Trigonometry Chapter 1 Concept Of Measurement Of Angle
⇔ Positive angle: If the rotating ray rotates anticlockwise direction, the angle formed is called positive angle.

∠AOB is a positive angle.
⇔ Negative angle: If the rotating ray rotates clockwise direction, the angle formed is called negative angle.
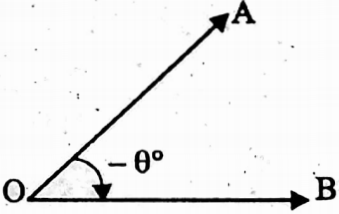
∠AOB is a negative angle.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths

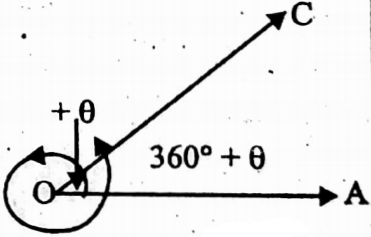
If a ray of an angle comes back to its first position after one complete rotation in anticlockwise direction, then the measurement of an angle is 360°, while in clockwise direction, the angle is then -360°.
∠AOB = + θ

∠AOC = 360° + θ
Class 10 Maths Trigonometry Chapter 1 Solutions
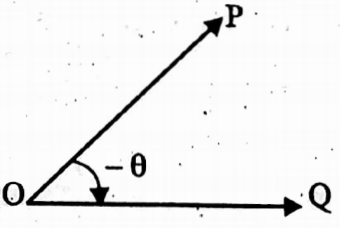
∠POQ = – θ
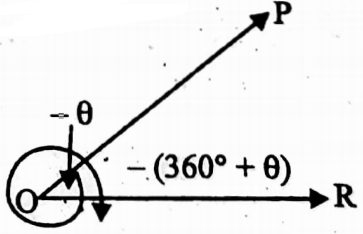
∠POR =- (360° + θ)
There are two general systems to measure trigonometrical angles are
- Sexagesimal system and
- Circular system.
⇔ Sexagesimal system: The angle formed by two perpendicular intersecting lines is called right angle.
1 right angle = 90°
1° = 60′
1′ = 60″
⇔ Circular system: The measure of an angle subtended at the centre by an arc having equal length with radius is called one radian and it is written as 1c.
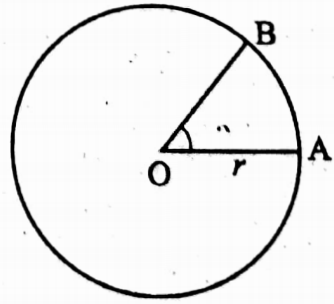
If \(\overline{\mathrm{OA}}=\widehat{A B}\) = r then ∠AOB = 1c
πc = 180°
Trigonometric Ratios Class 10 Solutions
Trigonometry Chapter 1 Concept Of Measurement Of Angle True Or False
Example 1. The angle, formed by rotating a ray centering its end point in an anticlockwise direction is positive.
Solution: The statements is true
Example 2. The angle, formed for completely rotating a ray twice by centering its end point is 720°
Solution: The statement is true.
Example 3. The circular value of (- 100°) is \(\frac{5 \pi^c}{9}\)
Solution: 180° = πc
\(1^{\circ}=\frac{\pi^c}{180}\) \(100^{\circ}=\frac{100}{180} \pi^c=\frac{5 \pi^c}{9}\)∴ The statement is True.
Example 4. The sexagesimal value of an angle formed by the end point of second hand of a clock in 1 minute rotation is 180°
Solution: In 1 minute the angle formed by the end point of second hand of a clock is 360°.
The statement is False.
Example 5. The circular value of each angle of an equilateral triangle is \(\frac{\pi^c}{3}\).
Solution: The sexagesimal value of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°.
180° = πc
∴ \(60^{\circ}=\frac{60 \pi^c}{180}=\frac{\pi^c}{3}\)
The statement is True.
Class 10 Trigonometry Chapter 1 Solved Examples
Trigonometry Chapter 1 Concept Of Measurement Of Angle Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. π radian is a ______ angle.
Solution: Constant [Because radian = 180°]
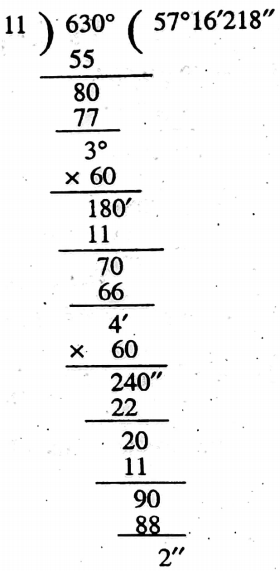
Example 2. In sexagesimal system 1 radian equal to _______ (approx).
Solution: \(\frac{22}{7}\) radian = 180°
1 radian = \(\frac{7}{22}\) x 180° = \(\frac{7 \times 90^{\circ}}{11}=\frac{630^{\circ}}{1.1}\)
= 57°16’22” (approx)
∴ 57°16’22” (approx.)
Wbbse Class 10 Trigonometry Notes
Example 3. The circular value of the supplementary angle of the measure is \(\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) is _______
Solution: The circular value of the supplementary angle of the measure is \(\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) is \(\left(\pi-\frac{3 \pi}{8}\right)\) or \(\frac{5\pi}{8}\)
∴ Answer is \(\frac{5 \pi}{8}\)
Example 4. The circular value of an angle in a ________ is \(\frac{\pi^c}{2}\)
Solution: Semicircle.
Example 5. The circular value of a clock at 9 a.m. is ______
Solution: \(\frac{\pi^c}{2}\)
Trigonometry Chapter 1 Concept Of Measurement Of Angle Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. If the value of an angle in degree is D and in radian is R; then determine the value of \(\frac{R}{D}\)
Solution: 180° = πc
\(D^{\circ}=\frac{D}{180} \pi^c\)According to question R = \(\frac{D}{180}\)
⇒ \(\frac{R}{D}\) = \(\frac{\pi}{180}\)
Example 2. Write the value of the complementary angle of the measure 63°35’15”
Solution: The complementary angle of 63°35’15” is (90° – 63°35’15”) is 16°24’45”
90° = 89°59’60” – 63°35’15” = 16°24’45”
Trigonometric Ratios Formulas Class 10
Example 3. If the measures of two angles of a triangle are 65°56’55” and 64°3’5”, then determine the circular value of third angle.
Solution: The measures of third angle of a triangle is {180°- (65°56’55” + 64°3’5″)}
= 180° – 129°59’60” = 180° – 130° = 50°
180° = πc or, \(50^{\circ}=\frac{50}{180} \pi^c=\frac{5 \pi^c}{18}\)
∴ The circular value of third angle \(\frac{5 \pi^c}{18}\)
Example 4. In a circle, if an arc of 220 cm length subtends an angle of measure 63° at the centre, then determine the radius of the circle.
Solution: Let the radius of the circle is r cm. Here arc (s) = 220 cm
Circular value of 63° = \(\left(\frac{63}{180} \times \frac{22}{7}\right)\) radian
= \(\frac{11}{10}\) radian
∴ θ = \(\frac{11}{10}\) radian
s = rθ
220 = r x \(\frac{11}{10}\)
⇒ r = \(\frac{220 \times 10}{11}\) = 200
∴ radius of the circle is 200 cm.
Example 5. Write the circular value of an angle formed by the end point of hour hand of a clock in 1 hour rotation.
Solution: Sexagesimal value of an angle formed by the end point of hour hand of a clock in 1 hour rotation is \(\frac{360^{\circ}}{12}\) or 30°
180° = πc
30° = \(\frac{30}{180} \pi^c=\frac{\pi^c}{6}\)
∴ The circular value is \(\frac{\pi^c}{6}\)
Example 6. Find the circular value of 30°30’30”.
Solution: 30°30’30”
= 30° + 30′ + 30″
= 30° + 30′ + \(\left(\frac{30}{60}\right)^{\prime}\) [60″ = 1′]
= 30° + 30′ + \(\frac{1^{\prime}}{2}\) = 30° + \(\left(30+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{\prime}\)
= 30° + \(\left(\frac{61}{2 \times 60}\right)^{\circ}\) [60″ = 1′]
= \(\left(30+\frac{61}{120}\right)^{\circ}=\left(\frac{3661}{120}\right)^{\circ}\)
\(180^{\circ}= \pi^c\)∴ \(\frac{3661^{\circ}}{120}=\frac{3661}{120 \times 180} \pi^c=\frac{3661}{21600} \pi^c\)
Class 10 Maths Trigonometry Important Questions
Example 7. If the measures of two angles of a triangle are 70°38’24” and 34°21’36” then determine the sexagesimal value and the circular, value of the third angle.
Solution: Sum of two angles is (70°38’24” + 34°21’36”)
= 104°59’60” = 104°60′ = 105°
The value of the third angle = 180° – 105° = 75°
180° = πc
\(75^{\circ}=\frac{75}{180} \pi^c=\frac{5}{12} \pi^c\)∴ The sexagesimal value is 75° and circular value is \(\frac{5 \pi^c}{12}\)
Example 8. Determine the length of an arc of a circle with radius 12 cm in lengths which makes an angle at the centre is 120°.
Solution: In a circle of radius r unit in length, if the circular value of an angle subtended by an arc of S unit in length at the center is θ, then S = rθ
given, r = 12 cm
and \(\theta=\frac{120}{180} \pi^c=\frac{2 \pi^c}{3}\)
∴ S = \(12 \times \frac{2 \pi}{3} \mathrm{~cm}\)
= \(8 \times \frac{22}{7} \mathrm{~cm}=\frac{176}{7} \mathrm{~cm}=25 \cdot 14 \mathrm{~cm} \text { (approx) }\)
∴ Length of the arc is 25.14 cm (approx)
