Mensuration Chapter 1 Area And Perimeter Of Triangle And Quadrilateral Useful Information And Formulae
Rectangle:
Let the length of a rectangle be a units and its breath be is units.
- Area of the rectangle = lengths x breadth = ab sq units. ∴ length = \(\frac{\text { area }}{\text { breadth }}\); breadth = \(\frac{\text { area }}{\text { length }}\)
- Perimeter of the rectangle 2 (length + breadth) = 2(a + b) units ∴ length breadth = semi perimeter.
- Diagonal of the rectangle = \(\sqrt{(\text { length })^2+(\text { breadth })^2}=\sqrt{a^2+b^2} \text { units. }\)
Square:
Let each side of a square be a units
- Area of the square = a2 sq. units.
- Perimeter of the square = 4a units ∴ side = \(\frac{\text { perimeter }}{4}\)
- Diagonal of the square = a√2 units ∴ area of the square = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (diagonal)2.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Maths
Rhombus:
- Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x product of the diagonals base x height.
- Perimeter of the rhombus = 4 x side.
Trapezium and parallelogram:
- Area of the trapezium = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x sum of the distance of the parallel side between them.
- Area of the parallelogram = base × height.
- Area of the four walls of a rectangular room = Perimeter of the floor x height of the room = 2 (lengths + breadth) x height.
Triangle:
Let the sides of a triangle be a units, b units and c units.
- Area of the triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x base x height.
- Area of the triangle = \(\sqrt{\mathrm{S}(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\) sq units. where S semi-perimeter of the triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (a+b+c) units.
- Height of the equilateral triangle = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) x side
- Median of the equilateral triangle = height of that triangle.
- Circum radius of the equilateral triangle = \(\frac{2}{3}\) x median.
- In radius of the equilateral triangle = \(\frac{1}{3}\) x median.
- Area of the equilateral triangle = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\) x (side)2.
- If the base of an isosceles triangle be a units and each of the two equal sides of b units, then height of that isosceles triangle \(\sqrt{b^2-\frac{a^2}{4}}\) units and area of that isosceles triangle = \(\frac{1}{2} \times a \times \sqrt{b^2-\frac{a^2}{4}}\) units.
Mensuration Chapter 1 Area And Perimeter Of Triangle And Quadrilateral Useful Information And Formulae Fill In The Blanks
Example 1. The length of the hypotenuse of an isoscels triangle is 3√2 cm, the area is _______
Solution: 4\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Example 2. When each side of an equilateral triangle is increased by 10%, its altitude increased by ________%.
Solution: 10%.
Example 3. When each side of an equilateral triangle is increased by 10%, its area increased by _________%.
Solution: 19%.
Example 4. The length of a median of an equilateral triangle of area 4√3 sq cm is ________ cm
Solution: 2√3
Example 5. In an isosceles right-angled triangle, the length of hypotenuse is √2 cm then the length of each equal sides is _______ cm.
Solution: 1.
Example 6. The length of two sides holding the right angle in a right-angled triangle are 3 cm and 4 cm. The length of the perpendicular drawn from the right angle to the hypotenuse is _______ cm.
Solution: 2 \(\frac{2}{5}\)cm.
Example 7. If each side of a square is increased by 10%, then the area is increased by ________ %.
Solution: 21%.
Example 8. The perimeter of a square is m metre. It is area is _______ sq m.
Solution: \(\frac{m^2}{16}\)
Example 9. The area of a square is 8k metre, the length of its diagonal is ________ m.
Solution: 4√k
Example 10. The perimeter of the square whose area is equal to sum of the areas of two square of sides 8 metre and 6 metre respectively is _______ metre.
Solution: 40.
Mensuration Chapter 1 Area And Perimeter Of Triangle And Quadrilateral Useful Information And Formulae True Or False
Example 1. The two diagonals of a rhombus are 24 m, 10 m. It is area is 120 sq cm.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 2. If the three sides of an equilateral triangle be (x + 3) cm, (y + 4) cm, (x + y) cm, then the triangle with the sides (2xy + 1) cm, (6x + 1) cm and (8y+ 1) cm is also an equilateral triangle.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 3. The length of a rectangle is 3 cm longer than its breadth. If its breadth be x cm, then the area is (x2 + x) sq cm.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 4. The length of a rectangle is 3 times that of its breadth. If the perimeter of the rectangle is 32 cm, its area is 4.8 sq cm.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 5. The area of an equilateral triangle is 9√3 sq cm. The length of the median is 3√3 cm.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 6. The centriod of an equilateral triangle ΔABC is G. If AB = 6 m, then AG = 2√3 cm.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 7. The measure of each side of two equal sides of an isosceles triangle is 10 cm and measure of its base is 16 cm. The area is 16 sq cm.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 8. A square and an equilateral triangle stand on same base. Area of the triangle = √3/2 x area of the square.
Solution: The statement is False.
Example 9. If number of metres of the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is equal to the number of sq metres of the area of the triangle. Measure of each side of the triangle is 4√3 metres.
Solution: The statement is True.
Example 10. D, E, and F are the midpoints of the sides BC, CA, and AB of a triangle ABC respectively. If the area of the triangle ABC = 24 sq em then ΔDEF = 6 sq cm.
Solution: The statement is True.
Mensuration Chapter 1 Area And Perimeter Of Triangle And Quadrilateral Useful Information And Formulae Short Answer Type Questions
Example 1. If the length of a square increased by 10%, then what % of the area will be increased?
Solution: Let length of the side be a unit.
∴ Area = a2 sq units
increased side = \(\frac{11a}{10}\) unit
increased area = \(\frac{121 a^2}{1 a}\)
area % increased = \(=\frac{\frac{121 a^2}{1 a}-a^2}{a^2} \times 100=21\)
∴ 21% of the area will be increased.
Example 2. If the length is increased by 10% and breadth is decreased by 10% of a rectangle, then what % of area will be increased or decreased?
Solution: Let length and breadth be a and b units area = ab sq units.
Increased length = \(\frac{11a}{10}\) unit
decreased breadth = \(\frac{9a}{10}\)
New area = \(\frac{99 a^2}{100}\) sq units.
area % decreased = \(\frac{\frac{a^2-99 a^2}{100}}{a^2} \times 100=1\)
∴ 1% of area will be decreased.
Example 3. The length of rectangle is 5 cm. The length of the perpendicular on a breadth of the rectangle from an intersecting point between two diagonals is 2 cm. What is the length and breadth?
Solution: OP = 5 cm.
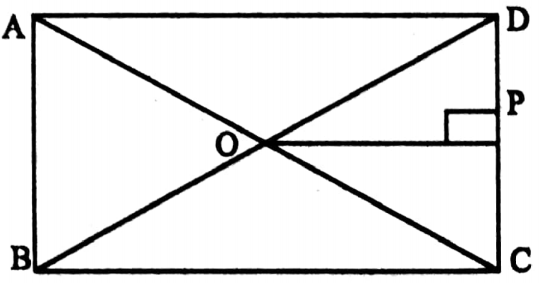
BC = 2 x 2 cm = 4 cm (from mid point theorem)
Let DC = x cm
∴ 42 + x2 = 52
x = 3
∴ The length and breadth 3 cm.
Example 4. The perimeter of a rectangle is 34 cm and area is 60 sq cm. Find the length of each diagonal.
Solution: If length and breadth are x cm, y cm then 2 (x + y) = 34
or, x + y = 17
xy = 60
(x + y)2 = 172
or, x2 + y2 = 172 – 2 x 60
= 289 – 120 = 169
∴ \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) = 13
∴ Length of each diagonal = 13 cm.
Example 5. The numerical values of area and height of an equilateral triangle are cuqal. Find the length of each side.
Solution: \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\) x (side)2
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) x (side)
∴ The length of each side = 2 units.
Example 6. The length of each side of an equilateral triangle is doubled. What % of area will be increased?
Solution: Let each side be a unit, area = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\) a2 sq unit
New area = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\) (2a)2 sq. unit = √3a2
% area increased = \(=\frac{\sqrt{3} a^2-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2}{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2} \times 100=\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{4} 4^2 \times \frac{4}{\sqrt{3} q^2} \times 1 a=300\)
∴ 300% of area will be increase.
Example 7. The length of sides of a right-angled triangle are (x – 2) cm, x cm and (x + 2) cm. Find the hypotenuse?
Solution: (x + 2)2 = x2 + (x – 2)2
or, (x + 2)2 – (x – 2)2 = x2
or, 4.x.2 = x2 or, x = 8
∴ Length of the hypotenuse 10 cm.
Example 8. A square drawn on height of equilateral triangle. Find ratio of areas of triangle and square.
Solution: Let length of each side of the equilateral triangle be x cm
∴ height = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)x cm
Required ratio = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \dot{x}^2:\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} x\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} x^2: \frac{3 x^2}{4}=1: \sqrt{3}\)
∴ Ratio of areas of triangle and square = 1: √3.
Example 9. In parallelogram ABCD, AB = 4 cm, BC 6 cm, ∠ABC 30°, find the area.
Solution: We draw ⊥ from A to BC which intersects AC at P.
Extend AP to Q such that AP = PQ
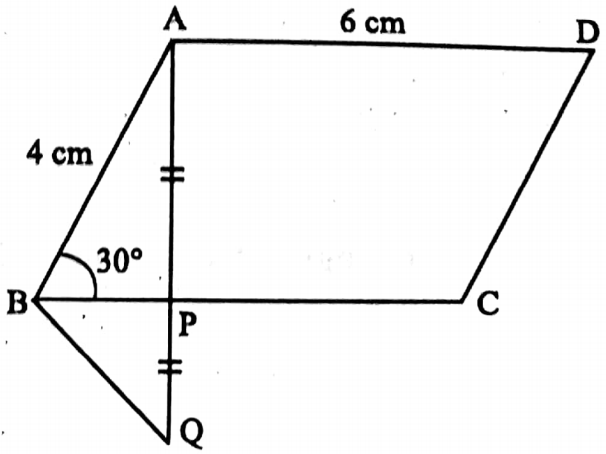
From ΔAPB and ΔQPB,
AP = QP, ∠APB = ∠QPB (= 90°)
BP in common.
∴ ΔAPB = ΔQΡΒ
∴ ∠ABP = ∠QBP = 30°
∠ABQ = 30° + 30° = 60°
∠BAP = 180° – ∠APB – ∠ABP
= 180° – 90° – 30° = 60°
∴ ∠BQP = ∠BAP 60°
In ΔABQ, ∠ABQ = ∠BAQ = ∠BQA = 60°
∴ ΔABQ is equilateral of side equal to 4 cm.
AP = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = AQ = 2 cm (AP = QP)
Required area = BC x AP = 6 x 2 sq cm = 12 sq cm.
Example 10. Length of height of a rhombus is 14 cm and length of side is 5 cm. Find the area.
Solution: Area = base x height
= 14 x 5 sq cm = 70 cm.
∴ Area of the rhombus is 70 cm.
