Geometry Chapter 4 Construction Of Triangles
Question 1. The length of the three sides of the triangle is given. Identify the cases where triangles can be Constructed or not Give reasons for the cases. 3.5cm, 4.5cm, 8cm
Solution:
Triangle inequality Theorem
This theorem states that the sum of the lengths Of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
Triangle having sides a, b, c
- a+b> c
- a+c>b
- b+c>a
1. 3.5cm, 4.5cm, 8cm
⇒ a = 3.5cm,
b = 45cm,
C = 8cm.
b + c > a
4.5+8 >3.5
12.5>3.5
∴ with these sides of a triangle Can be constructed.
Class 7 Geometry Chapter 4 Solutions
Read and Learn More Class 7 Maths Solutions

2. 3cm, 4cm, 5cm.
Let a = 3cm, (From Triangle inequality Theorem)
a+b > c
3+4 > 5
7>5
b = 4cm,
a+c>b
3+5 > 4
8>4
c=5cm
a+c > a
4+53
9>3
∴ with the sides of a, b, c lan constructed a triangle. is possible.
3. 4cm, 5cm, 10cm
Let a = 4cm, b=5cm, c = 10cm (from Triangle inequality Theorem)
a+b > c ⇒ 4+5>10 → False
a+c > b ⇒ 4+10>5 → True
b+c > a ⇒ 5+10>4 → True
∴ with this three side, we can construct a triangle in two ways.
4. 6cm, 7cm, 8cm.
Let a = 6cm, b= 7cm, c=8cm (From Triangle inequality Theorem)
a+b > c ⇒ 6 +7 > 8 → False
a+c > b ⇒ 6 7 8 > 7 → True
b+c > a ⇒ 7+876 → True.
∴ with these three sides, we can construct a triangle in two ways.
5. 6·4cm, 5.5cm, 7cm
Let a = 6·4cm, b = 5.5cm, c = 7cm (Triangle inequality Theorety.
a+b > c ⇒ 6·4 + 5.5 > 7 → True
a+c > b ⇒ 6·4+7 > 5.5 -> True
b+c>a ⇒ 5.5 +7 > 6·4 → True
∴ with the three given sides, we can draw the triangle.
Class 7 Maths Geometry Important Questions
Question 2. Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 4.5cm, BC= 6cm, and CA = 7.5cm. Also, measure its three angles with a protractor and write their measure.
Solution:
Given:
AB = 4.5cm
BC= 6cm
CA = 7.5m
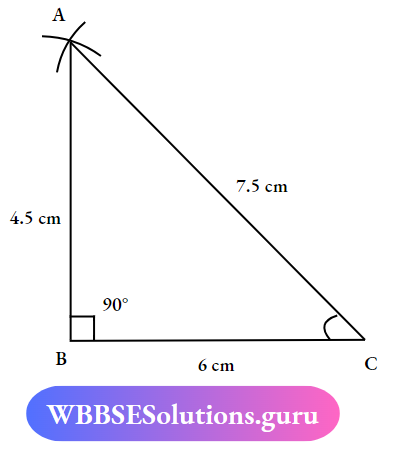
∠ABC = 90°
∠BCA = 35°
∠САВ = 55°
- Draw a line segment BC of length 6cm with the help of Scale and pencil
- Take the compass with a measurement of 4.5cm, and Draw an Arc From point B.
- Next, take measurement of 7.5cm. Draw an Arc From point ‘C’
- Mark the Joining points of the Arc and connect the Sides of a triangle with the point.
- Measuring the angle of a triangle with a protractor and noting down
Question 3. Construct an equilateral triangle having each side =5.5cm. Also, measure its angles.
Solution:
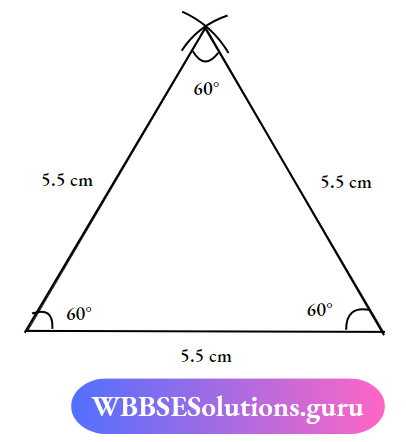
- Draw a Base of the length of 5.5cm with the help of a Scale and pencil
- Next, take the compass with a pencil take the measurement of 5.5cm and make an Arc From both sides of the line segment of the triangle Base
- Mark the Joining of Arcs
- Connect the lines from the Arc to both sides of the base of a triangle.
- All the sides of a triangle have a measurement of 5.5cm
- Measuring that all angles of a triangle are equal ie 60°
- Construction of the equilateral triangle is completed
Class 7 Maths Chapter 4 Geometry PDF
Question 4. Draw an isosceles triangle, the base of which is 4.8cm and the sum of the base angles of which is 105°
Solution:

sum of Base Angle = \(\frac{105}{2}\) = 52.5
- Draw a baseline of 4.8cm with the help of Scale and pencil.
- Given that the sum of base angles is 105° divided into 2 parts each angle has 52.5°
- Take a protractor and make the two angles of the baseline Draw a line through the angles until they intersect at a point:
- Now the Isosceles triangle with a base length of 4.8cm and a base angle of 52.5cm is formed.
Question 5. Draw a triangle PQR in which QR = 7cm, ∠PQR = 30°, and ∠PRG=60° measure the third angle.
Solution:

- Draw a line segment QR with a measurement of 7cm.
- Make the 30° Angle from the side and mark a point.
- Next, make the 60° Angle from the R side and mark a point.
- Now extend or draw a line with the particular angles made at a point where both lines will intersect each other and Note down that point as ‘p’
- Now take the protractor and measure the angle third angle it is 90°
Question 6. Draw a right angle triangle ABC in which AB=3cm, BC=4CM and ∠ABC = 90° Measure the length of the hypotenuse
Solution:
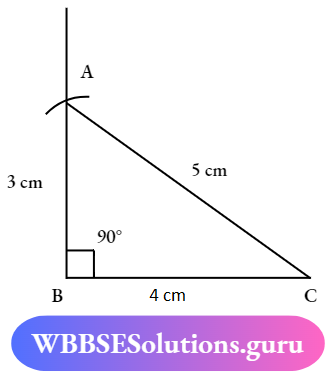
- Draw a line segment of length 4C and mark it as BC, with the help of scale and pencil
- Now make a 90° angle from point ‘B’ Draw a line Connect the angle.
- Next cut off the line with 3cm length and mark the point as ‘A’
- Joining the ‘Ac’ to form a right-angle triangle
- Now measure the length of ‘Ac’ and Note down the length of the hypotenuse is 5cm
WBBSE Class 7 Geometry Answers
Question 7. Draw an Isosceles right-angled triangle PQR in which the length of hypotenuse PR is 10cm
Solution:
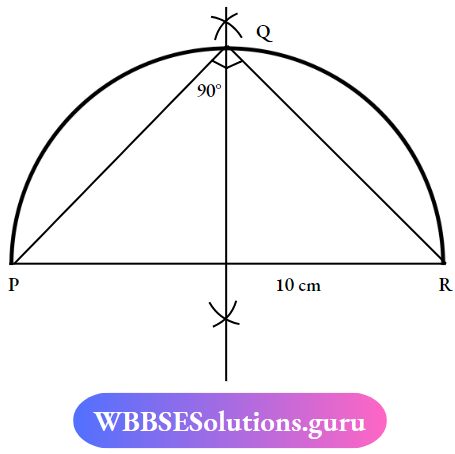
- Draw the hypotenuse PR of 10cm with the help of a scale and pencil.
- Next, make a bisector of PR by taking more than half of its length and making or drawing an arc on both sides.
- Connect the bisector. and take the compass and adjust to the midpoint PR where the bisector intersects and with the radius make the semi-circle as shown.
- Make a point where the Bisector and semicircle meets Note it and Join the the lines from PQ, and RQ. Isosceles right-angled triangle is formed.
Question 8. Draw a right-angled triangle ABC such that ∠ACB=90°. AB=7.5cm and ∠ABC = 30°
Solution:
Given AB = 7.5cm
∠ACB 90°, ∠ABC = 30°
Let the third angle be ‘x’
A sum of angles in a Δle = 180°
90°+30°+2° = 180°
х° = 180°-120°
x = 60°
∴ ∠BAC = 60°
- Draw AB with 7.5 cm
- Take the compass with some radius and draw an arc from A and Bas shown
- From the meeting point of the arc on AB draw an area on the first area which will make 600 Angles. Same as on the other side.
- Next, Draw the two Arcs from the intersection of two arcs on the B side. and the intersection of the Arc on AB. which makes the intersection” of the Points make 30° Angle.

5. Now take the midpoint of AB as the radius and draw a semicircle.
6. Now extend or draw the lines from A and B with the given. angle. which meet at a semicircle which makes a 90° angle
∴ The right-angled triangle is formed.
WBBSE Class 7 Geometry Answers
Question 9. Draw an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC=6cm and BC=4.8cm. Draw AD⊥BC and measure the length of A.D.
Solution:
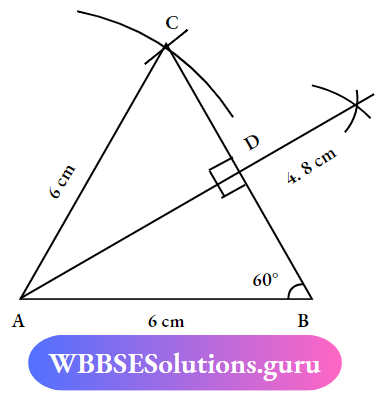
- Draw a line segment with a length of 6cm and name it AB with the help of scale and pencil.
- Take a compass with a measurement of 6cm and draw an Arc From point ‘A’
- Take the measurement of 4.8cm and draw an Arc From point ‘B’ and these two Arc intersect at a point mark the point as ‘C’
- Now Joining the other sides of the triangle to point ‘C’ the triangle ABC is formed.
- Draw a perpendicular to BC and Name it ‘D’ Next find the length of ‘AD’ with the help of scale.
- The length of AD is 5.5cm.
Question 10. Draw an isosceles triangle ABC in which the length of base BC is 4.8cm and the length of perpendicular AD.
Solution:
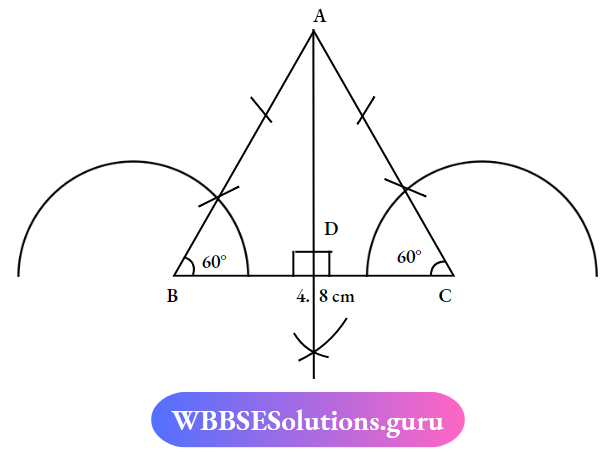
- Draw a baseline of length BC = 4.8cm with the help of Scale and pencil.
- Take the with any radius and draw an Arc from point B and point as shown.
- Next, take the compass and put the compass at the intersection of the baseline Arc which makes the angle of 60°. Do it on Both sides of the Intersection.
- Next, extend the lines through the Intersection of the two arcs. The extended lines form a triangle at point ‘A’
- Draw a perpendicular to BC and Name it ‘AD’
