Algebra Chapter 2 Polynomials
The Algebraic expression having one or more terms is called Polynomial Expression.
Multiplication of Algebra
Example 1. Let the length and breadth of a rectangle are (3x + 2y) unit and (x – 4y) unit respectively.
Solution: Area is (3x + 2y) x (x – 4y) sq. unit
= {3x (x – 4y) + 2y (x – 4y)} sq. unit
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths
= (3x2 – 12xy + 2xy – 8y2) sq. unit = (3x2 – 10xy – 8y2) sq. unit

Example 2. Multiplication: (a2 + ab + b2) by (a2 – ab + b2)
- Multiplicand: a2 + ab + b2
- Multiplier: a2 – ab + b2
Solution: Multiplication:

The product = a4 + a2b2 + b4
Alternating Method:
(a2 + ab + b2) (a2 – ab + b2)
= a2 (a2 – ab + b2) + ab (a2 – ab + b2) + b2 (a2 – ab + b2)
= a4 – a3b + a2b2 + a3b – a2b2 + ab3 + a2b2 – ab3 + b4 = a4+ a2b2 + b4
| WBBSE Class 8 English Functional Grammar | WBBSE Class 8 English Reading Skills |
| WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 English | WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths |
Example 3. Find the product by successive multiplication. (x2 – 1), (x2 + 2x2 – 5), (5 – x3 + x4)
Solution:

∴ The required product = x9 + x8 – 3x7 – 6x6 + 125x5 + 15x4 – 10x3 – 35x2 + 25
Example 4. Find the continued product of (a + b + c), (a – b + c), (a + b – c) and (b + c – a)
Solution:

∴ The required product = 2a2b2 + 2b2c2 + 2c2a2 – a4 – b4 – c4
Example 5. Find the product by successive multiplication: \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{c}\right),\left(\frac{b}{c}+\frac{c}{a}\right),\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{c}\right)\left(\frac{b}{c}+\frac{c}{a}\right)\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)=\left\{\frac{a}{b}\left(\frac{b}{c}+\frac{c}{a}\right)+\frac{b}{c}\left(\frac{b}{c}+\frac{c}{a}\right)\right\}\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{a}{c}+\frac{c}{b}+\frac{b^2}{c^2}+\frac{b}{a}\right)\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)\)
= \(\frac{a}{c}\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)+\frac{c}{b}\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)+\frac{b^2}{c^2}\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)+\frac{b}{a}\left(\frac{c}{a}+\frac{a}{b}\right)\)
= \( 1+\frac{a^2}{b c}+\frac{c^2}{a b}+\frac{a c}{b^2}+\frac{b^2}{a c}+\frac{a b}{c^2}+\frac{b c}{a^2}+1\)
= \(2+\frac{a^2}{b c}+\frac{b^2}{c a}+\frac{c^2}{a b}+\frac{a b}{c^2}+\frac{b c}{a^2}+\frac{c a}{b^2}\)
Example 6. Simplify: (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2) + (b − c) (b2 + bc + c2) + (c − a) (c2 + ac + a2)
Solution:
Given
(a – b) (a2 + ab + b2) + (b − c) (b2 + bc + c2) + (c− a) (c2 + ca + a2)
= a (a2 + ab + b2) – b (a2 + ab + b2) + b (b2 + bc + c2) – c (b2 + bc + c2) + c (c2 + ca + a2) – a (c2 + ca + a2)
= a3 + a2b + ab2 – a2b – ab2 – b3 + b3 + b2c + bc2 – b2c – bc2 – c3 + c3 + c2a + a2c – c2a – a2c – a3 = 0
Example 7. Simplify: \(\left(a^{-1}+b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-1}-b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)
Solution:
Given that
\(\left(a^{-1}+b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-1}-b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)= \(\{\left(a^{-1}\left(a^{-1}-b^{-1}\right)+b^{-1}\left(a^{-1}-b^{-1}\right)\right\}\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)
= \(\left(a^{-2}-a^{-1} b^{-1}+ a^{-1} b^{-1}-b^{-2}\right)\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)
= \(\left(a^{-2}-b^{-2}\right)\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)
= \(a^{-2}\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)-b^{-2}\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\)
= \(a^{-4}+q^{-2} b^{-2}-a^{-2} \cdot b^{-2}-b^{-4}\)
= \(a^{-4}-b^{-4}\)
\(\left(a^{-1}+b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-1}-b^{-1}\right)\left(a^{-2}+b^{-2}\right)\) = \(a^{-4}-b^{-4}\)
Example 8. Simplify: (a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
Solution:
Given
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca)
= a (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca)
+ b (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca)
+ c (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca)
= a3 + ab2 + ac2 – a2b – abc – a2c
+ a2b + b3 + bc2 – ab2 – b2c – abc
+ b2c + c3 – abc – bc2 – ac2
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca) = a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc
Algebra Chapter 2 Division
Method of division are of two types
- Exact division
- Inexact division
In case of Exact division, the remainder zero.
Here Dividend = Divisor x Quotient.
In case of Inexact division, after completion of division, we have quotient and remainder.
Here Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder.
Example 1. Divide (x2 – 4x – 5) by (x – 5)
- Divisor = (x- 5)
- Dividend = x2 – 4x – 5
Solution:
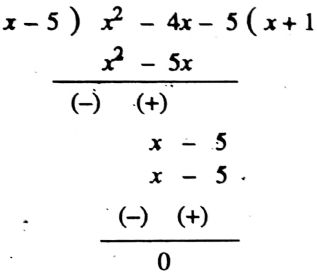
∴ The quotient is (x + 1) and remainder is 0.
Example 2. Divide (5x3y2 – 7x2y3 + 3xy4) by xy4
Solution:
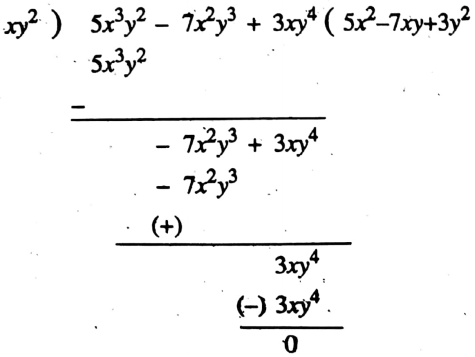
∴ The quotient is 5x2 – 7xy + 3y2 and remainder is 0.
Example 3. Divide the first expression by the second:
- (a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc), (a + b + c)
- (x4 – 2x3 – 15x2 + 16x + 35), (x2 + x – 7)
Solution:
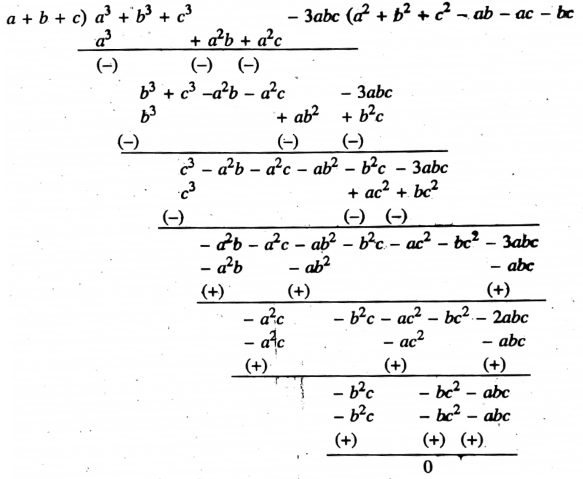
∴ Quotient = a2 + b2 + c2 – ab- bc – ca
Remainder = 0
2.
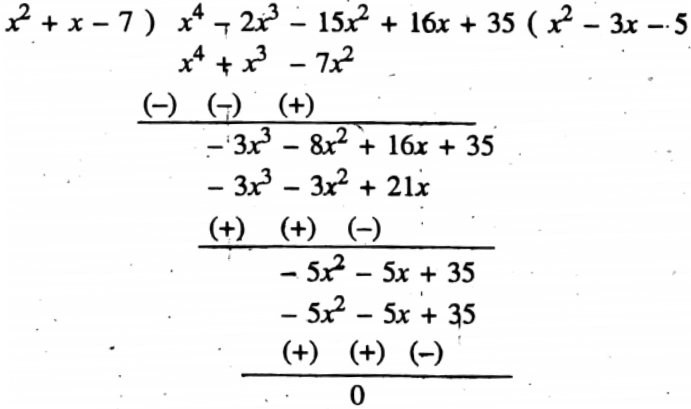
∴ Quotient = x2 – 3x – 5
Remainder = 0
Example 4. Divide (a – b) by \(a^{\frac{1}{3}}-b^{\frac{1}{3}}\)
Solution:

∴ Quotient = \(a^{\frac{2}{3}}+a^{\frac{1}{3}} b^{\frac{1}{3}}+b^{\frac{2}{3}}\)
Remainder = 0
Example 5. Find the quotient and the remainder of the following:
- (x3 + x2 + 25) by (x + 3),
- (81x4 + 4) by (3x – 1)
- (9a2 – 4a3 – 5 + a4 -19a) by (7 + a2 – a)
Solution:
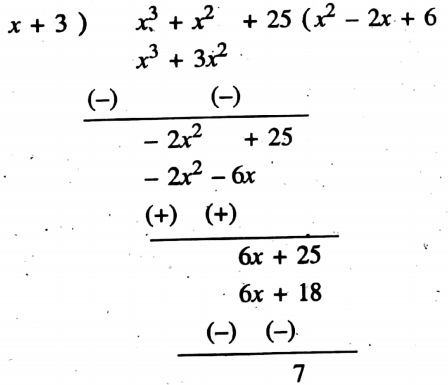
∴ The required quotient = x2 – 2x + 6 and remainder = 7
2.

∴ Quotient = 27x3 + 9x2 + 3x + 1
Remainder = 5
3. Dividend = 9a2 – 4a3 – 5+ a4 – 19a
= a4 – 4a3 + 9a2 – 19a – 5 [In descending power of a]
Divisor = 7 + a2 – a
= a2 – a + 7 (In descending power of a)
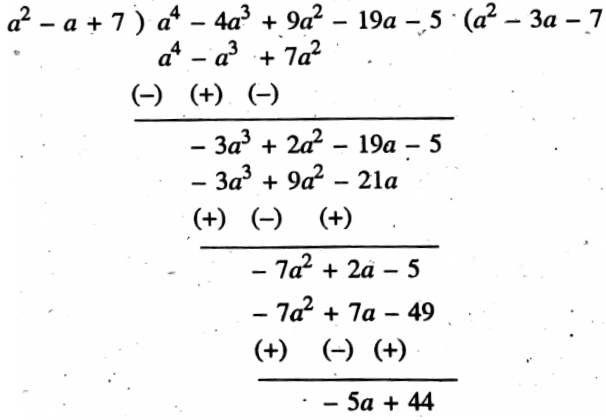
∴ The Quotient = a2 – 3a- 7
Remainder = 44-5a
Example 6. Divide (6x2 + 11xy + 6y2) by (3x – 2y)
Solution:
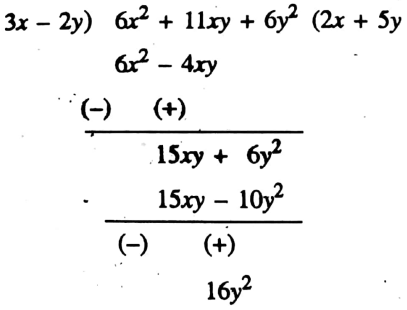
∴ Quotient = 2x + 5y
Remainder = 16y2
Example 7. In a division problem the divisor is (x2 – 3x + 5), the quotient is (2x – 7) and remainder.
Solution: Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
= [(x2 – 3x + 5) × (2x-7)] + (x + 3)
= [ 2x3 – 7x2 – 6x2 + 21x + 10x – 35] +[ x + 3 ]
= 2x3 – 13x2 + 32x – 32
Example 8. Choose the correct answer:
1. (x – 3)(x + 2) =
- x2 – 5x – 6
- x2 – x – 6
- x2 – x + 6
- x2 -5x + 6
Solution: (x-3) (x+2)
= x(x+2)- 3(x+2)
= x2 + 2x – 3x – 6 = x2 – x – 6
∴ The correct answer is 2. x2 – x – 6
2. (8x8 – 8x2 – 36x) ÷ 4x =
- 2x8 – 2x2 – 9
- 2x8 – 8x – 36
- 2x7 – 2x – 9
- 2x7 – 2x – 18
Solution: \(\frac{8 x^8-8 x^2-36 x}{4 x}=2 x^7-2 x-9\)
∴ The correct answer is 3. 2x7 – 2x – 9
3. (x2 – 14x + 45 ÷ (x – 5) =
- x – 9
- x + 5
- 9 – x
- x + 9
Solution:

∴ So the correct answer is 1. x – 9
Example 9. Write ‘True’ or ‘False’:
1. (x – a) (x – b) (x – c)…. (x − z) = 1
Solution: (x – a) (x – b) (x – c)…… (x – z)
= (x − a) (x – b) (x − c)….. (x – x) (x − y) (x − z)
= (x – a) (x – b) (x – c)…. (0) (x − y) (x – z) = 0
∴ The statement is false.
2. \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}\right)\left(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{d}\right)\left(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{c^2}{d^2}\right)\)=\(\frac{a^4}{b^4}-\frac{c^4}{d^4}\)
Solution:
Given that
\(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}\right)\left(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{d}\right)\left(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{c^2}{d^2}\right)=\left(\frac{a^2}{b^2}-\frac{c^2}{d^2}\right)\left(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{c^2}{d^2}\right)\)= \(\left(\frac{a^2}{b^2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{c^2}{d^2}\right)^2=\frac{a^4}{b^4}-\frac{c^4}{d^4}\)
∴ So the statement is true.
3. (x2 + 11x + 27) ÷ (x + 6) = x + 5 + \(\frac{(-3)}{x+6}\)
Solution:

∴ \(\left(x^2+11 x+27\right) \div(x+6)=(x+5)+\left(-\frac{3}{x+6}\right)\)
∴ So the statement is true.
Example 10. Fill in the blanks:
1. \((-2 a)^2 \times(-3 a)^3 \times\left(-\frac{1}{3} a\right)^3=\)________
Solution: \((-2 a)^2 \times(-3 a)^3 \times\left(-\frac{1}{3} a\right)^3\)
= \(4 a^2 \times-27 a^3 \times-\frac{1}{27} a^3=4 a^2\)
2. (x2 + xy + y2) (x − y) = ________
Solution: (x2 + xy + y2) (x − y)
= ( (x2 + xy + y2) × (x))
– ((y) × (x2 + xy + y2))
= x3 + x2y + xy2 – x2y – xy2 – y3
= x3 – y3
(x2 + xy + y2) (x − y) = = x3 – y3
3. (5x2 – 2x – 3) ÷ (x – 1) = ________
Solution:

Quotient is (5x+3).
(5x2 – 2x – 3) ÷ (x – 1) = (5x+3).
