WBBSE Chapter 5 Environment Its Resources And Their Conservation Topic C Environment And Human Population
Introduction to the concept of population:
The population consists of all the individuals of a species within a given area. At present the world population has reached 7.5 billion.
The three main factors that control population growth are natality (birth rate), mortality (death rate), and survivorship.

Natality (birth rate):
It is the new young ones produced in a specific period.
Mortality (death rate):
It is the number of deaths per unit of time in an area.
Survivorship:
It is the percentage of individuals living at various ages.
The age distribution determines the relative proportion of individuals of different age groups in a population.
A population has 3 ecological age groups:
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Life Science
Pre-reproductive, reproductive, and Post-reproductive.
The proportions of these three age groups determine whether the population is growing or mature (stable) or diminishing.
The growth rate of the population is the increase in the number of individuals in a population in a specific period. Mathematically,
\text { growth rate } & =\frac{\text { No. of birth }(b)-\text { No.of death }(\mathrm{d})}{\text { time interval } \times \text { Average population }} \\
& =\frac{\Delta n}{t \times P} \text { where } \Delta \mathrm{n}=(\mathrm{b}-\mathrm{d}) \text { and } \mathrm{t}=\text { time }
\end{aligned}\)
Fewer than 800 million people populated the earth in the mid-18th. Century.
Today, barely 250 years later, we are more than 7.5 billion and will continue growing until 2050.
The historical growth of the world population is depicted in
The great increase in human numbers resulting from increased survival and exponential population growth is known as population explosion.
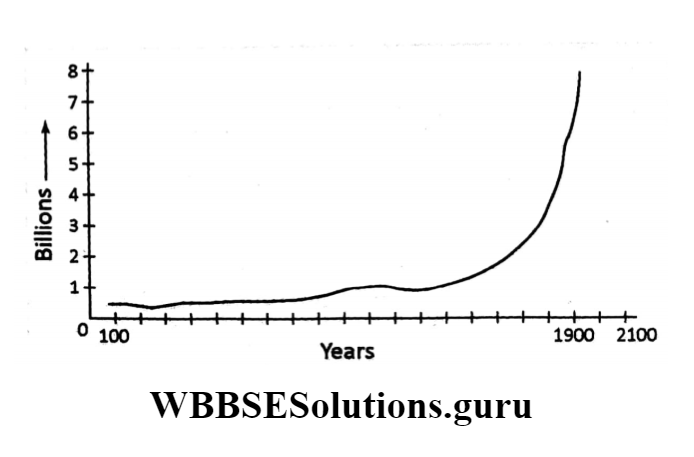
In the history of human beings, the birth and death rates have always been able to balance each other and maintain a population growth rate that is sustainable.
With growing advances in technology in past years, the growth of the population has boomed and has turned into a population explosion or overpopulation.
Overpopulation is an undesirable condition where the existing human population exceeds the carrying capacity of the earth.
Overpopulation will place great demands on resources and land, leading to widespread environmental issues in addition to impacting global economies and standards of living.
Most developed economies currently consume resources much faster than they can generate.
On the other hand, most developing countries with rapid population growth face the urgent need to improve living standards.
Environment And Human Population Class 10
Thus it is putting tremendous pressure upon natural resources to meet the present needs and destroying resources needed for the future.
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Problems Of An Ever-Increasing Population
The population is an important source of development, yet it is a major source of environmental degradation when it exceeds the threshold limits of the support systems.
Unless the relationship between the multiplying population and the life support system can be stabilized, development programs, however innovative they may be, are not likely to yield desired results.
Population impacts on the environment are primarily through the use of natural resources and production of wastes and are associated with environmental stresses like loss of biodiversity, air and water pollution, and increased pressure on arable land.
Human population issues are extremely important when it comes to our way of life and our future on this planet.
Some notable problems are-
Over-exploitation and depletion of natural resources:
Natural resources are those things that were formed from the biotic and abiotic factors in the atmosphere, and which are used by man for various purposes.
Natural resources are of two types-renewable resources (they can be made again and again according to the use of trees, paper, food crops, etc.) and non-renewable resources (they can’t be made once they are used up, metals, petrol, natural gas, coal, etc.).
Over-exploitation refers to harvesting a natural resource to the point of diminishing returns and destruction.
The term applies to natural resources such as:
wild medicinal plants, grazing pastures, game animals, fish stocks, forests, and water aquifers.
Over-exploitation can lead to resource destruction, including extinction. Due to the large increase in human population and due to the technological revolution, various natural resources are being consumed at an alarming rate.
In order to fulfill the food requirements of a large population, more and more land is being brought under cultivation, and more irrigation facilities are created through the construction of dams.
When harvesting exceeds the reproduction of plant and animal species, that poses a major threat to biodiversity. It results in an enhanced rate of desertification and rapid degradation of agricultural lands.
In order to increase the yield of crops, fertilizers, and pesticides are being used extensively. These chemicals thus enter the food chain at an enhanced rate and create imbalances in the environment.
The major causes behind the depletion of natural resources are over-consumption due to overpopulation, deforestation, extensive mining, technological and industrial development, erosion and pollution, and contamination of resources.
Deforestation and loss of ecosystem:
Deforestation is the destruction or clearing of forested lands, usually for the purposes of expanding agricultural land or for timber harvesting.
When the process is conducted by clear-cutting (removal of most or all of the canopy tree growth, leaving few or no life or
dead trees standing) or when mass forest burning occurs, significant losses of habitat and biodiversity may result, including the erosion of biological community structure and the extinction of species.
Forests are complex ecosystems that affect almost every species on the planet. According to National Geographic, 80% of the world’s plants and animals live in forests and many cannot live elsewhere.
When they are degraded, it can set off a devastating chain of events both locally and around the world.
The adverse environmental impacts associated with large-scale deforestation can include significant changes in ecological, hydrological, and climatic processes at local and regional levels.
Environment And Human Population Class 10
The ecological consequences include habitat loss and habitat fragmentation and adverse changes in local species richness and biodiversity.
Many endangered plants and animals live only in a certain kind of forest habitat. Those species can be lost entirely or can become extinct in the wild very easily.
Shrinking of agricultural land:
Shrinking agricultural fields is one of the biggest challenges for making food available to the world population. Cultivable land continues to shrink.
The decrease is mainly due to the diversion of cultivable land for construction, industries, and other development activities.
The continual plowing of fields, combined with heavy use of fertilizers, has degraded soil across the world with erosion occurring at a pace of up to 100 times greater than the rate of soil formation.
It may not pose an immediate problem for the nation’s food security but its long-term effect could be disastrous with a country needing more and more foodgrains to support its growing population.
A report from the agriculture ministry of India shows that as many as 20 states reported a decrease in cultivable land to the extent of 790,000 hectares in four years from 2007-08 to 2010-11.
Shortage of freshwater:
Though water covers 70% of our planet, however, freshwater the stuff we drink, bathe in, and irrigate our farm fields with is incredibly rare.
Only 3% of the world’s water is freshwater, and two-thirds of that is tucked away in frozen glaciers or otherwise unavailable for our use.
As a result, some 1.1 billion people worldwide lack access to water, and a total of 2.7 billion find water scarce for at least one month of the year.
Inadequate sanitation is also a problem for 2.4 billion people as a consequence they are exposed to diseases, such as cholera and typhoid fever, and other water-borne illnesses.
Two million people, mostly children, die each year from diarrheal diseases alone.
Many of the water systems that keep ecosystems thriving and feed a growing human population have become stressed. Rivers, lakes, and aquifers are drying up or becoming too polluted to use.
More than half the world’s wetlands have disappeared. Agriculture consumes more water than any other source and wastes much of that through inefficiencies.
Climate change is altering patterns of weather and water around the world, causing shortages and droughts in some areas and floods in others.
The causes of global water shortage may be summarised as pollution, overuse due to overpopulation, wastage, climate change, destruction of water catchment areas, etc.
Overpopulation will strain current water resources to their limits, cause an increase In water pollution and lead to an increase In civil and international conflicts over existing water supplies.
At the current consumption rate, this situation will only get worse. By 2025, two-thirds of the world’s population may face water shortages.
Coupled with that, increasingly high demand for water will also affect food production in water-stressed areas. Thus, ecosystems around the world will suffer even more.
Air and water pollution: Air and water are the two most important abiotic components of the environment.
Air pollution can be natural or man-made, but it’s the man-made pollutants that are the most destructive.
Major man-made air pollutants are:
greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and the destruction of the ozone layer. Carbon dioxide is one of the worst air pollutants; it’s mainly emitted from power plants, cars, planes, and other vehicles and comes from the burning of fossil fuels.
- Particulate matters
- SOX and NOX
- CFCs and other hydrocarbons.
Air pollution has been linked to health problems like asthma and lung disease, as well as the deterioration of the ozone layer (which protects us from harmful UV rays), the warming of the earth which may destroy the habitats of many animals, photochemical smog, fog and add rain.
If water is cloudy, smelly and has garbage floating In It, then It’s easy to know that It’s polluted, but clear and clean-looking water can be polluted as well with toxic chemicals.
Polluted waters are not safe to drink or bathe In and can cause Illness after several years of exposure.
Humans create water pollution by adding chemicals and oils to the water from factories, mining, oil spills from commercial tankers, throwing garbage Into open waters from boats or onshore, and because of untreated sewage and agricultural pollution.
Severe water pollution shall result In:
The abundance of microbes, waterborne diseases, creation of Oxygen deficient aquatic systems, algal bloom, accelerated eutrophication, and Increase of toxic elements In water bodies.
Green House Effect And Global Warming:
The major greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide, and water vapor.
The rising concentration of these gases due to man-made reasons Is responsible for a noticeable rise In the mean global temperatures.
In the troposphere, greenhouse gases provide an effective thermal Insulation while In the stratosphere many of these gases are responsible for causing ozone depletion.
The Consequences Of Global Warming Are:
climate change, rapid rise In mean sea level, submerging of largescale low-lying areas, unprecedented changes In wind and precipitation patterns, wastage of freshwater reserves, decline In agriculture, and losses of genetic resources on a large scale.
Destruction of wetlands and its consequences:
A wetland Is a land area that Is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally.
Examples: lakes, ponds, streams, estuaries, lagoons, bogs, swamps, etc.
Keeping pace with population overgrowth, and a rapid rise in infrastructure development, agriculture, industry, and household consumption are major causes of degradation and destruction of wetlands.
The destruction of wetlands is a concern because they are some of the most productive habitats on the planet,
Wetlands are critical to our biodiversity since wetlands act as the biological “kidneys” of the landscape by filtering out any water that would otherwise directly run into a water system.
The loss of wetlands can cause a change in the water chemistry of major water systems that those wetlands would otherwise filter out.
With increasing emissions from cars, fertilizer and pesticide use, and animal grazing there are increasing numbers of pollutants entering our waterways.
These pollutants are changing the natural balance of nutrients in our lotic systems and having long-term consequences on the function and community composition of those systems,
Acting as stormwater management systems, wetlands help reduce the impacts of runoff after a rain storm or snowmelt event. Such runoff typically transports high concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus and suspended solids from road surfaces to waterways,
Wetlands remove up to 90 percent of nitrates from groundwater through a process called denitrification.
Wetlands also play an important role in sediment management and erosion reduction.
They provide habitats for large-scale biodiversity, rare or threatened species, game fish, and plants for medicines and dyes.
Scarcity of food:
Malthus postulated that food growth proceeds at an arithmetic rate, while population grows at a geometric rate meaning that population grows faster than food and at a certain point population outstrips food growth leading to misery.
Food scarcity is a bigger problem than ever as human population numbers continue to swell, putting additional stress on already fragile food production and distribution systems.
The more people there are, especially in poor countries with limited amounts of land and water, the fewer resources there are to meet basic needs. If basic needs cannot be met, development stalls, and economies begin to unravel.
In some poor countries, attempts to increase food production and consumption are undermined by rapid population growth; migration from rural to urban areas; unequal land distribution; shrinking landholdings; deepening rural poverty; and widespread land degradation. Lower birth rates, along with better management of land and water resources, are necessary to avert chronic food shortages.
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Environment And Human Health
Because of the permanent interaction between man and his environment, our health, to a considerable extent, is determined by environmental quality. The environment in which we live, work, and relax, is determining our health and well-being.
The relationship between environment and health is extremely complex. Many health problems are directly associated with environmental pollution. A few important examples are discussed below.
Lung diseases:
Lung disease is any problem in the airways or the lung tissues that prevents the lungs from working properly. Two such important lung diseases are Asthma and Bronchitis. Both Asthma and Bronchitis are Airway diseases.
These diseases affect the tubes or airways that carry oxygen and other gases into and out of the lungs. They usually cause a narrowing or blockage of the airways.
Asthma :
Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory breathing problem due to narrowing of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm leading to narrowing of bronchi, production of extra mucus, and difficulty in breathing.
Symptoms :
Common symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and breathing difficulty. For some people, asthma is a minor nuisance.
For others, it can be a major problem that interferes with daily activities including sleeping, and may lead to a life-threatening asthma attack.
Primary causes :
The following are the primary causes of asthma :

1. Environmental factors :
Air pollution, both in and out of the home, can impact the development and triggering of asthma. Environmental factors that trigger asthma include pollution, suspended particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, ozone, cold temperatures, and high humidity.
The most common causes of asthma attacks are extremely small and lightweight particles transported through the air and inhaled into the lungs. Thus heavy air pollution tends to cause a higher recurrence of asthma.
Smoggy conditions release both ozone and sulfur dioxide causing coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Changes in weather might also stimulate attacks.
Cold air can lead to airway congestion, constricted airways, extra secretion of mucus, and other asthma symptoms. Humidity might also lead to breathing difficulties for populations in some areas.
2. Allergies:
A strong link exists between allergies and asthma, For some people the environmental triggers are allergens. Allergens are usually natural substances, such as plant pollen and mold spores, animal dander (tiny pieces of animal hair and skin), and fecal material from dust mites and cockroaches.
Environment And Human Population Class 10
Allergens produce an exaggerated response in the immune system in which a specific antibody initiates the inflammatory response. These same allergens may cause little or no reaction in non-allergic people.
Asthma also occurs in people who do not have allergies. In these people, chemical irritants trigger an inflammatory response that is initiated in a different way than in allergen-triggered asthma.
For example, some people are sensitive to certain common chemical irritants, such as perfume, hairspray, cosmetics, and household cleaners.
3. Smoking tobacco:
Tobacco smoke is directly linked to asthma, wheezing, respiratory infections, and overproduction of mucus. It also increases breathlessness in the airways. In addition, the children of parents who smoke have a higher risk of developing asthma.
2. Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is a respiratory disease in which the mucus membrane in the lungs’ bronchial passages gets inflamed.
As the irritated membrane swells and grows thicker, it narrows or shuts off the tiny airways in the lungs, resulting in coughing spells that may be accompanied by phlegm and breathlessness.

Symptoms :
For either acute or chronic bronchitis, symptoms include:
- Cough
- Production of mucus (sputum) which can be clear, white, or yellowish-grey in color and rarely may be streaked with blood.
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Slight fever, headache, and chills
- Chest discomfort.
Causes :
Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis, also called a chest cold, is very common without lasting effects, although the cough may linger for weeks. It is usually caused by influenza viruses, the same viruses that cause colds and flu.
Chronic bronchitis, a more serious condition, is a constant irritation or inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes. Chronic bronchitis involves a productive cough that lasts for at least three months with recurring bouts occurring for at least two consecutive years.
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Environment Notes
Risk factors responsible for chronic bronchitis are :
- Cigarette smoking
- contaminated air or air pollution
- Exposure to irritants on the job
- Low resistance.
Chronic bronchitis may result from a series of acute bronchitis episodes, or it may evolve gradually due to heavy cigarette smoking or breathing air contaminated with other environmental pollutants, including workplace (occupational) exposures.
In addition to cigarette smoking, the list of causative substances includes coal dust, oil mist, cement dust, welding fumes, organic dust, engine exhausts, fire smoke, and second-hand cigarette smoke.
There is a variety of components of welded materials and welding methods that may have chronic detrimental effects, including permanent disability to welders.
In the line of duty, firefighters may experience occupational exposure to gases, chemicals, particulate, and other substances with potentially damaging short and long-term effects on the respiratory system.
There are indications that repeated inhalations of smoke during routine firefighting activities can result in chronic bronchitis and abnormal lung function.
Low resistance to chronic bronchitis may result from another acute illness, such as cold or other immune disorders. Older adults, infants, and young children have greater vulnerability to infection.
2. Cancer:
Cancer is a group of more than 200 different diseases characterized by an uncontrolled growth of cells that disrupts body tissues and organs.
Cancerous cells grow and multiply to form tumors that invade local tissues, destroy them and eventually gain access to the circulatory system to scatter throughout the body.
Malignancy refers to the ability of a tumor to ultimately cause death. Metastasis is an outstanding characteristic of malignancy. Metastasis is the tendency of tumor cells to be carried from their site of origin by way of the circulatory system to invade almost every tissue and organ of the body to destroy the host.
Symptoms :
Usually In the beginning, there are no warning signs of cancer. Later, the signs of cancer are related to the location of the tumor.
As cancer progresses, it commonly causes loss of muscle tissue, pale skin, pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, blood in the urine, unexpected weight loss, indigestion, fever, etc.
Types of Cancer:
There are two major types of cancers according to the simplest method of classification:
- Carcinoma and Sarcoma.
- Carcinomas occur in epithelial tissues, which cover the body (skin) and line the inner cavitary structures of the organs (such as
- the respiratory or GI tract etc).
Sarcomas develop in the connective tissues, including fibrous tissues, adipose tissues, muscles, bones, blood vessels, and cartilage.
Causes of Cancer:
There is no single cause of cancer. Cancer development depends on things such as family history (genetics), health, nutrition, personal habits, and the environment.
1. Environmental factors :
External environmental causes of cancer are factors in the environment that increase the risk of cancer such as different pollutions, UV radiation, etc. In addition to lung cancer, other cancers have been linked to environmental toxins (poisons).
For example, pesticides, herbicides, and radioactive substances have the potential to cause cancer. Asbestos, chromium, and coal tar have been linked to lung cancer.
It is difficult to determine, however, what proportion of cancer is due to exposure to these agents, because the length of time between exposure and the appearance of cancer is usually prolonged.
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Environment Notes
Smoking and tobacco :
Experts agree that tobacco is the single biggest avoidable cause of cancer in the world. Cigarettes, cigars, and pipe tobacco are made from dried tobacco leaves, and ingredients are added for flavor and to make smoking more pleasant.
The smoke from these products is a complex mixture of chemicals produced by the burning of tobacco and its additives. Tobacco smoke is made up of more than several chemicals, including many known to cause cancer (carcinogens).
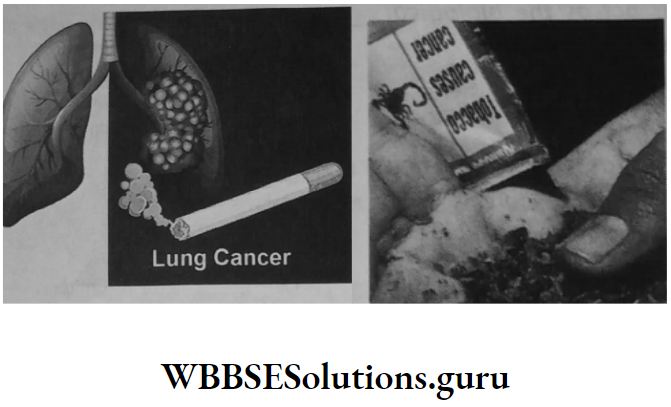
Poisons in tobacco smoke can damage or change a cell’s DNA. When DNA is damaged, a cell can begin growing out of control and create a cancer tumor.
The number of years a person spends smoking affects his/her cancer risk most strongly. Smoking causes at least 15 different types of cancer.
Apart from lung cancer, it causes cancers of the mouth, pharynx (upper throat), nose and sinuses, larynx (voice box), esophagus, liver, pancreas, stomach, kidney, bowel, ovary, bladder, cervix, and some types of leukemia.
Impact Of Human Population On Environment Class 10
Chewing tobacco is a common type of smokeless tobacco. The risk of certain types of cancer increases if a person chews tobacco. This includes esophageal cancer and various types of oral cancer, including cancers of the mouth, throat, cheek, gums, lips, and tongue.
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. We are now adding about _____________ people to the planet every 12 years.
Answer: One billion
Question 2. _____________ resources are of two types- renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
Answer: Natural
Question 3. Sustained_____________ can lead to the destruction of the renewable natural resource.
Answer: Overexploitation
Question 4. Forests are complex that affect almost every species on the _____________planet.
Answer: Ecosystems
Question 5. Environmental pollution, _____________, and smoking tobacco are the primary causes of asthma.
Answer: Allergies
Question 6. Pollution has been linked to health problems like asthma and lung disease, as _____________
Answer: Air
Environment And Human Population Class 10 MCQs
Question 7. Global _____________ and climate change refers to an increase in average global temperatures.
Answer: Warming
Question 8. A wetland is a_____________ area that is saturated with water.
Answer: Land
Question 9. _____________postulated that food growth proceeds at an arithmetic rate while population grows at a geometric rate.
Answer: Malthus
Question 10. 1°_____________ is a respiratory disease in which the mucus membrane in the lung’s bronchial passages becomes inflamed.
Answer: Bronchitis
Question 11. Wetlands act as biological of the_____________ landscape.
Answer: Kidneys
Question 12. _____________diseases affect the tubes that carry gases into and out of the lungs.
Answer: Airway
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Write True Or False
Question 1. As the century begins, natural resources are increasing, threatening public health and development.
Answer: False
Question 2. Most undeveloped economies currently consume resources much faster than they can regenerate.
Answer: False
Question 3. We are now adding one billion people to the planet every 12 years.
Answer: True
Question 4. Trees, paper, food crops, etc. are renewable natural resources.
Answer: True
Question 5. Sustained over-exploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource.
Answer: True
Question 6. Forestation is the destruction or clearing of forested lands.
Answer: False
Question 7. Forests are complex ecosystems that affect almost every species on the planet.
Answer: True
Question 8. Water covers 90% of our planet, and it is easy to think that it will always be plentiful.
Answer: False
Question 9. Air pollution is always man-made.
Answer: False
Environment And Human Population Class 10 MCQs
Question 10. Carbon dioxide is one of the worst air pollutants.
Answer: True
Question 11. Wetlands act as the biological “heart” of the landscape.
Answer: False
Question 12. Better management of land and water resources is necessary to avert chronic food shortages.
Answer: True
Question 13. Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airway passage.
Answer: True
Question 14. There is no single cause of cancer.
Answer: True
Question 15. Smoke, cold air, or obnoxious odor are allergens.
Answer: False
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Match The Column
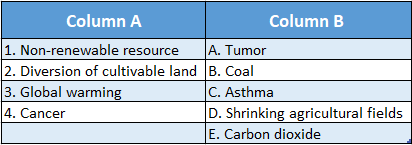
Answer: 1-B,2-D,3-E,4-A
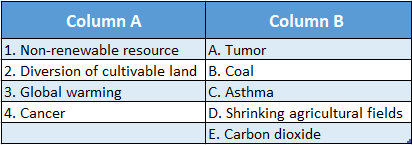
Answer: 1-E,2-C,3-A,4-D
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What does the vital index mean?
Answer: \(\text { Vital index }=\frac{\text { Natality }}{\text { Mortality }} \times 100\)
Question 2. What are natural resources?
Answer: Natural resources are those things that were formed from the biotic and abiotic factors in the atmosphere, and which are used by man for various purposes.
Question 3. What is the over-exploitation of natural resources?
Answer: Over-exploitation refers to harvesting a natural resource to the point of diminishing returns and destruction.
Question 4. What is deforestation?
Answer: Deforestation is the destruction or clearing of forested lands, usually to expand agricultural land or for timber harvesting.
Question 5. What percentage of the world’s water is fresh water?
Answer: About 3%
Question 6. What kind of pollution is smog?
Answer: Air pollution
Environment And Human Population Class 10 MCQs
Question 7. Name one important air pollutant.
Answer: Carbon dioxide
Question 8. What is meant by wetland?
Answer: A wetland is a land area that is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally.
Examples: Lakes, ponds, estuaries, lagoons, etc.
Among the following four terms, one includes the other three. Find out that term and write it: COPD, Airway disease, Asthma, bronchitis Airway disease.
Question 10. Choose the odd one and write it:
Answer: Greenhouse effect, wetland destruction, green revolution, shortage of fresh water.
The green revolution, because the other three are the ill effects of an ever-increasing population.
Question 11. What is passive smoking?
Answer: Passive smoking is the involuntary (but detrimental) inhaling of smoke from other people’s cigarettes or cigars.
Question 12. List out the two most common forms of cancer caused due to cigarette smoking.
Answer: Lung and throat cancer.
WBBSE Chapter 5 Topic C Environment And Human Population
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the ill effects of the over-exploitation of natural resources?
Answer:
Ill effects of the over-exploitation of natural resources
Over-exploitation refers to harvesting a natural resource to the point of diminishing returns. Sustained over-exploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource.
The term applies to natural resources such as:
wild medicinal plants, conventional energy sources (like coal, petroleum, etc), grazing pastures, game animals, fish stocks, forests, and water aquifers.
Due to the large increase in human population and technological revolution, various natural resources are being consumed at a very rapid rate.
This over-exploitation of natural resources is disturbing the environment in the following ways:
- Deforestation
- Desertification
- Extinction of species and biodiversity
- Soil erosion
- Oil Depletion and Future Energy Crisis
- global warming
- Pollution at an alarming rate
- Natural calamities
- Forced migration
- Economy crisis.
Since resources are limited, the consequences of over-exploitation of resources are detrimental to the environment and earth.
Question 2. What Are The Types Of Natural Resources?
Answer:
Natural Resources Are Of Two Types:
renewable resources (they can be made again and again according to the use, e.g.: trees, paper, food crops, etc.) and non-renewable resources (they can’t be made once they are used up, for Example metals, petrol, natural gas, coal, etc.).
Question 3. What is the shrinking of agricultural lands?
Answer:
The shrinking of agricultural land
Shrinking agricultural fields is one of the biggest challenges for making food available to the world population. Cultivable land continues to shrink.
The decrease is mainly due to the diversion of cultivable land for construction, industries, and other developmental activities. It is also shrinking due to depleting groundwater levels and extreme weather conditions.
It may not pose an immediate problem for the nation’s food security but its long-term effect could be disastrous with a country needing more and more food grains to support its growing population.
Environment And Human Population Class 10 MCQs
Question 4. Why is a wetland considered the kidney of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Wetlands are critical to our biodiversity and the protection of wetlands is essential.
Wetlands act as the biological “kidneys” of the landscape by filtering out any water that would otherwise directly run into a water system.
They store, assimilate and transform contaminants like nitrogen and phosphorus lost from the land after a rainstorm or a snowmelt event before they reach the waterways.
Like a giant kidney, wetlands help to dilute and filter materials that could otherwise harm the lakes, rivers, and other waterways.
Wetlands remove up to 90 percent of nitrates from groundwater through denitrification. Microbes living in wetlands absorb and break down nitrogen improving water quality.
Wetlands play an important role in sediment management and erosion reduction. Wetland vegetation traps sediment suspended in water and their roots hold riverbank soil together.
Wetlands also regulate the flow of water from land, soaking up excess flood water and then slowly releasing it to maintain summer flows or recharge groundwater.
Healthy peat wetlands help to combat global warming as they soak up excess carbon.
Question 5. What is asthma?
Answer:
Asthma
Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory breathing problem due to the narrowing of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm leading to the production of extra mucus and difficulty in breathing. Common symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic, and environmental factors, allergies, and smoking tobacco.
Question 6. What is bronchitis?
Answer:
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a respiratory disease in which the mucus membrane in the lungs’ bronchial passages becomes inflamed.
As the irritated membrane swells and grows thicker, it narrows or shuts off the tiny airways in the lungs, resulting in coughing spells that may be accompanied by phlegm and breathlessness.
Symptoms include coughing up mucus, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, slight fever, chills, and fatigue.
Question 7. How are tobacco smoking and cancer related?
Answer:
Experts agree that tobacco is the single biggest avoidable cause of cancer in the world. Cigarettes, cigars, and pipe tobacco are made from dried tobacco leaves, and ingredients are added for flavor and to make smoking more pleasant.
The smoke from these products is a complex mixture of chemicals produced by the burning of tobacco and its additives. Tobacco smoke is made up of more than thousands of chemicals, including many known to cause cancer (carcinogens).
Some carcinogens present in tobacco smoke are nicotine, hydrogen cyanide, formaldehyde, benzene, nitrosamines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.
Poisons in cigarette smoke can weaken the body’s immune system, making it harder to kill cancer cells. Poisons in tobacco smoke can damage or change a cell’s DNA.
When DNA is damaged, a cell can begin growing out of control and create a cancer tumor. Smoking causes at least 15 different types of cancers such as lung, mouth, esophagus, liver, stomach cancer, etc.
Causes Of Overpopulation Class 10
Question 8. What is the Malthusian theory of population?
Answer:
The Malthusian theory of population is a theory of population growth and food supply growth proposed by an English scholar named Thomas Robert Malthus.
Malthusian theory:
Population and food supply:
Malthus theorized that populations grow in geometric progression but food production increases in arithmetic progression. Thus populations grow faster than the supply of food. This leads to a shortage of food.
Population control:
Malthus argued that because there will be a higher population than the availability of food, many people will die from the shortage of food.
Question 9. How does environmental pollution cause cancer?
Answer:
External environmental pollutions increase the risk of cancer. In addition to lung cancer, other cancers have been linked to environmental toxins.
Water pollution:
Contaminated drinking water enhances the risk of cancer. The five most pervasive drinking water contaminants that are linked to cancer are 1, 4- Dioxane, Arsenic, Chromium- 6, disinfection byproducts, and nitrates.
These carcinogens are linked with bladder, lung, skin, stomach, liver, intestinal and ovarian cancers.
Air pollution:
Air pollution triggers defects in DNA repair function, alterations of the immune response, and the growth of new blood vessels that allow tumors to spread.
Several cancers linked to air pollution are lung, breast, liver, bile duct, gall bladder, pancreas cancers, etc. Some of the airborne carcinogens include diesel engine exhaust, solvents, metals, dust, and particulate matter.
Soil pollution:
The inhalation of soil particulate matter and the ingestion of contaminated food can potentially result in serious conditions. Cancer, including leukemia, may be caused by contact with soils contaminated with chemicals like benzene, gasoline, etc.
Exposure to polychlorinated biphenyl is linked to liver cancer. Heavy metals like chromium, lead, and mercury found in soil are carcinogenic.
Question 10. Mention the names of a few lung diseases caused by air pollution.
Answer:
Exposure to air pollution may cause several lung diseases like Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer.
