Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Introduction Concept Of The Movements Of The Earth
All those questions mentioned above were interrogated by our ancestors and they thought that the primary cause was the earth-centric movement of the sun.
But, scientists have proved that it is the Earth that is moving around the sun as well as around its invisible axis. The earth is spinning around its axis in approximately 24 hours.
This movement is known as Rotation. Simultaneously, the Earth is also revolving around the sun for approximately 365 days. This movement of the earth is known as the Revolution. All the members of the solar family, like the earth, have two motions-Rotation and Revolution..
Read And Learn Also WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography and Environment
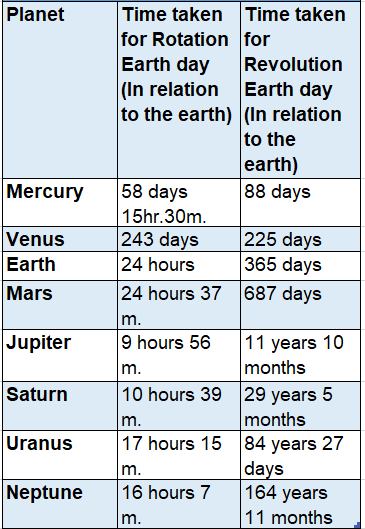
For example, Mercury, the closest planet to the Earth takes approximately, 58 Earth days (with the Earth) to spin around its axis, i.e. one day of the Mercury.
Along this rotation, the Mercury also travels around the sun in 88 earth days (about the earth), i.e. one year of the Mercury. Next to Mercury is the planet Venus which takes 243 Earth days and 225 Earth days to rotate and revolve respectively.
Other planets take more time as the distances increase with the sun. For example; Jupiter takes 11 years 10 months, Saturn takes 29 years 5 months, Uranus takes 84 years 27 days and Neptune takes 164 years 11 months.
WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
But the time taken by each planet to revolve around the sun once is one year for that particular planet if not considered the time of the earth. For rotation, the distant planets take less time than the Earth.

Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Brief History Of Observation On Earths Movements
In ancient times, people thought that the sun was moving around the Earth. In the fifth century B.C. mathematician and astronomer Pythagoras and his disciples said first about the movement of the earth around the sun.
But no one believed this concept and even in the fourth century B. C. Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) also, did not believe it. After the birth of Christ, in the second century, Ptolemy also believed the concept of Aristotle.
Indian mathematician and astronomer of ancient times, namely Aryabhatta, in 499 A.D. explained the movements of the sun and other stars as the effect of the movement of the earth around its axis.
But, till the medieval period, most people did not believe in the Pythagorean concept or the explanation of Aryabhatta.
Finally, in 1543 A. D. mathematician and astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus of Poland strongly explained the movement of the earth centering the sun.
Although, many people at that time followed the earth-centric movement of the sun.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Important Questions WBBSE
Later on, Galileo, Kepler, Newton, and all eminent scientists were able to establish the movements of the planets by mathematical calculations and by visual proof with the help of a telescope.
Since then, people have been convinced and accepted the concept of the movements of the Earth and other planets.
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Rotation
The spinning of the earth around its axis, since its origin, is known as Rotation. The time takes to rotate the earth around its axis is 23 hours, 56 minutes 4 seconds, i.e. nearly 24 hours or 1 day.
So, the Rotation of the earth is also known as Diurnal motion.
Direction Speed Effects Of Rotation
1. Direction of Rotation of the Earth:
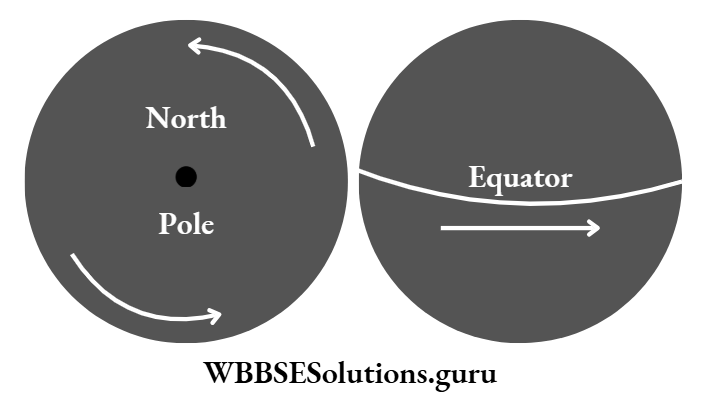
Have you noticed the sun and other stars move from east to west? The earth is moving from the west to the east: It so happens just like from a running train we see the objects outside move in the opposite direction.
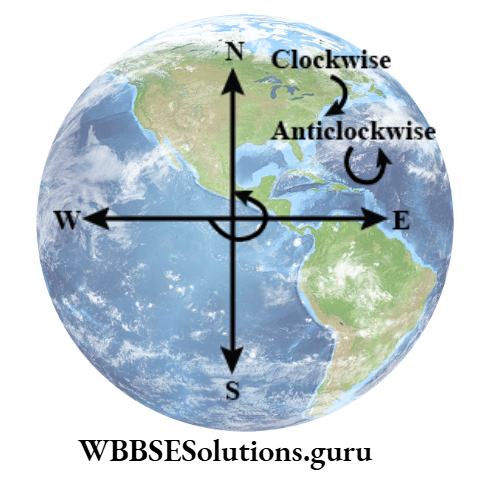
Around the poles, as it is not easy to find out the east and west directions, the direction of rotation at the north pole is anti-clockwise and at the south pole, Night is clockwise.
2. Speed of Rotation of the Earth:
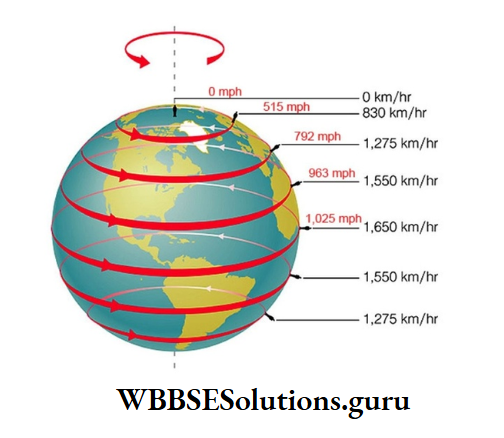
Due to its spherical shape, circumferences of “the earth at all parts are not equal in size. But, they take 24 hours to rotate once.
As the circumference of the earth is maximum at the equator (0°) and decreases gradually towards the two extremities at points, the speed of rotation of the earth also decreases away from the equator where it is 1630 km per hour.
It is 1536 km per hour at Kolkata (22°30′ north), 1438 km per hour at 30° north latitude, 990 km per hour at 60° north latitude, and finally zero (0) at 90° latitude. So, at the poles, there are no relative movements.
3. Effects Of Rotation Of The Earth:
Rotation of the earth results in major events like the formation of day and night, deflection of planetary winds and ocean currents, tides, and ebb, etc.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Important Questions WBBSE
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Alternation Of Day And Night
The rotation of the earth causes the alternation of day and night. The earth is round and is lighted and heated by the sun.
So during rotation, the hemisphere of the earth that faces the sun receives sun rays, and therefore, enjoys day while the opposite hemisphere remains in darkness and experiences night.
The demarcating line between the lighted and dark parts of the earth is known as a shadow circle and the transitional phases of day and night are dawn, dusk, morning, evening, noon, and midnight.
Shadow Circle
The circumference of the earth along which the lighted and dark parts of the earth cross each other is known as a shadow circle.
It moves westward on the surface of the earth with eastward rotation of the earth.
It bisects the equator which experiences 12 hours day and 12 hours night year round because of the inclination of the earth’s axis at 66° angle to its orbital plane.

Morning And Evening
A place on the earth’s surface that crosses the shadow circle comes out from the darkness and eventually, experiences morning while the place located opposite to it crosses the shadow circle to enter the darkness and experiences evening.
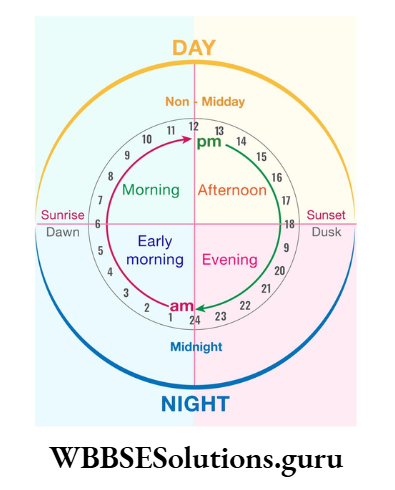
Dawn And Dusk
The diffused sunlight seen in the sky before sunrise is known as dawn and the diffused sunlight seen in the sky after sunset is known as dusk or twilight.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Pdf
Noon And Midnight
When the sun stays at the zenith or the celestial meridian of a place it experiences noon or midday. The place is the opposite it remains in darkness and experiences midnight.
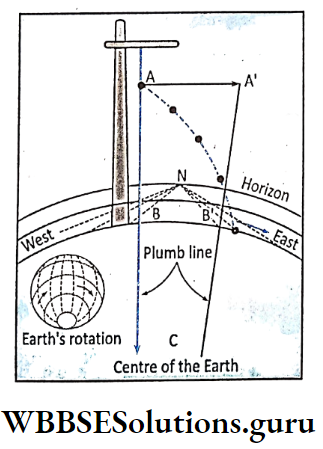
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Coriolis Effect
In 1835, G. G. Coriolis (1792-1843), a French mathematician discovered the tendency of freely moving particles to deflect from their normal course.
This deflection is known as Coriolis. effect or Coriolis force after the name of the discoverer.
It is due to the Coriolis effect that ocean currents and planetary winds attached to the earth do not move directly in a north-south direction.
They deflect to the right in the northern hemisphere and the left in the southern hemisphere. The speed of the earth’s rotation is maximum at the equator while the minimum is at the poles.
So, the wind blowing towards the equator moves with less speed than that moves away from the equator. But the wind tries to maintain its initial speed and becomes deflected.
So, they deflect to the right in the northern hemisphere and the left in the southern hemisphere.
Example. Trade winds blowing toward the equatorial low-pressure belt are deflected as northeast trade wind in the northern hemisphere and southeast trade wind in the southern hemisphere.
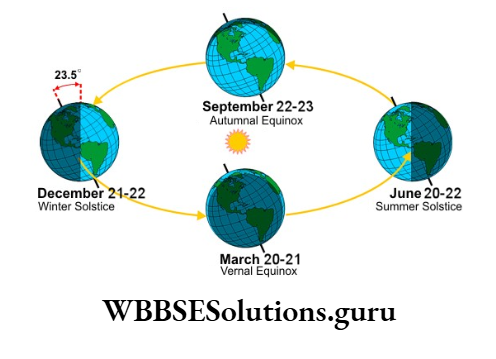
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Inclination Of The Earths Axis And Its Significance
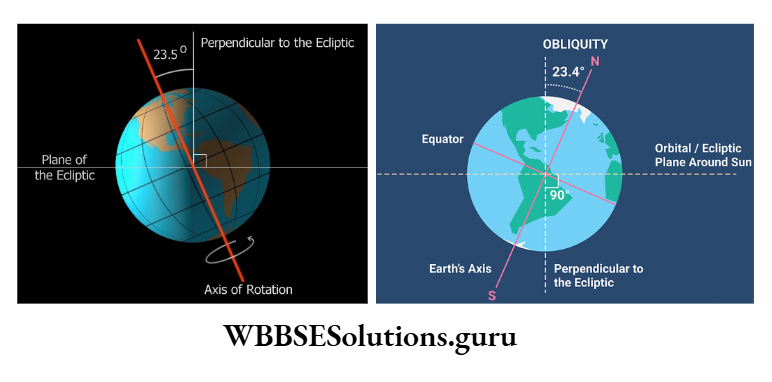
Due to the rotation of the. earth from the west to the east an invisible imaginary line joining the north pole and the south pole passing through its center has formed. This is known as the axis of the earth.
It is actually, tilted at a 23°30′ angle from the vertical i.e. 90°. The axis of the earth is tilted on its orbital plane pointing always to the pole star.
The earth revolves along with its rotation around the sun in a fixed path or orbit to which its axis inclines at a 66°30′ angle.
It is Due to the tilting of the earth’s axis at 66°30′ angle, the northern and southern hemispheres are tilted towards the sun for six months alternately.
This results in variations in the length of day and night on the earth’s surface, variations in temperature at different times of the year, and ultimately the change of seasons.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Pdf
If the axis of the earth was perpendicular to the orbit, the days and nights would be 12 hours each everywhere on the earth’s surface like the equatorial region. No change of seasons would take place.
If the axis of the earth was parallel with the orbit of the earth, like Uranus, each hemisphere would remain in light or darkness at least for six months.
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Revolution
Together with Rotation, the earth revolves around the sun, along an elliptical orbit to which its axis inclines at 66+ angle, in the anti-clockwise direction. This movement of the earth is known as the Revolution.
It takes 365 days 5 hours 48 minutes 46 seconds to revolve once around the sun or approximately 365 days or one year. So, the Revolution of the earth is also known as the Annual motion of the earth.

Direction Speed Effects
1. Direction Of Revolution Of The Earth :
The earth along its rotation from the west to the east revolves around the sun in an anti-clockwise direction with its axis always tilted at a 66½º angle to its orbit or fixed path of revolution.
2. Speed Of Revolution Of The Earth :
The earth moves about 30 km each second along its orbit in the anti-clockwise direction. So the velocity of the earth’s revolution is about 30 km per second or 1,08,000 km/hour.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 2 Notes
3. Effects Of Revolution Of The Earth:
Revolution of the earth around the sun results in the concept of Leap year, Perihelion-Aphelion positions of the earth, sun’s ecliptic or apparent annual motion of the sun.
variation in the length of day and night, equinoxes- solstices, change of seasons, etc.
Leap Year Aphelion And Perihelion
The earth takes 365 days 5 hours 48 minutes 45.51 seconds or 46 seconds to revolve once around the sun. But for calculation, it is rounded off as 365 days.
So in each year there is an excess of 6 hours (5 hours 48 minutes 46 seconds) which may be added at the end of the 4th Find out the leap years year which becomes 366 days (6 hours x 4 = 24 hours or 1 day).
This extra one day is added in February and that year is called Leap Year. A leap year is divisible by 4, for Example. 2012 and 2016 are leap years.
But all the century years are not leap years even if they are divisible by 4 because there is an inbuilt excess of 11 minutes 14 seconds in each year (6 hours-5 hours 48 minutes 45-51 seconds = 11 minutes 14-09 seconds).
And cumulative 44 minutes 56 seconds (11 minutes 14-09 seconds x 4) in each leap year. Century years are, therefore, granted as a leap year, if only, these years are divisible by 400, for Example. 2000 is a leap year but 1800, 1900, and 2100 are not leap years.
Aphelion And Perihelion:
The earth revolves in a fixed path called orbit which is elliptical. The sun is located at one of its two foci. So, the distance between the sun and the earth is not the same with an average distance of 150 million km approximately.
Aphelion
The earth goes farthest from the sun on 4th July, about 152 million km away during its revolution along the elliptical orbit. This is called Aphelion (the Latin word Apo means away, and helion means sun).
Due to greater distance, the sun appears smaller in size and the speed of the earth’s revolution becomes slower. The sun is visible 9 days more at the north pole than at the south pole during the revolution of the earth.

Perihelion
The earth comes closest to the sun on 3rd January at a distance of 147 million km during its revolution along the elliptical orbit. This is called the Perihelion position of the earth.
The Latin word ‘Peri’ means near and ‘helion’ means sun. Due to the shorter distance, the sun appears bigger and the speed of the earth’s revolution also becomes faster.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 2 Notes
The yearly Apparent Movement Of The Sun
Did you notice that the sun rises in due east and sets in due west in March and September only? Otherwise, the sun rises and sets either north or south of these positions. This apparent movement of the sun in a year is due to the revolution of the earth along an elliptical orbit.
On the 21st of March and 23rd of September, the sun rises and sets due east and west respectively. But on other days the sun shifts to either north or south of those positions.
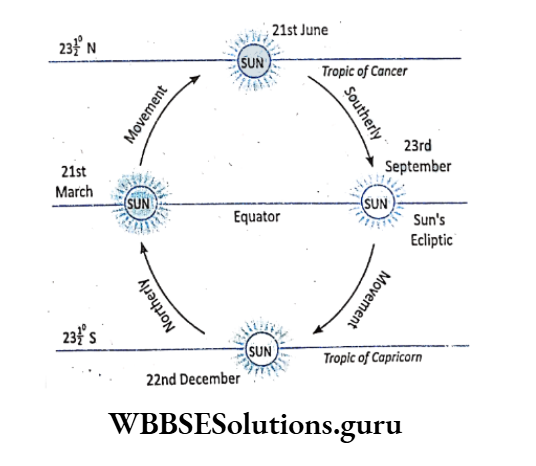
As a result, the sun appears to move in a north-south direction within 23°30′ north and 23°30′ south latitudes. This apparent path of the sun in the sky is known as Sun’s Ecliptic.
The northerly apparent movement of the sun is northwards from 22nd December to 21st June i.e. from the Tropic of Capricorn to the Tropic of Cancer.
The southerly apparent movement of the sun is from 21st June (tropic of cancer) to 22nd December (tropic of Capricorn). This apparent movement of the sun is known as Sun’s Ecliptic.
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Variation In The Length Of Day And Night Equinoxes And Solstice
Excepting the equatorial region, places on the earth’s surface experience either longer days and shorter nights or vice-versa at different times of the year.
Only on the 21st of March and 23rd of September, days and nights are equal on all parts of the earth.
Causes Of Variation In The Length Of Day And Night
Two major factors are responsible for variation in the length of day and night
- Revolution of the earth and
- The inclination of the earth’s axis at 66°30′ angle on the orbital plane of the earth. Other factors are the spherical shape of the earth, rotation of the earth, elliptical shape of the orbit, etc.
Explanation Of Variation In The Length Of Day And Night:
If you observe minutely the different positions of the earth in its orbit at different times of the year you may easily understand the variation in the length of day and night.
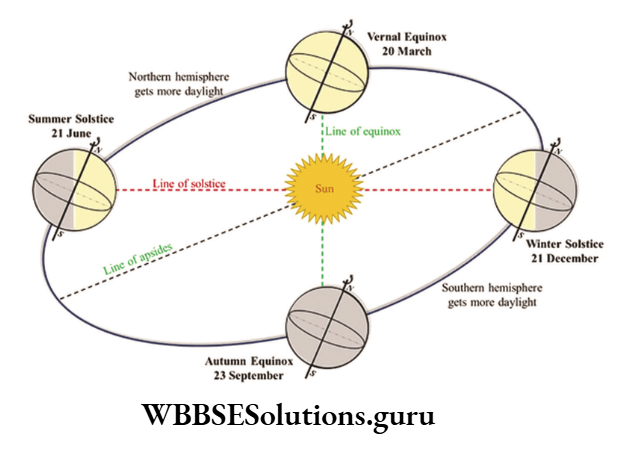
21st June
On this date, the sun lies over the tropic of Cancer and the northern hemisphere inclines towards the sun.
So the northern hemisphere enjoys the longest day and shortest night while the southern hemisphere experiences the longest night and shortest day.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 2 Notes
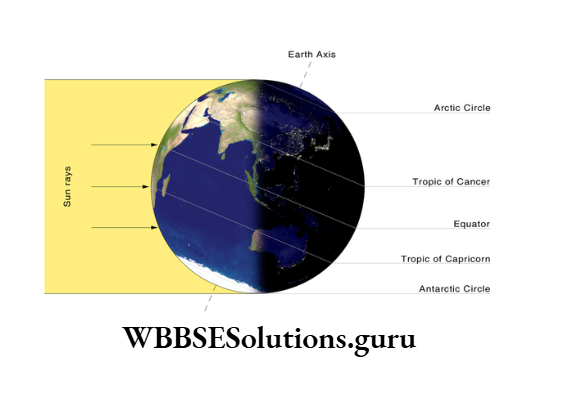
Places beyond the Arctic Circle (66 N) experience 24 hours a day while places beyond the Antarctic Circle experience 24 hours of night.

Summer Solstice :
23°30′ North latitude is the northern extremity of the northerly apparent movement of the sun.
So 23°30′ north latitude is called the tropic of Cancer (Tropic means turning point) and the 21st of June is known as summer solstice (solstice means sun’s stopping time) as it is summer in the northern hemisphere.
23rd September
With the end of the summer solstice, the southerly apparent movement of the sun begins and the southern hemisphere comes nearer the sun. On 23rd September the sun lies at the zenith (90°) over the equator.
Shadow circle coincides with the earth’s axis. So days and nights are equal to 12 hours on all parts of the earth.
Autumnal Equinox:
The day which experiences equal day and night is known as the equinox (equal means equal and nox means night). As it is autumn in the northern hemisphere the day is known as the Autumnal equinox.
22nd December
As the journey of the earth goes on, the southern hemisphere comes nearer the sun and on 22nd December the sun lies, over the Tropic of Capricorn.
The days become longer than nights in the southern hemisphere, while the nights become longer than days in the northern hemisphere.
Places beyond the Arctic Circle enjoy 24 hours of the night while the places beyond the Antarctic Circle experience 24 hours a day.
Winter solstice:
23°30′ south latitude is the southern extremity of the southerly apparent movement of the sun, So 23°30′ south latitude is called the Tropic of Capricorn.
22nd December is known as winter solstice as it is winter in the northern hemisphere.
21st March
With the end of the winter solstice, the sun turns its apparent journey northward and lies at the zenith over the equator on 21st March.
Shadow circle, once again, coincides with the earth’s axis. So days and nights are equal to 12 hours in duration over all parts of the earth.
Vernal Equinox:
Like the autumnal equinox, on 21st March, it is spring in the northern hemisphere. So, the 21st of March is known as Spring or Vernal equinox.
WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Change Of Seasons
Our earth is a seasoned traveler. Try to feel how autumn cools into winter and spring warms up to summer following the year-long apparent circuit of the sun.
These changes are responsible for temperature variations. On that basis, a year is divided into seasons that rotate in a cycle.
Change of seasons is mainly caused by variations in temperature which depends on variations in the length of day and night and variations in the inclination of sunrays falling on the earth.
Variation In The Length Of Day And Night
Excepting the equator, days and nights are not equal in all the places on the earth. This variation in the length of day and night causes summer when days are longer than nights thereby storing excess heat daily.
When nights are longer than days excess heat is released thereby cooling the earth’s surface daily leading to winter.

Variation In Inclination Of Sunrays Falling On The Earth’s Surface
Due to the spherical shape of the earth and the inclination of the earth’s axis at 66 angles sunrays fall on the earth’s surface at different angles on different parts of the earth.
Vertical rays concentrate on smaller areas and travel shorter distances in the atmosphere while inclined rays spread over a wider area and travel long distances in the atmosphere.
Therefore, vertical rays are responsible for summer while inclined rays are responsible for winter.
Chapter 2 Movements Of The Earth Circle Of Seasons
Four seasons namely
- Summer,
- Autumn,
- Winter and
- Spring is rotating on the earth’s surface in both hemispheres.
Summer In the Northern Hemisphere And Winter In the Southern Hemisphere
From May to July, about 1 ½ months before and after the 21st of June days are longer in the northern hemisphere. So, the temperature is maximum. Therefore, it is summer in the northern hemisphere and winter in the southern hemisphere.

Autumn In the Northern Hemisphere And Spring In the Southern Hemisphere
From August to October, about 1 month before and after 23rd September temperature becomes moderate as the temperature gradually decreases in the northern hemisphere and increases gradually in the southern hemisphere.
WBBSE Notes For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
So, it is autumn in the northern hemisphere and spring in the southern hemisphere.
Winter In the Northern Hemisphere And Summer In the Southern Hemisphere
From November to January, about 1 month before and after 22nd December nights are longer in the northern hemisphere. So, the temperature is minimum in the northern hemisphere resulting in winter while it is summer in the southern hemisphere.
Spring In the Northern Hemisphere And Autumn In the Southern Hemisphere
February to April, about 1 month before and after 21st March temperature increases in the northern hemisphere but decreases in the southern hemisphere.
So, temperature becomes moderate and spring follows the winter in the northern hemisphere and autumn follows summer in the southern hemisphere.