2)^2+(y-3)^2}\) units
According to question, \(\sqrt{(x-2)^2+(y+3)^2}=\sqrt{(x+2)^2+(y-3)^2}\)
⇒ (x – 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = (x + 2)2 +(y – 3)2 [squaring both side]
⇒ (y + 3)2 – (y – 3)2 = (x + 2)2 – (x – 2)2
⇒ 4.y.3 = 4.x.2 [By applying (a + b)2 – (a – b)2 = 4ab]
⇒ 3y = 2x
∴ The correct answer is 2. 2x = 3y
The relation between x and y is 2x = 3y.
