Algebra Chapter 2 Graph
⇒ The region within angle XOY is called 1st quadrant.
⇒ The region within angle YOX’ is called the 2nd quadrant.

⇒ The region within angle X’OY’ is called the 3rd quadrant and the region YOX is called the 4th quadrant.
⇒ We get the distance from Y-axis is X coordinate and the distance from X-axis is the Y coordinate.
⇒ O is called the origin. The X coordinate is called the abscissa and the Y-co-ordinate is called the ordinate.
⇒ The co-ordinate of origin O is (0, 0).
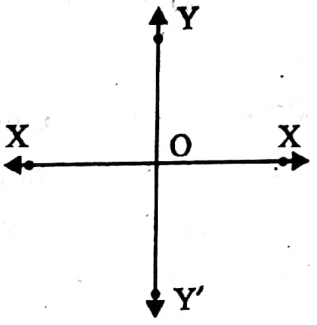

⇒ Signs of abscissa and ordinate in the different quadrants is shown.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Maths
Algebra Chapter 2 Graph Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. Co-ordinate of origin is ______
Solution: (0, 0)
Example 2. Equation of X axis is ______
Solution: y = 0
Example 3. Equation of Y axis is ______
Solution: y = 0
Example 4. X + 8 = 0 is parallel to _______ axis.
Solution: Y axis
Example 5. (0, 8) point lies on ______ axis.
Solution: Y axis
Example 6. (-6, 0) lies on ______ axis.
Solution: X axis
Example 7. (-3, +5) lies in the ________ quadrant.
Solution: 2nd
Example 8. Distance of A (6, 8) from Y axis is ________ units.
Solution: 6
Example 9. 2x + 3y = 12 intersects X axis at ________
Solution: (6, 0)
Example 10. 2x + 3y 12 intersects Y axis at _________
Solution: (0, 4)
Algebra Chapter 2 Graph True Or False
Example 1. The equation of the straight line parallel to X axis is x = c (c is a constant)
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 2. (-8, 5) lies in the 3rd quadrant.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 3. (6, 0) lies in X axis.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 4. \(\frac{X}{2}-\frac{Y}{2}\) = 1 intersects Y axis at (0, 2).
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 5. The distance of the point (-a, -b) from X axis is a units. (where a, b > 0).
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 6. The distance of the point (8, 6) from the origin is 10 units.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 7. y = -x is passing through origin.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 8. 2x + 3y = 5 passes through origin.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 9. The angle between the lines y = constant and x = constant is 90°.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 10. The line joining the points (a, b) and (-a, -b) passes through the origin.
Solution: The statement is True.
Algebra Chapter 2 Graph Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. Let us write the coordinates the point of intersection of the graph of equation 2x + 3y = 12 and the X axis.
Solution: At X axis ordinate = 0
∴ 2x + 0 = 12 or, x = 6
⇒ The point of intersection is (6, 0).
Example 2. Let us write the coordinates of the point of intersection of the graph of the equation 2x – 3y = 12 and the Y axis.
Solution: At Y axis, abscissa = 0
∴ 0 – 3y = 12 or, y = -4
⇒ The point of intersection is (0, -4).
Example 3. Let us write the distance of the point (6,-8) from X axis and Y axis.
Solution: Distance from X axis= 8 units.
⇒ Distance from Y axis = 6 units.
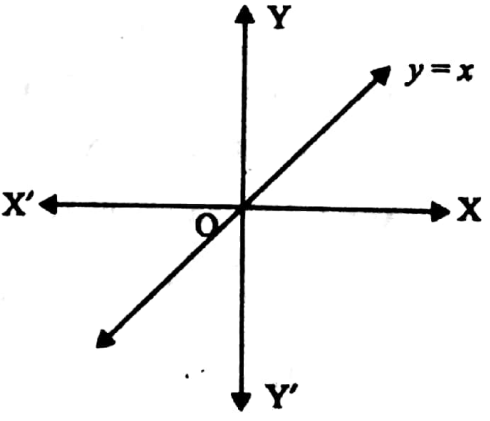
Example 4. Let us write the angle derived from the equation XY from the positive direction of X axis.
Solution: y = x straight lines make 45° angle with the positive side of X axis.
Example 5. Answer the following
- ΔAPC =?
- ΔBPD =?
Solution:
- AC (54) unit = 1 unit
height ΔAPC 3 units
ΔAPC = \(\frac{1}{2}\).1.3 sq units
= 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) sq units. - BD = (6 – 5) unit = 1 unit
height of ΔBPD = 2 units
ΔBPD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 1 x 2 sq units = 1 sq unit

Example 6. 2x + 3y = 11 intersects X axis at (α, β) then find α, β.
Solution: At X axis y = 0
∴ 2x + 3 x 0 = 11
⇒ or, x = +\(\frac{11}{2}\)
∴ The intersection point is (\(\frac{11}{2}\),0)
∴ α = \(\frac{11}{2}\), β = 0
Example 7. Find the point of intersection of the straight lines y = x and 3x – 2y = 0
Solution: By putting y = -x in 3x – 2y = 0, 3x – 2(-x) = 0
⇒ or, 5x = 0
⇒ or, x = 0 and y = 0
∴ The point of intersection is (0, 0)
Example 8. Find the point of intersection of x = 2, y = 3.
Solution: The straight line x = 2 is parallel to Y axis and the straight
⇒ line y = 3 is parallel to X axis.
∴ The point of intersection is (2, 3).

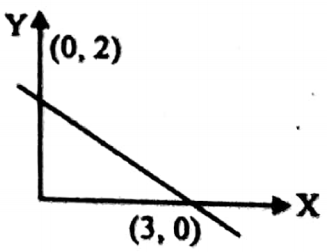
Example 9. Find the area of the triangle formed by the coordinate axes and the straight lines 2x + 3y = 6.
Solution: At X axis, y = 0
∴ 2x + 0 = 6, x = 3
⇒ The straight line intersects X axis at (3, 0)
⇒ Similarly at Y axis, Y = 0
∴ 2.0 + 3y = 6, y = 2
⇒ The straight line intersects Y axis at (0, 2)
⇒ D = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 3 x 2 sq. units = 3 sq. units.