Arithmetic Chapter 3 Partnership Business
⇔ If two or more persons start a business with their respective capitals, then the business is called a Partnership business.
⇔ The profit or loss in the business is divided on the basis of the ratio of their investment if otherwise is not started.
It is of two kinds:
⇔ Simple partnership: When the capital of the partners are invested for the same period of time.
⇔ Compound partnership: If the capital of the partners is invested for different periods of time. Here at first, we calculate the equivalent capital (with respect to time) of each partner.
⇔ We calculate the equivalent capitals in respect of 1 month. The individual capital is multiplied by the no. of months of the capital invested.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths

Arithmetic Chapter 3 Partnership Business True Or False
Example 1. At least 3 persons are needed in a partnership business.
Solution: False
Example 2. Ratio of capital of Raju and Ashif in a business is 5: 4 and if Raju gets profit share of ₹ 80 of total profit. Ashif will get a profit share of ₹ 100.
Solution: False
Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Chapter 3 Solutions
Example 3. If A and B invest an equal amount of money for 9 months and 8 months respectively, then the profit will be distributed in the ratio 9:8.
Solution: True
Example 4. The ratio of capital of three partners in a partnership business is 2 : 3 : 3 and the ratio of time is 3 : 2 : 2, then each will get equal share of profit.
Solution: True
Example 5. If the ratio of capital of A, B, C is \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{5}\): \(\frac{1}{4}\), then the profit will be distributed in the ratio of 4:5:6.
Solution: True
Example 6. At least two partners are needed for a partnership business.
Solution: False
Example 7. Honerrary allowance is distributed after the profit is shared.
Solution: True
Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Chapter 3 Solutions
Example 8. In a simple partnership, business capitals are invested for the same period of time.
Solution: True
Example 9. In a compound partnership business capitals are invested for the different period of time.
Solution: False
Example 10. To find equivalent capital, investment is added with respect to the time.
Solution: False
Example 11. For a compound partnership business, at first we calculate the ratio of their initial capitals.
Solution: True
Compound Interest Class 10 Solutions
Arithmetic Chapter 3 Partnership Business Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. Partnership business is ______ type.
Solution: Two
Example 2. Without any other conditions in partnership business if the capitals of all partners are invested for the same time, then such a business is called _______
Solution: Simple
Example 3. Without any other conditions in partnership business, if the capitals of all partners are invested for different time periods, then such a business is called _________
Solution: Compound
Example 4. In a partnership business, share of profit is distributed in _______ ways.
Solution: 3
Class 10 Arithmetic Chapter 3 Solved Examples
Example 5. When the investment of the partners in involved in a business for different time period of time then it is called a ______ business.
Solution: Joint partnership
Example 6. A and B’s shares in a business are equal, but the profit is distributed in the ratio of 4: 5. The business was a _____ partnership.
Solution: Joint
Example 7. The profit is shared only after the dissbursement of _______
Solution: Honorrary
Example 8. The business partners collect the total amount of capital by investing equally or at a _________ ratio.
Solution: Unanimous
Wbbse Class 10 Arithmetic Notes
Arithmetic Chapter 3 Partnership Business Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. In a partnership business, the ratio of capitals of Samir, Idrish, and Antony are as \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{5}\): \(\frac{1}{4}\). If they make a profit of ₹ 3700 at the end of the year. Let us write by calculating profit share of Antony.
Solution: Ratio = \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{5}\): \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 10: 12: 15
Share of Antory = ₹ 3700 x \(\frac{15}{37}\) = ₹ 1500
∴ Profit share of Antony is ₹ 15000
Example 2. If in a partnership business the ratio of capitals of Pritha and Rabeya is 2 : 3 and the ratio of Rabeya and Jesmin is 4 : 5. Let us write by calculating the ratio of capitals of Pritha Rabeya and Jesmin.
Solution: Ratio of capitals of Pritha and Rabeya = 2 : 3 = 8 = 12
Ratio of capitals of Rabeya and Jesmin = 4 : 5 = 12 : 15
Required ratio = 8: 12: 15
∴ The ratio of capitals of Pritha, Rabeya, and Jesmin is 18: 12: 15
Example 3. The total profit is ₹ 1500 in a partnership business of two persons. If the capital of Rajib is ₹ 600 and profit is ₹ 900, let us calculate how much was the capital of Abtab.
Solution: Profit of Abtab = ₹ (1500 – 700) = ₹ 600
∴ Rohit of capitals = Ratio of profit
6000 : x = 900 : 600 or, x = 4000
Capital of Abtab = ₹ 4000
∴ The capital of Abatab is ₹ 4000
Example 4. Ratio of capitals of 3 persons is 3: 8: 5 and the profit of 1st is 7 60 less of the 3rd. Calculate the total profit in this business.
Solution: Clearly profit is ₹ 3x, ₹ 8x, ₹ 5x (x is a ratio constant, x > y)
∴ 5x- 60 = 3x or, 2x = 60, or, x = 30
∴ Total profit = ₹ 16x = ₹ 16 x 30 = ₹ 480.
Compound Interest Formulas Class 10
Example 5. Jayanti, Ajit and Kunal started partnership business investing ₹ 15000. At the end of the year. Jayanti, Ajit and Kunal received ₹ 800, ₹1000, ₹1200 respectively on profit share. Let us calculate the amount of Jayanta’s capital that was invested in the business.
Solution: Ratio of profit = 800 : 1000 : 1200 = 8 : 10 : 12
= 4:5:6 = Ratio of capitals
Jayanti’s capital =
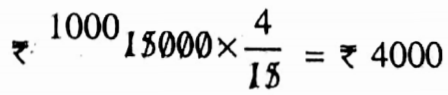
∴ The amount of Jayanta’s capital that wat invested in the business is ₹ 4000
Example 6. Shyam invested ₹ 2000 for 9 months and Kunal invests 7 1500 for few months in a business. If the total profit be ₹ 484 and Shyam gets ₹ 264 as is share of profit. Then calculate the time for which Kunul’s capital was invested.
Solution: Ratio of equivalent capitals = (2000 x 9) : (1500x)
= (20 x 9) : 15x = 12 : x
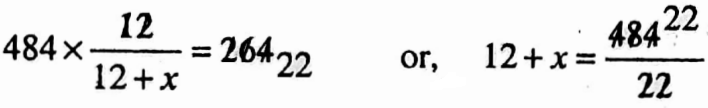
∴ x = 10
∴ Time required 10 months.
∴ The time for which Kunal’s capital was invested is 10 months.
Example 7. Share of capitals of A, B, and C in a business is \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{5}\): \(\frac{1}{4}\) At the end of the year profit is Rs. 37000. Final profit share of C.
Solution: \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{5}\): \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 10: 12: 15
Profit of C = ₹ 37000 x \(\frac{15}{37}\) = ₹ 1500
∴ Final profit share of C is ₹ 1500.
Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Important Questions
Example 8. Selim, Joy, and John started a partnership business with capitals ₹ 5000, ₹ 4500, ₹ 7000 respectively. If the profit is ₹ 11550. Find the profit share of Joy.
Solution: Ratio of capitals = 5000 : 4500 : 7000 = 50 : 45 : 70 = 10 : 9 : 14
Profit of Joy =
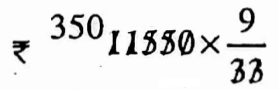
= Rs. 3150.
∴ The profit share of Joy is ₹ 3150.
