WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Shape Of The Earth
Facts At Your Fingertips:
- Amongst eight planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) of the solar system, the most unique is the planet Earth which is the habitat of life.
- The earth originated about 4.5 to 4.6 billion years ago, about 500 million years after the birth of the sun.
- It took about 2.5 billion years for the creation of life on the earth since the origin of the earth.
- Earth is the third in position next to Mercury and Venus with an average distance of 150 million km from the sun and the sunlight takes 8 minutes to reach the Earth with a velocity of 3 lakh km/sec.
- Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system and is revolved by the only satellite called the Moon.
- Land (29%) and water (71 %) bodies are antipodal and located around the poles.
- The envelope of the atmospheric layers consisting of oxygen helps to sustain life on the earth.
- The actual shape of the earth is ‘Oblate Spheroid’ and is better described as ‘Geoid’.
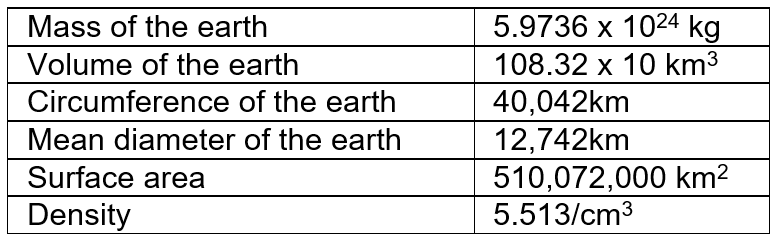
- The average circumference is about 40,000 km.
- The approximate mass of the earth is 5976 x 108 metric tonnes.

WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Concept Of Shape Of The Earth
Evolution Of The Concept Of The Shape Of The Earth:
Flat Earth
The flat earth concept is an archaic belief that the earth’s shape is a plane or disc. This concept was held by many ancient cultures even in Greece until the Classical Period.
Read And Learn Also WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography and Environment
Ancient Chinese people believed that China was the only landmass which represented the earth and it was surrounded by oceans filled with dragons and giant fishes.
Phoenicians portrayed the earth as a flat disc floating in the ocean surrounded by a spherical sky.

WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography Chapter 1
Spherical Earth
The concept of spherical earth appeared in Greek philosophy with Pythagoras (6th century B.C.). Aristotle accepted the spherical shape of the earth on empirical grounds around 330 B.C.
Indian astronomer, Aryabhatta (476-550 A.D.) stated that the earth is spherical with a circumference of 39,968 km.
Myth Of The Flat Earth :
The modern misconception that educated Europeans at the time of Columbus believed in a flat earth concept and his voyages refuted that belief has been referred to as the myth of the flat earth.
The paradigm of spherical earth gradually spread and was first accepted with the circumnavigation expedition (1519-1522) of Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastian Elcano.
The spherical shape of the earth which was more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates back to the 18th century. In the 19th century, the flattening of the earth as an ‘ellipsoid’ was accepted.
WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Proofs From The Earliest Days Till Today
Portuguese exploration of Africa and Asia, Columbus’ voyage to America (1492) and finally F. Magellan’s circumnavigation of the earth (1522) is the practical evidence of the global shape of the earth.
Evidence For Spherical Earth
Sighting Of Boat:
At sea, it is possible to see the mast of a boat before the hull appears.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 PDF
Position Of The Sun:
The sun is seen lower In the sky as one moves away from the tropics.
Length Of Day Light:
The length of daylight varies more between summer and winter the farther you are away from the equator.

Lunar Eclipse:
The Earth throws its circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse.

Circumnavigation:
It is possible to circumnavigate the earth.
Gain Or Loss Of A Day :
Travellers who circumnavigate the earth observe the gain or loss of a day.
Satellites:
An artificial satellite can circle the Earth continuously.
Aerial Photograph:
The aerial photograph taken from space shows the disc shape of the Earth.
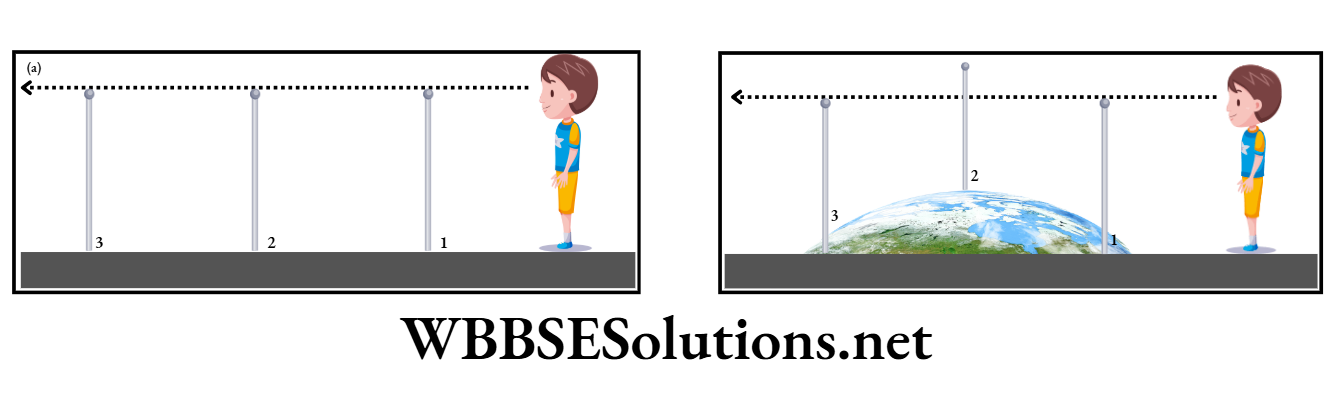
Bedford Level Experiment:
An experiment carried out by Dr Wallace along the Bedford Canal of Britain also proves the curvature of the earth.
He fixed three poles of equal length at regular intervals along the canal and found that the central pole was seen slightly above the poles at both ends.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography and Environment Chapter 1 Notes
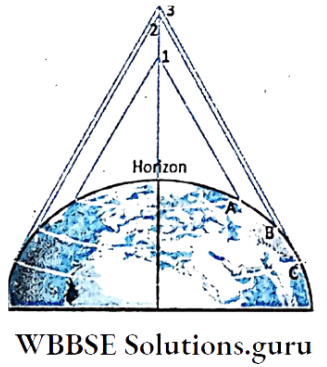
Horizon Of The Earth:
As one goes up sees the horizon spherical as well as wider.
WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Earth As An Oblate Spheroid
Proofs Of Oblate Spheroid Shape Of The Earth:
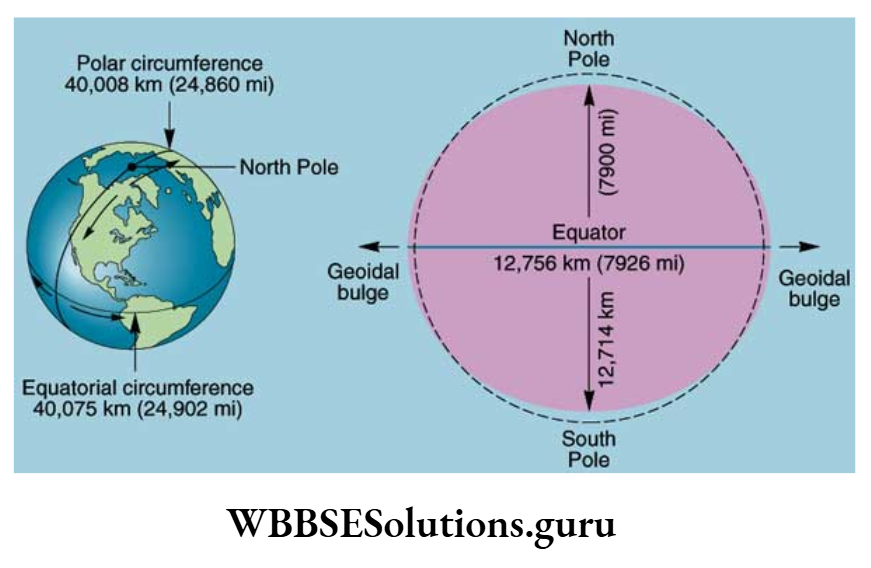
Variation In Diameter:
The Equatorial diameter is 43 km longer than ‘the polar diameter. So the earth is flattened at the poles with a bulge at the equator.
Swing Of Pendulum :
An experiment carried out by French astronomer Jean Richer in 1671 revealed that the oscillation of the pendulum of a clock in 24 hours took 2 minutes less at Cayenne island (nearly 0°) than at Paris. (53°N).
The greater the force of gravity longer the period of oscillation of the pendulum. So Cayenne is nearer to the centre of the earth- than Paris.
Weight Of An Object:
Any object weighs more at the poles than at the region near the equator. So the equatorial diameter is longer than the polar diameter.
Observation Of Star :
The star that is seen above the horizon (0°) at the equator will be seen at an angle of 1° above the horizon, traveling 111 km away from the equator.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography and Environment Chapter 1 Notes
WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Concept Of Geoid
The earth’s surface is not smooth like the geometrical shape of an oblate spheroid. It is intervened by high mountains and deep seas like Everest (8,848 m above sea level and the Dead Sea (392 m below sea level).
So the earth is often referred to as a ‘GEOID’ which means ‘earth shaped’ that is not identical with any other geometrical shapes.
In Geodesy (combination of survey and mathematical analysis), the shape of the earth i.e. Geoid is defined by the mean sea level surface.
Practically, differences in height between mountain peaks and sea bottoms are ignored when reduced in scale to a small globe which is, actually, spherical for practical purposes.

WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Size Of The Earth
Size Of The Earth In Proportion To The Other Planets:
Earth Profile:
Among the eight solar system members, by size, Jupiter is the largest while Mercury is the smallest planet and the Earth is fifth in size.
In other words, Jupiter is 1319 times the size of the Earth, while Mercury is half the size of the Earth. Neptune is four times the size of the Earth.
Four planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, are bigger than the Earth, while Mercury, Venus and Mars are smaller than the Earth.
Find Out The Position Of The Planets According To Their Sizes:
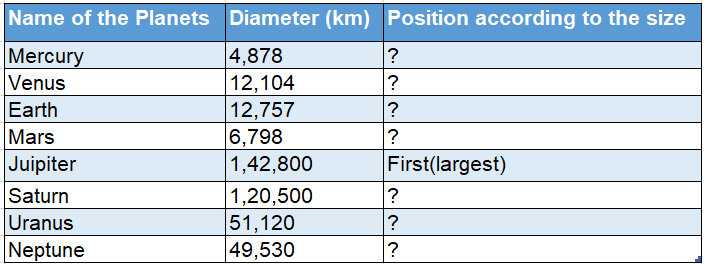

Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Important Questions WBBSE
WBBSE Unique Position Of The Earth In The Solar System
Unlike the other planets, the Earth is a unique member of the solar system. Its unique position i.e. 150 million km away from the sun enables the earth to receive optimum temperature i.e. 15°C (average).
Due to its proximity to the sun, Mercury is the hottest planet with day temperature rising to 450°C while Venus experiences 482°C (the atmosphere contains more carbon dioxide and sulphuric acid).
On the other hand, due to its distant location, the planet Mars is severely cold with summer temperature drops below freezing point.
Distant planets namely Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune are bitterly cold. The temperature of Uranus and Neptune remains always – 200°C.
Position Of The Planets From The Sun :
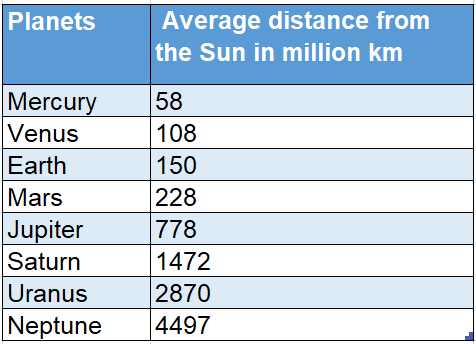
WBBSE Earth As The Home Of Humankind
We are really lucky that our habitat is the earth only planet in our solar system.
Scientists inferred that the sustainability of life is possible only on the earth which can support life in all its forms from living microorganisms to highly intelligent human beings.
It is possible only because of its (earth’s) breathable atmosphere, a suitable climate with a moderate amount of carbon dioxide, and water the most important chemical necessary for life.
Adequate light received from the sun and probably, life wouldn’t exist if the earth was not in a position with an ideal distance from the sun with an average temperature of 15°C.
Time For Action-Save The Planet:
Man has deteriorated his beautiful habitat, the earth. His unwise actions are responsible for global warming, and the pollution of air, soil and water.
Now the time has come to act to repair what has been damaged and to prepare the future so that the earth will provide a fair shelter for its inhabitants once again.
WBBSE Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet Measurements Of The Earth
Circumference:
How Big Is The Earth?
The average circumference of the earth is 40,000 km. Along the equator, it is 40,075 km. While the polar circumference is 40,009 km.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Important Questions WBBSE
Area
The area of the earth can easily be calculated by applying the formula 4πг2 (π= 22/7, r = radius i.e. 12,736 km or on average (12,800 km). So the area of the surface of the earth is 4 x 22/7 x (6400)2 km or 5, 10,072 Km2 It consists of 71% water and 29% land.
Use Of Gps
GPS or Global Positioning System is a space-based satellite navigation system made up of a network of 24 artificial satellites in orbit. It provides the location of any place in the world in any type of climate.
The location of the place is determined in terms of
- Latitude,
- Longitude,
- Altitude and
- Time
GPS consists of 24 artificial satellites orbiting the Earth twice a day in six specific orbits and a GPS receiver on the Earth.
Out of 24 satellites only four of these satellites are visible from any place at any time.
From these four satellites, four types of signals are received, such as latitude, longitude, altitude and time by the GPS receiver.

Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Important Questions WBBSE
Works Of Gps

In GPS, Orbiting satellites transmit signal information to the Earth receiver. The GPS receiver compares the time, a signal is transmitted by a satellite with the time it was received.
The difference in time is measured by an electronic clock fitted in it. The GPS receiver, thus, determines the user’s exact location.
Nowadays, GPS receiver is used in automobiles, ships, aeroplanes, laptops, mobile, and wristwatches.
Now, it is widely used in the preparation of maps, transportation, and defence, as traveller’s guides, to collect weather information, etc.
