Mensuration Chapter 4 Sphere
⇔ A sphere is a solid boundary by one surface and it may be seen to be generated by the revolution of a semi circle about its diameter an axis.
⇒ If the radius of a sphere be r, then
⇒ The area of the surface = π x (diameter)2 = 4πr2 sq. units
⇒ Volume = \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3 cubic units.
⇒ The volume of a hollow sphere = \(\left(\frac{4}{3} \pi R^3-\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\right) \text { cu. units }=\frac{4}{3} \pi\left(R^3-r^3\right) \text { cu. units }\)
⇒ (External radius = R units, internal radius = r units)
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
⇒ The area of the whole surface and the volume of a hemisphere
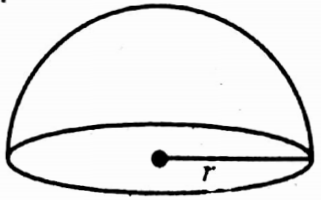
- Area of curved surface = 2πr2 sq. units
- Area of whole surface = 3πr2 sq. units
- Volume = \(\frac{2}{3}\)πr2 cu. units.

Mensuration Chapter 4 Sphere True Or False
Example 1. If we double the length of radius of a solid sphere, the volume of sphere will be doubles.
[Hints: \(\frac{4}{3} \pi(2 r)^3=8 \times \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\)]
Solution: False
Class 10 Mensuration Chapter 4 Solved Examples
Example 2. If the ratio of the curved surface areas of two hemisphere is 4: 9, the ratio of their lengths of radius is 2 : 3.
Hint: \(\frac{2 \pi r_1^2}{2 \pi r_1^2}=\frac{4}{9} \Rightarrow \frac{r_1}{r_2}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution: True
Example 3. Curved surface area of sphere = 4 x (area of the circle with radius r units)
Solution: True
Example 4. The curved surface area ≠ whole surface area for a solid sphere.
Solution: False
Example 5. No. of plane surface area of a sphere is 1.
Solution: False
Example 6. Volume of a solid hemisphere = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x volume of sphere with same radius.
Solution: True
Wbbse Class 10 Mensuration Notes
Example 7. If the length of outer radius and inner radius of hollow sphere are R and r units respectively, volume of metal is required to make the hollow sphere is \(\frac{4}{3}\)π (R3 – r3) cu. units.
Solution: True
Example 8. No. of corner points of a sphere is 2.
Solution: False
Mensuration Chapter 4 Sphere Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. The name of the solid which is composed of only one surface is _______
Solution: sphere
Example 2. The number of surface of a solid hemisphere is _______
Solution: 2
Example 3. If the length of radius of a solid hemisphere is 2r units, its whole surface area is ________ sq. units.
Solution: 12
Example 4. An icecream is a shape of a cone and a _________
Solution: hemisphere
Surface Area And Volume Of Sphere Class 10
Example 5. If curved surface area and volume of a sphere are S and V respectively, then relation between S and V is _______
Solution: S3 = 36 πr2
Example 6. If length of radii of a cylinder and a hemisphere are equal, then ratio of their volumes is ________
Solution: 3: 2
Example 7. Volumes of a sphere of radius r units and a cube of length a units are equal, r : a = _________
Solution: 3 √21: 23 √11
Example 8. Volume of a biggest solid cone made from a solid hemisphere of radius r unit is ________
Solution: πr3
Example 9. If length of the radius of a hemisphere ps 2r units, then total surface area is _______ cu.
Solution: 12 πr2
Example 10. If ratio of length of radii of two sphere is 2 : 3, then ratio of their volumes is _______
Solution: 8: 27
Class 10 Maths Mensuration Important Questions
Mensuration Chapter 4 Sphere Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. The numerical values of volume and whole surface area of a solid hemisphere are equal, let us write the length of radius of the hemisphere.
Solution: \(\frac{2}{3} \pi r^3=3 \pi r^2\)
or, r = \(\frac{9}{2}\) = 4.5 units
Example 2. The curved surface area of a solid sphere is equal to the surface area of a solid cylinder. The lengths of both height and diameter of cylinder are 12 cm. Write the length of the radius of the sphere.
Solution: 2π (6).12 = 4 πr2
or, r2 = \(\frac{12 \times 12}{4}\)
∴ r = 6 cm
Example 3. Whole surface area of a solid hemisphere is equal to the curved surface area of the solid sphere. Let us write the ratio of lengths of radius of hemisphere and sphere.
Solution: \(3 \pi r_1^2=4 \pi r_1^2\)
or, \(\frac{r_1^2}{r_2^2}=\frac{4}{3}\)
∴ \(r_1: r_2=2: \sqrt{3}\)
Example 4. If curved surface area of a solid sphere is S and volume is V, write the value of \(\frac{S^3}{V^2}\) (not putting the value of π).
Solution: S = 4πr2, V = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
∴ \(\frac{s^3}{V^2}=\frac{\left(4 \pi r^2\right)^3}{\left(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\right)^2}\) = 9 x 4 = 36
Example 5. If the lengths of radius of a sphere is increased by 50%, let us write how much percent will be increased of its curved surface area.
Solution: Change of curved surface area
[r1 and r2 are the lengths of radii of hemisphere and sphere respectively]
= \(4 \pi\left\{\left(r+\frac{r}{2}\right)^2-r^2\right\} \text { sq. units }\)
= \(4 \pi\left(\frac{9 r^2-4 r^2}{4}\right) \text { sq. unit }\)
= \(\pi \times 5 r^2\)
% change = \(\frac{5 \pi r^2}{4 \pi r^2} \times 100 \text { sq.u }=125 \text { sq units. }\)
Class 10 Mensuration Chapter 4 Solved Examples
Example 6. The external and internal radii of a hollow sphere are 4 cm and 3 cm respectively. Find the volume of metal.
Solution: Volume = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi\left(4^3-3^3\right)\) cu. cm
= \(\frac{4}{3}\) x \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 37 cu. cm = 155\(\frac{1}{21}\)
Example 7. Find the ratio of the whole surface areas of a hemisphere and a sphere of the same radius.
Solution: Let the length of the radius = r unit
Required ratio = 3 πr2 : 4 πr2 = 3 : 4.
Example 8. A cylinder and a sphere have equal volume. The diameter of the cylinder is equal to the radius of the sphere. Find the relation between the height of the cylinder and radius of that.
Solution: Let the length of the cylinder = r unit, height = h unit
∴ radius of the sphere = 2r unit
ATP, \(\pi r^2 h=\frac{4}{3} \pi(2 r)^3\)
or, h = \(\frac{32}{3}\) r
Example 9. The perimeter of the base of a solid iron hemisphere is 6\(\frac{2}{7}\) metres. Find its volume.
Solution: 2πr = 6\(\frac{2}{7}\)
or, r = \(\frac{44 \times 7}{7 \times 2 \times 22}=1\)
Volume = \(\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\right)=\frac{2}{3} \pi r^3=\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times(1)^3\)
= \(\frac{44}{21}=2 \frac{2}{11} \text { cu. metres. }\)
Wbbse class 10 Maths Mensuration Solutions
Example 10. A sphere of diameter 1 metre is cut out from a wooden cube of edge 1 metre. Find the volume of the remaining wood in the cube.
Solution: Volume of sphere = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^3\) cu. mt.
= \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) cu. mt.
= \(\frac{22}{7 \times 6}\) cu. mt.
= \(\frac{11}{21}\) cu. mt.
∴ Volume of remaining woods = (13 – \(\frac{11}{21}\)) cu.mt = \(\frac{10}{21}\) cu.mt
