Reading Skill Seen Lesson 6 The Sea
Word meaning:
Stanza 1
hungry (হাংরি)—ক্ষুধার্ত ; grey (গ্রে ) – ধূসরবর্ণ; rolls (রোস্) – গড়াগড়ি খায়; beach (বীচ্)—সমুদ্রতীর; clashing (ক্ল্যাশিং)—ঠোকাঠুকি করে; shaggy (শ্যাগি) — রুক্ষ; gnaws (ন্যস্)—অনবরত কামড়ায়, চিবায়; rumbling (রাম্বলিং)—গুড় গুড় শব্দময় ; tumbling (টাম্বলিং)— গড়াগড়ি দিচ্ছে এমন; moans (মোস্) –বিলাপ করে; greasy (গ্রীসি) — তৈলাক্ত; paws (প্যজ্) – থাবাগুলি ।
Stanza 2
roars (রোরস্)— গৰ্জ্জন করে ; rocks (রক্স) — টলমল করে ; bounds (বাউন্ডস্) – লাফ দেয়; snuffs (স্না) —নাকের মধ্যে টেনে নেয়; sniffs (স্নি)— শোঁকে; cliffs (ক্লি)—খাড়া উঁচু পাহাড় ; howls (হাউস্ )–গর্জন করে; hollos (হলোজ) – উচ্চৈঃস্বরে ডাকে ।
Read And Learn Also WBBSE Class 8 English Reading Skills
Stanza 3
quiet (কোয়ায়েট্)—শান্ত ; dune (ডিউন্) – বালিয়াড়ি; reedy tune (রীডি টিউন) – বাদ্যযন্ত্রের সুর; scarcely (স্কেয়ারলি) – কোনোমতে; snores (স্নোর্স্)—নাক ডাকে।
Substance:
The poet here describes a sea at different times by comparing it to a huge, grey-hungry dog. The sea- dog rolls on the beach the whole day biting and chewing the rolling stones in the wave-like bones, and groans for more.
At night the moon swings in the stormy cloud with the roaring night wind. The sea dog shakes off his wet limbs over the cliffs and howls loud. But in summar in May or June, the mighty sea- dog becomes quiet. Even the grasses on the dune stop playing their high pitch tune. The sea then lies still on the beach.
বঙ্গানুবাদ :
কবি এখানে বিভিন্ন সময়ের সমুদ্রকে একটি বিশাল, ধূসর ও ক্ষুধার্ত কুকুরের সঙ্গে তুলনা করেছেন। সমুদ্র-কুকুর সৈকতের উপর সারাদিন গড়াগড়ি দিয়ে ঢেউয়ের মধ্যে লুটোপুটি খাওয়া পাথরগুলোকে হাড়ের মত চিবোয় আর কামড়ায় এবং আরও হাড়ের জন্য কাতরাতে থাকে। রাত্রিবেলা গর্জনশীল রাতের বাতাসে ঝোড়ো মেঘে চাঁদটা দুলতে থাকে। সমুদ্র-কুকুর তখন তার দেহের ভিজে অঙ্গ-প্রত্যঙ্গ সব তটের পাথরের উপর ঝেড়ে ফেলে এবং তীব্র চিৎকার করে। কিন্তু গ্রীষ্মকালে মে অথবা জুন মাসে শক্তিমান্ সমুদ্র-কুকুর শান্ত হয়ে পড়ে। বালিয়ারির উপরের ঘাসগুলিও তাদের তীক্ষ্ণ সুর বাজানো বন্ধ রাখে (অর্থাৎ নিয়মিত ছন্দে খেলা করে না)। বালির তটে সমুদ্র তখন স্থির হয়ে শুয়ে থাকে।

Reading Skill Seen Lesson 6 The Sea Examples
Read the texts below and do as directed.
Question 1. The sea is a hungry dog,
Giant and grey.
He rolls on the beach all day.
With his clashing teeth and shaggy jaws
Hour upon hour he gnaws
The rumbling, tumbling stones,
And ‘Bones, bones, bones!’
The giant sea dog moans,
Licking his greasy paws.
| WBBSE Class 8 English Functional Grammar | WBBSE Class 8 English Reading Skills |
| WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 English | WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths |
1. Answer the questions below:
- What does the sea look like?
- What does the sea do all day?
- How has the sea been described in the poem?
- What does the sea dog moan for?
Answer:
- The sea looks like a giant, hungry dog grey in colour.
- The sea rolls on the beach all day.
- The sea has been described as a huge hungry dog that rolls on the beach all day long with his clashing teeth and shaggy jaws.
- The sea dog moans for bones.
2. Choose the correct answers from the alternatives given:
Question 1. The sea is compared to a-
- Fierce lion,
- Wolf,
- Hungry dog.
Answer: 3. Hungry dog
Question 2. The sea looks-
- Blue,
- GZrey,
- White.
Answer: 2. GZrey
Question 3. Stones are compared to
- Bones,
- Teeth,
- Nuts.
Answer: 1. Bones
Question 4. The sea dog has-
- Broken teeth,
- Rough teeth,
- Clashing teeth.
Answer: 3. Clashing teeth
3. Complete the sentences with information from the text.
Question 1. With his clashing teeth and rough jaws, the sea ________
Answer: With his clashing teeth and rough jaws, the sea rolls on the beach all day.
Question 2. The hungry sea-dog gnaws ____________
Answer: The hungry sea dog gnaws the rumbling and tumbling stones.
Question 3. When the giant sea dog moans, he ________
Answer: When the giant sea dog moans, he licks his greasy paws.
4. Find words in the text which have the following meanings:
- The seashore,
- Rough,
- The mouth and teeth of a person or an animal,
- Bites and chews,
- Very large.
Answer:
- Beach;
- Shaggy,
- Jaws,
- Gnaws;
- Giant.
Question 2. And when the night wind roars
And the moon rocks in the stormy cloud,
He bounds to his feet and snuffs and sniffs,
Shaking his wet sides over the cliffs
And howls and hollos long and loud.
But on quiet days in May or June,
When even the grasses on the dune
Play no more their reedy tune,
With his head between his paws
He lies on the sandy shores,
So quiet, so quiet, he scarcely snores.
1. Answer the questions below:
- Who rocks in the stormy cloud?
- When does the moon rock?
- When do the quiet days come?
- When do the grasses stop playing their reedy tune?
- What does the sea dog do is May or June?
Answer:
- The moon rocks in the stormy cloud.
- The moon rocks in the stormy cloud when the night wind roars.
- The quiet days come during May and June.
- The grasses on the dune stop playing their reedy tune during May and June.
- In May and June the sea dog lies on the sandy shores quietly keeping his head between his paws.
2. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false statements.
Question 1. The moon rocks in a calm weather.
Answer: False
Question 2. The sea shakes his wet sides over the cliffs.
Answer: True
Question 3. The quiet days come before May.
Answer: False
Question 4. The weather remains calm in May and June.
Answer: True
Question 5. On quiet days the sea seldom snores.
Answer: True
3. Complete the sentences with information of the text.
Question 1. In the stormy cloud the moon ____________
Answer: In the stormy cloud the moon rocks when the night wind roars.
Question 2. In May or June the grasses on the dune ___________
Answer: In May or June the grasses on the dune do not play their reedy tune.
Question 3. In quiet days in May or June, the sea dog lies ________
Answer: In quiet days in May or June, the sea dog lies on the sandy shores quietly keeping his head between the paws.
Question 4. The sea-dog shakes his ________
Answer: The sea dog shakes his wet sides over the cliffs.
4. Match the words in A with their opposite meanings in B.
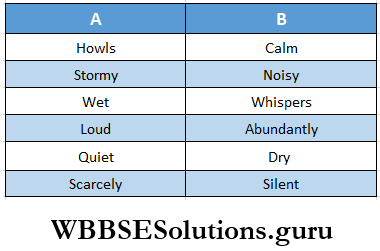
Answer:

