Arithmetic Chapter 1 Simple Interest
⇔ In a simple interest system, interest is calculated only on the principal. The principle remains same for the entire time period.
⇔ Amount (A) = Principal (P) + Total interest (I)
⇔ If Rs P is the principal, r% is the rate of interest per annum and t is the number of years, then
⇔ \(\text { S. I. }(I)=\text { Rs. } \frac{prt}{100}\)
⇔ Amount = Rs.\(\left(p+\frac{p r t}{100}\right)\) = P
⇔ Time = \(\left(\frac{\text { Total interest }}{\text { Interest on the principal for } 1 \text { year }}\right) \text { years }\)
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths

Arithmetic Chapter 1 Simple Interest True Or False
Example 1. A man takes a loan is called a debtor.
Solution: True
Example 2. If the principal and the rate of simple interest in percent per annum be constants, then the total interest and the time are in inverse relation.
Solution: False
Arithmetic Progression Class 10 Solutions
Example 3. If a certain sum of money doubles itself in 10 years, ten r = 20% per annum.
Solution: False
Example 4. A borrowed Rs. P at 10% per annum simple interest the amount will be at the end of 10 years will be 2P.
Solution: False
Example 5. If the interest on Rs. x for t years is Rs. y, then rate % is \(\frac{100 y}{x t}\)%
Solution: True
Arithmetic Chapter 1 Simple Interest Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. A man who is given a loan is called _______.
Solution: Creditor
Example 2. The amount of ₹ 2P in t years, at the rate of simple interest of \(\frac{r}{2}\) % per ainiuam is ₹ (2P + _____)
Solution: \(\frac{P r t}{a}\)
Example 3. The ratio of the principal and the amount (P. + S.I) in 1 year is 8 : 9, r% = ________
Solution: 12 \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Class 10 Arithmetic Chapter 1 Solved Examples
Example 4. The simple interest at the rate of x% p.a. for x years, will be Rs. x on a sum of _______
Solution: Rs. \(\frac{100}{n}\)
Example 5. The simple interest on Rs. 500 for 6 years at 5% per annum is___________
Solution: Rs. 150
Arithmetic Chapter 1 Simple Interest Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. By what principal at the rate of 6\(\frac{1}{4}\) % per annum for 1 day will be Re 1?
Solution: Simple interest = \(\frac{P R T}{100}\)

or, P = 5840
∴ principal = Rs. 5840
Example 2. The rate of simple interest is reduced to 4% to 3\(\frac{3}{4}\)% and for this, Amal Babu’s annual income decreases by ₹ 60. Find Amal Babu’s principal.
Solution: \(P \times\left(\frac{4}{100}-\frac{15}{4 \times 100}\right)\) = Rs.60
or, \(P \times \frac{1}{4 \times 100}\) = Rs. 60
or, P = 24000
Principal = Rs. 24000
Arithmetic Progression Formulas Class 10
Example 3. What is the rate of simple interest when the interest of some money in 4 years, will be \(\frac{8}{25}\) part of the principal let us determine it.
Solution:
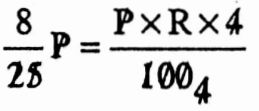
R = 8
Rate = 8% per annum.
Important results:
1. Simple interest = \(\frac{P T R}{100}\)
2. \(R=\frac{S. I \times 100}{P \times T}\)
3. \(T=\frac{S. I \times 100}{P \times R}\)
4. A = P + S.I
5. A = \(\mathrm{P}\left(1+\frac{\mathrm{T} \times \mathrm{R}}{100}\right)\)
6. P = \(\frac{\mathrm{A} \times 100}{100+\mathrm{TR}}\)
Example 4. If rate to interest is R1% for T1 years, R2% for next T2 years, R3% for next T3 years, and so on, and total interest is simple interest then P is
Solution: \(P=\frac{S . I \times 100}{R_1 T+R_2 T_2+R_3 T_3+\cdots}\)
Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Important Questions
Example 5. When sum of money becomes n times in T years, then rate of interest is given by
Solution: \(\mathrm{R}=\frac{100(n-1)}{T} \% \text { per annum }\)
Example 6. If a sum of amounts to ₹ A1 in T1 years and ₹ A2 in T2 years at simple interest, then rate of interest is given by
Solution: \(R=\frac{100\left(A_2-A_1\right)}{A_1 T_2-A_2 T_1}\)
Example 7. If a sum of amounts to ₹ A1 at R1% per annum and ₹ A1 at R1% per annum for same duration, then
Solution: \(T=\frac{100\left(A_2-A_1\right)}{A_1 R_2-A_2 R_1}\)
