WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding What Is Chemical Bond? Why Chemical Bonds Are Formed?
By natural process, atoms of the same element or different elements have a tendency to combine with each other to form different molecules.
So, there exists a force of attraction between the atoms that holds them together in the molecule in order to get stability.
A chemical bond means a chemical force of attraction by which two or more ions/atoms/molecules/elements are held together to form a stable state.
We know that valency is the combining capacity of an atom of a particular element with other elements.
WBBSE Notes For Class 10 Physical Science And Environment
On the basis of the electronic concept of valency, we will learn about two types of chemical bonds, which are—
- Ionic or electrovalent bonds and
- covalent or molecular bonds.
Ionic bonds are formed through the complete transfer of electrons from the outermost shells between a metal and a non-metal.
For example solid NaCI (Na+cr), MgCI2 (Mg2+2Cr), CaO (Ca2+ O2—), etc. Here (Na+cr) is an ionic compound.
On the other hand, covalent bonds are formed through the mutual sharing of one or more electron pairs between two or more non-metals.
For example: H2(H-H), O2(O=O), N2(N=N), etc. H2 and O2 are covalent compounds.
- Metals have a tendency to lose electrons.
- Non-metals have a tendency to accept electrons.
- Metals get oxidized, while non-metals get reduced.
- As ionization potential is inversely proportional to the tendency to lose electrons, metals should have low ionization potential. As electron affinity is directly proportional to the tendency of accepting electrons, so non-metals should have high electron affinity.

WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding Properties Of Ionic Compounds
The crystalline structure of sodium chloride where Na+ (cations) and Cl¯ (anion) ions are held together by a very strong electrostatic force of attraction, mainly because of which different bulk properties in ionic solids are observed, such as:
Physical state: Ionic compounds are generally hard and brittle solids.
In ionic compounds, particles are only ions (both cations & anions) due to the transfer of electrons.
Melting point (m.p.) and boiling point (b.p.): Because of the very strong electrostatic force of attraction, ionic compounds have high m.p. & high b.p. Lot of temperature (energy) is required for melting & boiling of ionic solids.
For example: for solid NaCI m. p. is = 820 e and b. p. = 1600°C.
Electrical conductivity: They conduct electricity in a molten state or aqueous state but not in a solid state.
Reason: In solid-state (Na+CP) — the Na+ & Cl– ions are tightly bound with each other and the ions are not free to move to conduct electricity.
But when Na+CP is molten (which means heated enough) or in the aqueous state (which means NaCI in water), the Na+ and Cl” ions break down and become mobile.
Know: Water molecules have a property to lessen the force between two charges and this is known as dielectric property.
Exception: CaF2, Ba3(PO4)2—for these compounds, the electrostatic force of attraction is so huge that water cannot separate out the ions.
Solubility: Usually highly soluble in water. You know from your daily experience that NaCI is such a compound.
But they are insoluble in organic solvents like alcohol/acetone/benzene/toluene/CCI4/CS2 etc. because water is itself a polar solvent.
 WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding Discovery Of Noble Gases Ionic Bonding
WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding Discovery Of Noble Gases Ionic Bonding
Discovery of noble gases: We know that Earth’s atmosphere contains very little amount of noble gases mainly argon.
In the last decade of the 19th century, English scientist Rayleigh and Scottish scientist Ramsay were able to separate out the noble gases or inert gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn) which are chemically inactive.
In the first half of the 20th century, Lewis and Kossel separately predicted that except He atoms (which have 2 electrons), other noble gas atoms have 8 electrons in their outermost / valence shell.
Electronic configuration: 2He (2), 10Ne (2, 8), lgAr (2, 8, 8), 36Kr (2, 8, 18, 8), 54X(2, 8, 18, 18, 8), 86Rn(2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8).
According to Gilbert Newton Lewis, an American physical chemist, noble gas atoms have complete outermost shells, which made them stable in comparison to rest atoms.
So we can say that for this special type of electronic configuration, the noble-gas atoms are especially stable.
Thus, the stability of an atom is decided by its electronic configuration.
There are two stability rules-
Octet Rule: If an atom has 8 electrons in an outermost shell then the atom becomes stable,
Duplet Rule: If an atom has only one shell and 2 electrons in the outermost shell then also the atom becomes stable.
3Li, 1H follows the duplet rule to become stable. All the atoms other than noble-gas atoms are trying to follow the octet rule to acquire stability.
An atom can achieve an octet or a duplet structure in two ways:
- Either by transfer of electrons or
- By mutual sharing of electron pairs.
The respective type of chemical bonding is
- ionic bonding and
- covalent bonding.
Let us now see the electronic configuration of elements of the third period and their corresponding ions
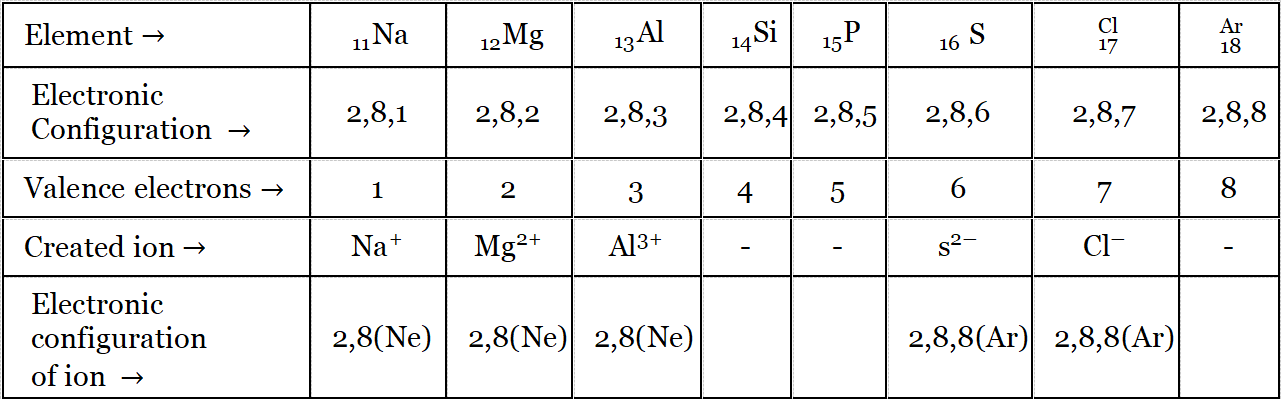
Note:
Na, Mg, and Al try to acquire electronic configurations like their nearest inert gas Ne
S (Group-14) and Cl (Group-17) try to acquire electronic configuration like their nearest inert gas Ar.
Si (Group-14), and P (Group-15) do not form ions.
Ionic bonding: Kossel established the existence of Na+ & CP ions in ionic compounds. NaCI from the idea of conductivity and other experiments.
It has also been established that ionic bonding takes place when a metal and a non-metal try to acquire an electronic configuration like their nearest inert gas.
Let us take some examples:
Bonding in NaCI (Na+CP): Electronic configuration: nNa = 2 + 8 + 1 and 17CI = 2 + 8 + 7
Neither Na nor Cl has stable electronic configurations. To avail stability, the Na atom needs either to give away le_ or to accept 7 more e¯s in the outermost shell.
Similarly, the C1 atom needs either to accept le¯or give away all the 7 e¯s from the outermost shell. For the Na atom, it is easier to give away le¯ than to accept 7 e¯s (because less energy is utilized).
A similar reason is applicable to the Cl atom. So for attaining a stable electronic configuration, the Na atom will lose le¯ from its valence cell to become the Na+ ion & Cl atom will gain that single e– to become the CP ion. Basically, this is a complete transfer of electrons.
These Na+ and CP ions attract each other by strong electrostatic Schematic diagram force and they form ionic compound NaCI.

the relative position of Na+ and CP ions in the schematic diagram of the NaCI crystal lattice)
Here, the no. of electrons lost or gained by the atoms at the time of formation of the ionic bond is called electrovalency.
In this example, the electrovalency of Na+= 1 and that of Cl¯ = -1.
Note :
When metals of Group 1 and 2 react with non-metals of Group 16 and 17, ideal ionic bonding is formed,
Due to the strong electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anions, the ionic lattice structure of NaCI is very stable.
Definition: To acquire the nearest noble-gas-like stable electronic configuration, cations, and anions are formed through the transfer of electrons from neutral metal and non-metal atoms.
The electrostatic force of attraction which holds oppositely charged ions together is called the ionic bond. The new compound so-formed is called an ionic compound.
This type of combining capacity is called ionic valency or electrovalency.
Representation of ionic bonding in terms of electron dot (•) / cross (x) structure:

Note: Li+ & H ions in the LiH compound fulfill the duplet rule in their outermost shells with no question of making an octet.
Why for ionic compounds, the concept of formula mass is more appropriate than molecular mass?
Ionic compounds are made up of huge no. of cations and anions arranged in a 3-dimensional stable ionic structure (strong electrostatic force of attraction).
They contain ions only no molecules are there.
So the concept of molecular mass is not appropriate in the case of ionic compounds-rather, formula mass is more appropriate.
For example, not saying molecular mass of NaCl = 23 + 35-5 = 58-5, we will say, the formula mass of NaCI = 58-5 or molar mass of NaCI = 58-5 g/mol.
Solid NaCI contains Na+and Cl” ions which are not free to move due to the existence of a strong electrostatic force of attraction between the ions even when an external potential difference is applied across a NaCI crystal.
But when NaCI is in a molten or aqueous state, then the ions become free to move and can conduct electricity.
That’s why we say that ionic solids have low intrinsic electrical conductivity in contrast to that in their molten or solution states.
WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding Properties Of Covalent Compounds
In order to achieve a stable electronic configuration like the nearest noble gases, atoms of two or more non-metals come together.
This coming together and mutual sharing of one or more electron pairs leads to the formation of a chemical bond known as covalent bonding.
The new compound so formed is called covalent compound and this type of combining capacity is called covalency.
Some common compounds in which covalent bonding is found to exist are naphthalene, sugar, water, ethanol, methane, chloroform, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen chloride, ammonia, etc.
Let us see some of their physical properties:

From this table, we come to know about some common properties of covalent compounds, which are—
Physical state: Covalent compounds exist as gases, liquids, or soft solids because of the very weak intermolecular force of attraction (weak Van der Waals force) existing between the molecules.
Due to this fact, a covalent bond is weak in comparison to an ionic bond. In covalent compounds, particles are molecules with no existence of ions.
Melting point (m.p.) and boiling point (b.p): Covalent compounds have low m.p. and low b.p.
Because of the very weak intermolecular force of attraction, solid covalent compounds can easily melt and boil, a liquid covalent compound is volatile in nature and a gaseous covalent compound exists in vapor form.
Solubility: Generally, covalent compounds are insoluble in polar solvents like water, but soluble in non-polar solvents like alcohol, and ether.
Exception: Cane sugar, glucose, H2S, NH3 HCI (g), ethanol, etc are soluble in water.
Electrical conductivity: They are non-conductors in a solid, molten, or aqueous state. Because covalent compounds do not contain ions to conduct electricity.
Exception: Aqueous conduct electricity in very little proportion.
WBBSE Chapter 8 Ionic And Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding
According to the proposal of G. N. Lewis (1916) about electron pairs, the concept of covalent/ chemical bonding has grown up.
Covalent bonding is said to exist between non-metal atoms and covalent compounds are formed through mutual sharing of electrons.
Here we will discuss Lewis dot diagrams (where only the valence electrons are represented by a dot (•) / cross (x) (2D structure). Let us understand covalent bonding with the help of examples:
Bonding in F2molecule: Electronic configuration: gF = 2 + 7.
Each F atom has 7 e_s in its valence shells. They need 1 more e¯ to attain stable e-configuration like the nearest noble gas Ne (complete octet).
Two F atoms come together and they share le each in a valence shell to complete the octet. Ultimately a molecule of F2 is formed.
Since a single pair of e” is shared between two F atoms, the bond is known as a single covalent bond and is represented by a single dash (—) between two F atoms.
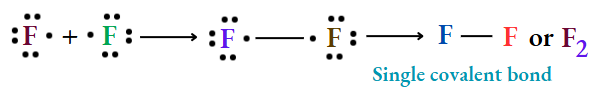
Bonding in H20 (water molecule): Electronic configuration: XH = 1 & 80 = 2 + 6.
Each H atom needs 7 e¯ in its valence shell to complete the duplet and the 0 atom needs 2 more e¯s to complete the octet. So, in a water molecule (H20) two single covalent bonds are formed.
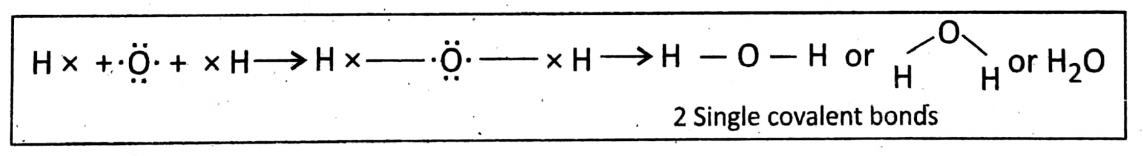
Bonding in CO2 molecule: Electronic configuration : 6C = 2 + 4 and gO = 2 + 6. Each O atom needs 2 more e¯s to complete the octet and the C atom needs 4 more e¯s to complete the octet.

So, when two O atoms and one C atom come together, each O atom will share 2 e¯s from the valance shell with 2 e¯s of the C atom in the valance shell so that all atoms acquire stable electronic configuration.
Since each O atom shares 2e¯s with the C atom, so two double covalent bonds are produced keeping C at the center and O atoms at two ends.
Bonding in N2 molecule: Electronic configuration: 7N = 2 + 5.
N atom has 5 e¯s in its valence shell. It needs 3 more e¯s to complete its octet.
So, when two N atoms come together, each N atom will share its 3 e¯s with another N atom and becomes stable.

So, each N atom shares 3 e¯ s with each other. Since the two N atoms share 3 pairs of e¯s, there is a triple covalent bond between two N atoms.
Few more examples of covalent bonding:
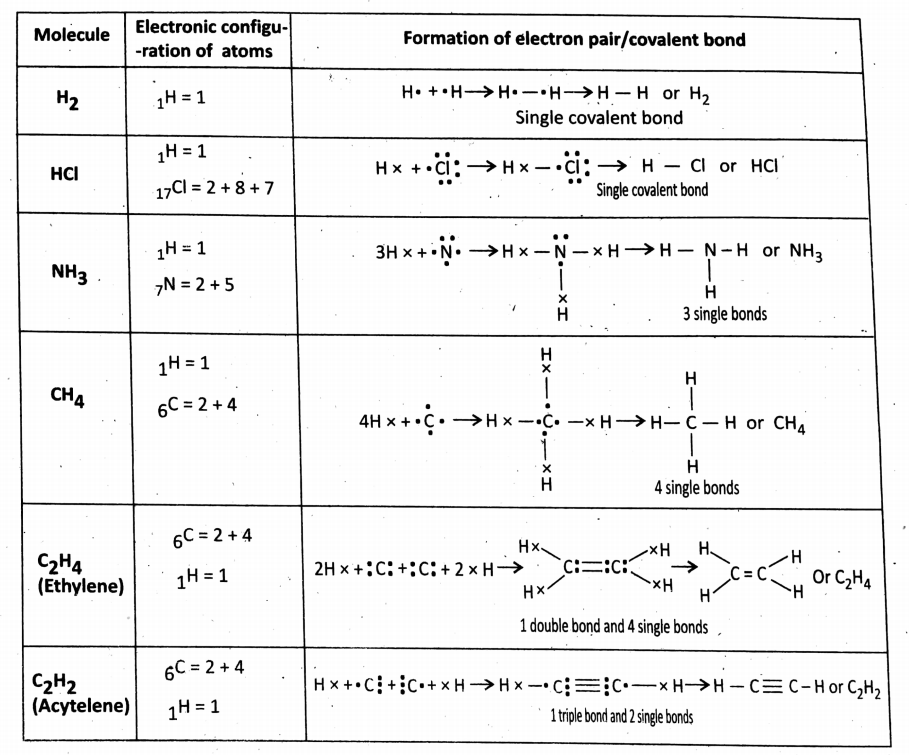
Note: (1) The no.of Electrons shared by an atom for the formation of shared electron pairs to covalent compounds is called the covalency of that particular atom.
For example: As H or Cl Or F Atom Shares One explain Pair so the covalency of H or Cl or F is 1. O atom shares two pairs of electrons,

So its Covalency =2 n atom Shares 3 Pairs Of electrons, So its Covalency = 2 N atom dot structure of O-does does not support the experimental result of the paramagnetic property of O2 molecules paramagnetic property refers to the ability to get attracted to the magnetic field).
