- Lesson 1 The Wind Cap
- Lesson 2 Clouds
- Lesson 3 An April Day
- Lesson 4 The Great Escape
- Lesson 5 Princess September
- Lesson 6 The Sea

Summative Evaluation Test
Reading Skills
Writing Skills


Question 1. what is congruency?
Solution:
Congruency is the property of two geometrical Figures if one of them can be made to coincide with the other by means of reflection, transformation, translation, or rotation of their combination.
If the two Geometrical Figures are of the same shape and size they are said to be congruent to each other.
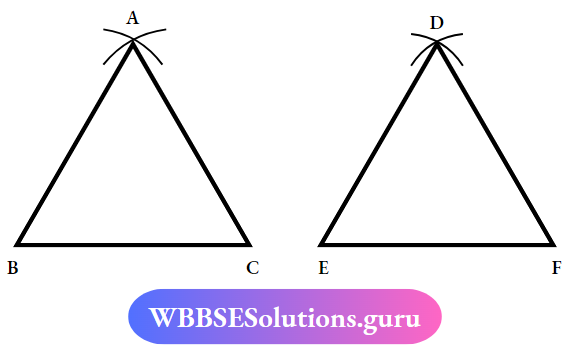
In two triangles ABC and DEF, IF AB = DE, BC= EF, CA= DF
∠A = ∠A, ∠B = ∠E, ∠C = ∠F
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
Question 2. Write the condition of the congruence of a triangle.
Solution:
Congruence of triangle
Two triangles are said to be congruent if their respective side angles are equal and when they are placed upon one another cover each other completely.

In two triangles ABC, DEF.
Condition:
IF AB=DE, BC= EF, CA= FD, and
∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E, ∠C = ∠F
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
Question 3. What is SSS congruency of a triangle? SSS (Side-Side – Side)
Solution:
If the lengths of three sides of a triangle are equal to the lengths of three sides of the other triangle then the triangles are congruent.
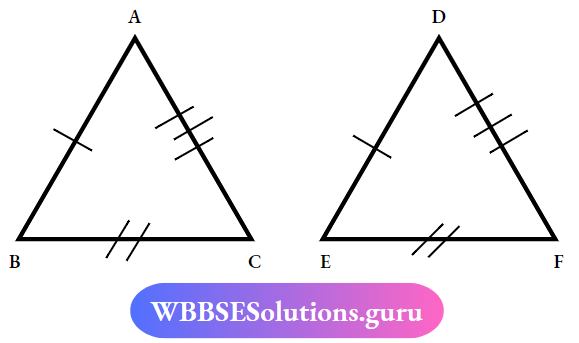
In ΔABC and ΔDEF
AB= DE, BC= EF and AC = DF
∴ ΔAB C ≅ ΔDEF
Question 4. what is the SAS congruency of a triangle SAS (Side- Angle- side)
Solution:
Two triangles are congruent if the length of two sides and the measurement of the included angle of one triangle are equal to the length of two sides and the measurement of the included angle of the other triangle
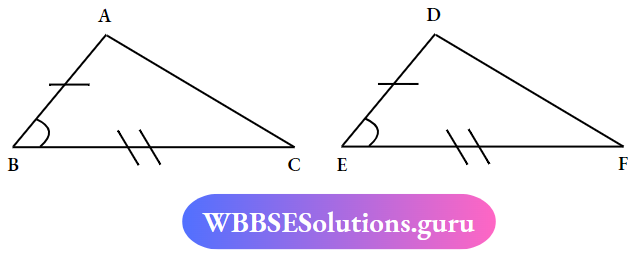
In ΔABC and ΔDEF
AB = DE, ∠ABC = ∠DEF and BC= EF
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
Question 5. What is AAS congruency of a triangle AAS (Angle- Angle-side)
Solution:
Two triangles are congruent if the measurement of any Pair of angles and length of one pair of corresponding Sides are equal to other triangle.
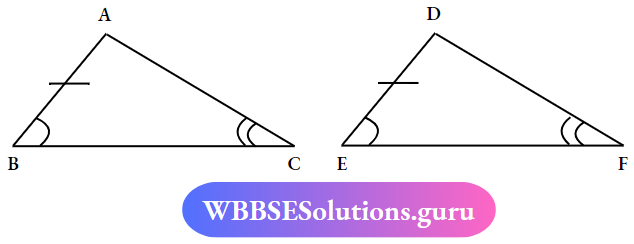
In ΔABC and ΔDEF
∠B= ∠E, ∠C = ∠F and AB = DE
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF.
Question 6. What is RHS congruency of a triangle? RHS (Right Angle- Hypotenuse – Side)
Solution:
If in two right-angled triangles, the length of the hypotenuse and the length of one triangle is equal to the length of the hypotenuse and the length of one side of the other triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
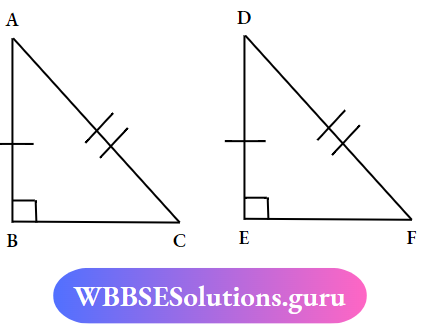
In ΔABC and ΔDEF
∠ABC ≈ ∠DEF = 90°
Hypotenuse AC = Hypotenuse DF and AB = DE
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
Question 7. Find out whether the triangles are congruent
Solution:
AB = PQ, ∠A = ∠P
BC = QR, ∠B = ∠Q
CA = PR, ∠C = ∠R
Then the triangles are incongruent
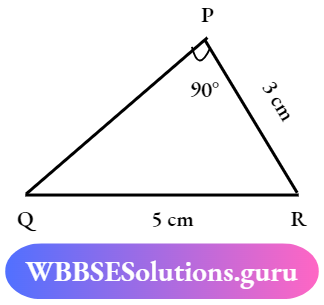
Here,
AB ≠ PQ, ∠A = ∠P
BC = QR, ∠Q ≠ ∠B
CA ≠ PR, ∠C ≠ ∠R
∴ The triangles are non- congruent.
2.
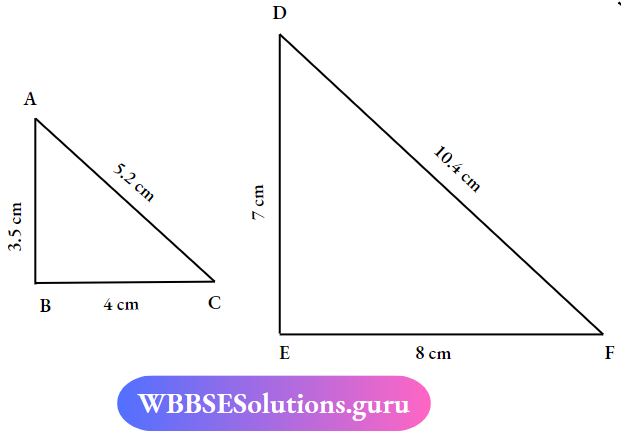
Here,
AB ≠ DE
BC ≠ EF
CA ≠ DF
∴ The ΔABC and ΔDEF are not congruent.
3.
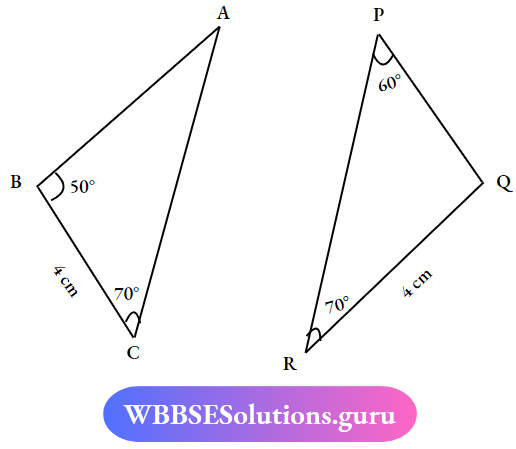
Let us Name the triangles First
BC = QR, ∠C = ∠R
∠B = ∠Q Sum of angles in a Δle is 180.
∠P = ∠A
According to the AAS Condition, the two triangles are in Congruence.
4.

In ΔABC and ΔDEF
∠ABC = ∠DEF = 90°
Hypotenuse AC = DF and AB = DE,
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
5.
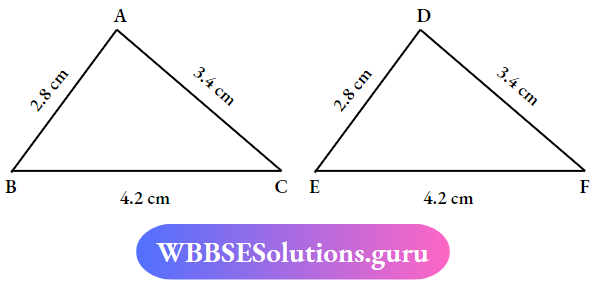
According to SSS Congruent
AB = DE
BC = EF
AC = FD
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF
6.
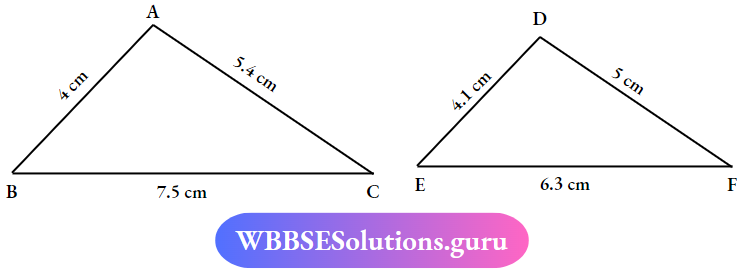
Let us Name the triangles First ΔABC, ΔDEF
Given the sides of Δle
AB ≠ DE
BC ≠ EF
AC ≠ FD
∴ The ΔABC and ΔDEF are non-congruent.
Question 1. Find the least number of data required to construct a
Solution: 2. Square
Question 2. Draw a quadrilateral ABCD where AB=3.8cm, BC= 3cm, CD=4cm, AD= 2.5cm and ∠BAD=75°
Solution:
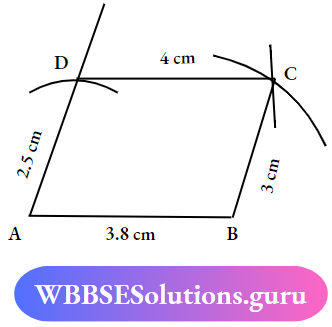
Class 7 Geometry Chapter 8 Exercise Solutions
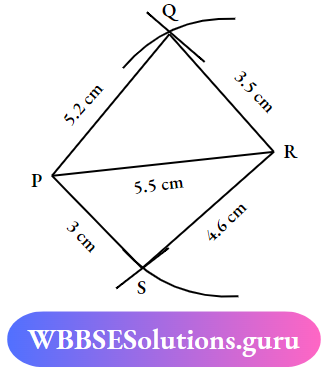
Question 3. Construct a quadrilateral PQRS in which PQ = 5.2cm, QR=3.5cm, RS= 4.6cm, SP = 3cm, and PR = 5.5cm
Solution:
Question 4. Construct a quadrilateral EFGH in which EH = 3.5cm, EF = 5cm, FG = 4.5 cm, ∠HEF = = 8.5° and ∠EFG =75°
Solution:

WBBSE Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 8
Question 5. Construct a periodogram ABCD where AB = 4.6cm, BC = 7cm, and ∠ABC = 60°
Solution:

Question 6. Construct a rectangle PARS where pq=6cm and QR = 8cm
Solution:
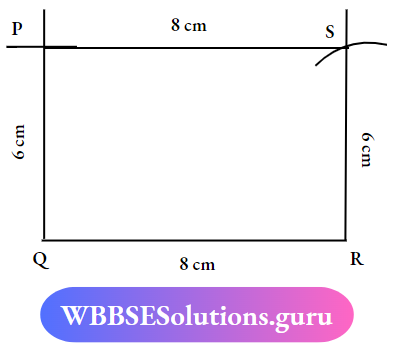
Class 7 Maths Chapter 8 Geometry PDF
Question 7. Construct a square in which the length of each side is 4.8cm.
Solution:
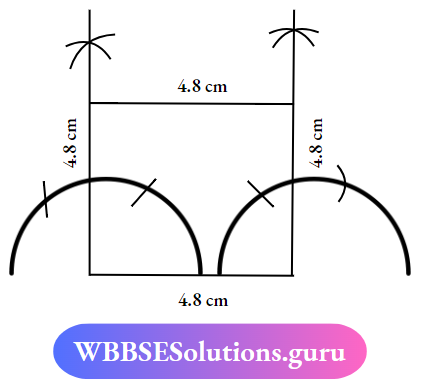
Question 8. onstruct a rhombus ABCD in which AB = 5cm) and /B = 45°.
Solution:
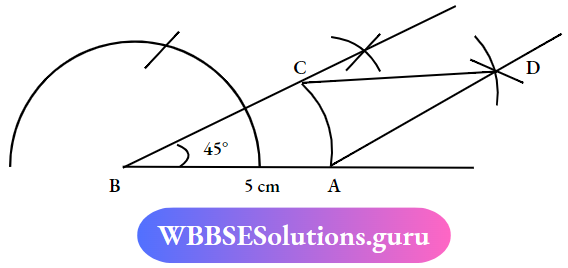
WBBSE Class 7 Maths Geometry Chapter 8
Question 9. Construct a square PQRS in which PR= 5.2cm.
Solution:

Question 10. Construct a Rectangle ABCD in which AC = 4.5cm and ∠ACB=60°
Solution:
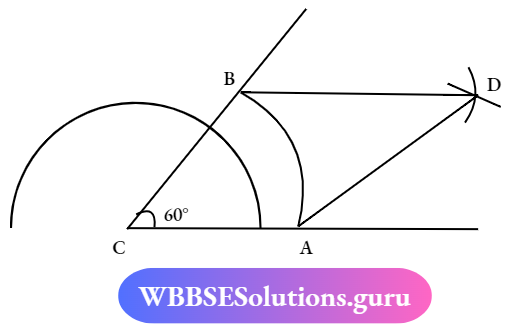
Question 1. Choose the correct answer.
1. The number of lines of symmetry of a square
∴ The option(4) 4 is the correct answer.
2. The number of lines symmetry of a circle is
∴ The option (4) Infinite is the correct answer.
3. There is no centre of rotation of
∴ The option (3) Isosceles trapezium is correct answer
Read and Learn More Class 7 Maths Solutions
4. In which Figure has no line of symmetry
∴ The option (2) P is the correct answer.
Class 7 Geometry Chapter 9 Exercise Solutions
5. In which Figure has a line of symmetry and rotational symmetry both?
∴ The option (3) Circle is the correct answer

Question 2. write true or False:
1. Isosceles triangle has no line of symmetry → True
2. The number of rotational symmetry of the circle is ‘2’ → False
3. The angle of rotation of the rectangle is 90°→ False
4. The order of rotational Symmetry of a square is 4. → True
5. The largest number of lines of symmetry of a triangle is 3 → True.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 9 Geometry PDF
Question 3. Fill in the blanks:-
1. Trapezium has no Line of symmetry or rotational Symmetry
2. The number of lines of Symmetry of a regular Pentagon is 1
3. The number of lines of symmetry of an isosceles right-angled triangle is 1
4. The angle of rotation symmetry of a parallelogram is 180°
5. ______ triangle has only one line of Symmetry. Isosceles
Question 4. Which of the following figures has two lines of Symmetry and the angles or rotational symmetry is 180°
Solution:

→ Rectangle has two lines of Symmetry and angles or rotational symmetry is 180°

→ Parallelogram has no axis of Symmetry
→ It has No Angle of rotational symmetry.

→ Isosceles trapezium has 1 line of Symmetry.
→ It has No Angle of rotational symmetry

→ Square has 4 lines of symmetry
→ Angle of rotational Symmetry is +90°
Class 7 Geometry Chapter 9 Important Questions
Question 5.
1. what is symmetry?
Solution:
→Symmetry means an exact similarity in shape and size between parts of an object of a figure.
2. what is a line of symmetry?
Solution:
A figure is said to be a line of Symmetry of linear symmetry of these exists a straight line that divides into two identical halves that completely coincide with each other when folded about that line.
The straight line is called the line of symmetry of the line of reflection

3. what is rotational symmetry?
Solution:
→ In a Figure that coincides with its images when it is rotated about a point through an angle less than 360° the Figure is said to be rotational Symmetry.
The point across which the Figure rotates is called the center of rotation.
WBBSE Class 7 Maths Geometry Chapter 9
4. what is the angle of rotational symmetry?
Solution:
For a Figure or object that has rotational symmetry the angle of turning during rotation is called the angle of rotation.
For Example: when a square is rotated by qo’ it appears the same after rotation. So the angle of rotation of the Square is 90°
Question 6. Find the angles of rotation of the following.
Solution:
Question 1. Choose the correct Answer
1. The measurement of the sum of four angles of any quadrilateral is
∴ Option (3)360° is the correct answer
2. The each angle of a rectangle is.
∴ Option (2) right angle is the correct answer
Read and Learn More Class 7 Maths Solutions
3. The opposite angles of the parallelogram are
∴ Option (1) equal is the correct answer
WBBSE Class 7 Maths Geometry Chapter 7
4. The angle of each square is.
∴ Option (2) right angle is the correct answer.
Question 2. Write true or false
1. An isocelges trapezium is a parall dogram. → False
2. The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other at right angles → The statement is False
3. Quadrilateral has two diagonals → The Statement is True
Question 3. Fill in the blanks:
1. The sum of the measurement of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram is 180°
2. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are Parallel to each other.
3. Quadrilateral has two diagonals
4. The length of the diagonals of an isosceles trapezium is equal.
Question 4. Each rhombus is a special type of square Explain.
Solution:
Class 7 Geometry Chapter 7 Exercise Solutions
Question 5. Write the difference between the Parallelogram and the rectangle.
Solution:

Class 7 Maths Chapter 7 Geometry PDF
Question 6. Write the difference between a rectangle and a square
Solution:

Question 7. Write the properties of the parallelogram
Solution:
Properties of parallelogram
WBBSE Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 7
Question 8. What is a convex quadrilateral, and what is a concave quadrilateral
Solution:
Convex Quadrilateral
A convex quadrilateral is a four-sided Polygon that has interior angles that measure less than 180° each The diagonals are contained entirely inside of these quadrilaterals. PQRS is a convex Quadrilateral.
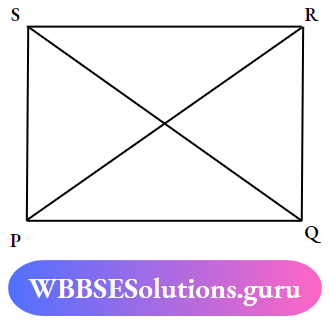
Concave Quadrilateral:
If the quadrilateral has an interior angle greater than 180° It is called a concave quadrilateral.
ABCD is a quadrilateral whose interior ∠BCD >180°